Intro
Discover the ultimate Fodmap List Printable Guide, featuring low FODMAP foods, IBS triggers, and digestive health tips to manage symptoms and create a personalized diet plan.
The FODMAP diet has gained popularity in recent years, particularly among individuals who suffer from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other digestive issues. FODMAPs, which stand for Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Mono-saccharides, and Polyols, are types of carbohydrates that can be difficult for some people to digest. By understanding which foods are high in FODMAPs and limiting their consumption, many individuals have found relief from symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits. In this article, we will delve into the world of FODMAPs, exploring what they are, how they affect the body, and providing a comprehensive FODMAP list printable guide to help you navigate your dietary choices.
The concept of FODMAPs was first introduced by a team of researchers at Monash University in Australia, who discovered that certain types of carbohydrates were not fully absorbed in the small intestine and instead fermented by bacteria in the large intestine, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms. Since then, the low FODMAP diet has become a widely recognized and effective treatment for IBS and other gastrointestinal disorders. The diet involves a three-phase approach: elimination, reintroduction, and modification. During the elimination phase, all high FODMAP foods are removed from the diet for a period of 2-6 weeks, allowing the gut to heal and symptoms to subside. The reintroduction phase involves gradually reintroducing each type of FODMAP to assess tolerance, while the modification phase involves making long-term dietary changes based on individual tolerance.
Understanding FODMAPs

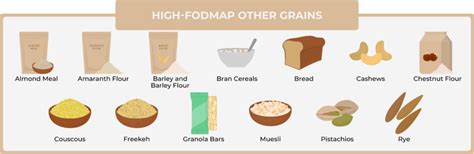
To better understand FODMAPs, it's essential to break down the different types of carbohydrates that fall under this category. These include fructose, lactose, fructans, galactans, and polyols. Fructose is a simple sugar found in many fruits, vegetables, and grains, while lactose is a sugar found in milk and other dairy products. Fructans are a type of carbohydrate found in wheat, barley, and rye, as well as some vegetables like onions and garlic. Galactans are found in legumes, such as beans and lentils, while polyols are found in stone fruits, like cherries and apricots, as well as some sugar substitutes like sorbitol and xylitol. Each of these types of FODMAPs can be problematic for individuals with IBS and other digestive issues, and understanding which foods contain them is crucial for managing symptoms.
FODMAP List Printable Guide

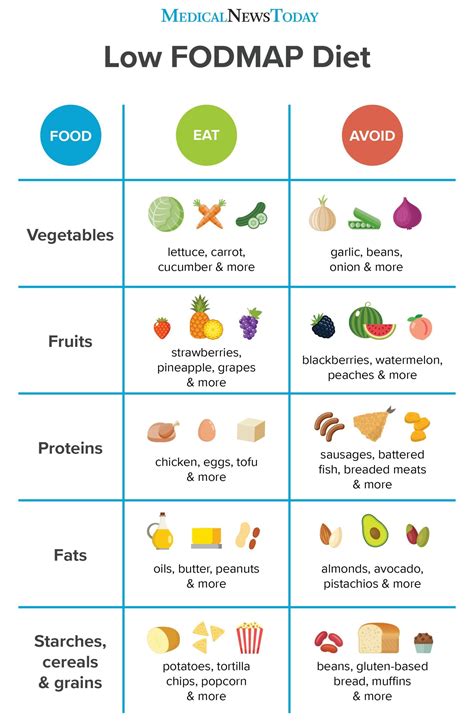
The following FODMAP list printable guide provides a comprehensive overview of high and low FODMAP foods, making it easier to make informed dietary choices. It's essential to note that serving sizes play a significant role in FODMAP content, and even small amounts of high FODMAP foods can trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals.
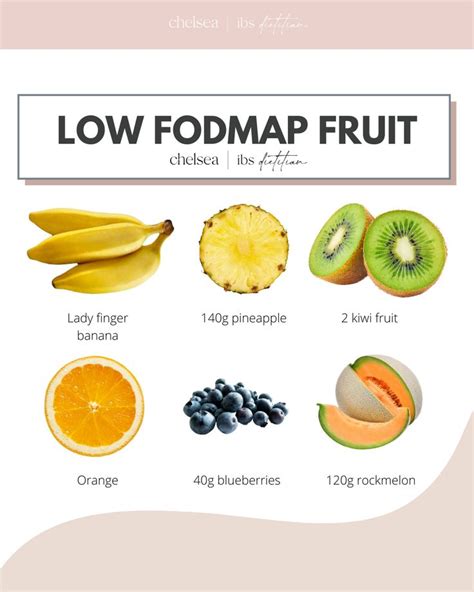
- High FODMAP fruits: apples, pears, watermelon, mangoes, cherries, and apricots
- Low FODMAP fruits: bananas, berries, citrus fruits, and grapes
- High FODMAP vegetables: onions, garlic, beans, cabbage, and broccoli
- Low FODMAP vegetables: bell peppers, cucumbers, carrots, and lettuce
- High FODMAP proteins: wheat, barley, and rye
- Low FODMAP proteins: meat, poultry, fish, and eggs
- High FODMAP dairy: milk, ice cream, and soft cheeses
- Low FODMAP dairy: lactose-free milk, hard cheeses, and yogurt
Managing FODMAPs in Your Diet

Managing FODMAPs in your diet requires a thorough understanding of which foods are high and low in these types of carbohydrates. By limiting or avoiding high FODMAP foods, individuals with IBS and other digestive issues can experience significant relief from symptoms. However, it's essential to approach the low FODMAP diet in a structured and systematic way, working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to ensure that nutritional needs are met. Additionally, it's crucial to keep in mind that everyone's tolerance to FODMAPs is different, and what may trigger symptoms in one person may not affect another.
Benefits of the Low FODMAP Diet

The benefits of the low FODMAP diet are numerous, with many individuals experiencing significant improvements in digestive health and overall well-being. By reducing or eliminating symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits, individuals can enjoy a better quality of life, with improved energy levels, mood, and cognitive function. Additionally, the low FODMAP diet can help to reduce inflammation in the gut, which is associated with a range of chronic diseases, including arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Challenges of the Low FODMAP Diet

While the low FODMAP diet can be highly effective in managing digestive symptoms, it can also be challenging to follow, particularly in social situations or when eating out. Many high FODMAP foods are staples in modern diets, and avoiding them can require significant changes to eating habits. Additionally, the diet can be time-consuming and expensive, particularly if individuals need to purchase specialized low FODMAP products. However, with the right guidance and support, many individuals find that the benefits of the low FODMAP diet far outweigh the challenges.
Gallery of FODMAP Foods
FODMAP Foods Image Gallery







Frequently Asked Questions
What are FODMAPs?
+FODMAPs are types of carbohydrates that can be difficult for some people to digest, leading to a range of uncomfortable symptoms.
What is the low FODMAP diet?
+The low FODMAP diet is a dietary approach that involves limiting or avoiding high FODMAP foods to manage digestive symptoms.
How do I know if I have a FODMAP intolerance?
+If you experience symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits after consuming high FODMAP foods, you may have a FODMAP intolerance.
Can I still eat my favorite foods on the low FODMAP diet?
+While some high FODMAP foods may need to be limited or avoided, many low FODMAP alternatives are available, and with a little creativity, you can still enjoy your favorite foods.
How long does it take to see results on the low FODMAP diet?
+Results can vary, but many individuals experience significant improvements in digestive health within 2-6 weeks of starting the low FODMAP diet.
In
Final Thoughts

