Intro
Discover 5 essential Warfarin tips for safe anticoagulation therapy, including dosage management, blood clot prevention, and potential interactions, to minimize risks and optimize treatment outcomes.
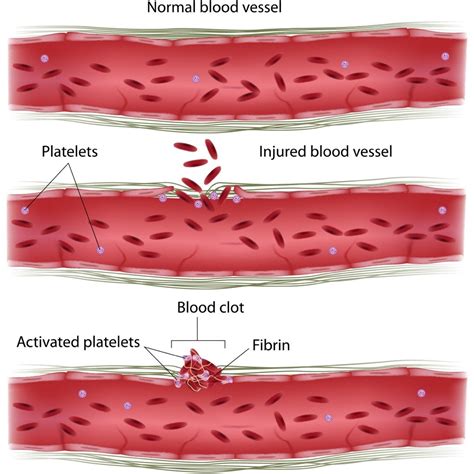
Warfarin is a commonly prescribed anticoagulant medication used to prevent and treat blood clots. It works by inhibiting the production of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors in the liver, thereby reducing the risk of thrombosis and embolism. However, warfarin can be a challenging medication to manage, as its effectiveness and safety depend on maintaining a narrow therapeutic range. Here are some essential tips for individuals taking warfarin to ensure safe and effective treatment.
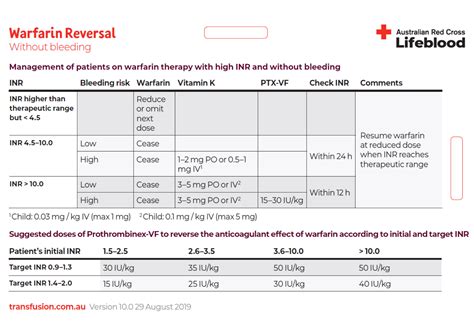
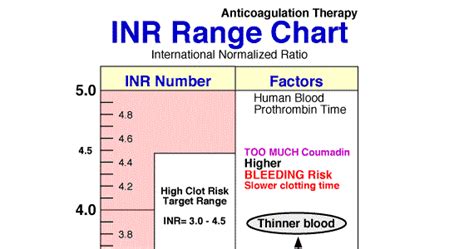
Warfarin requires regular monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR) levels to ensure that the blood is within the therapeutic range. If the INR is too low, the blood may not be thin enough, and the risk of clotting may increase. On the other hand, if the INR is too high, the blood may be too thin, and the risk of bleeding may increase. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to determine the optimal INR range for their specific condition and to schedule regular blood tests to monitor their INR levels.
Understanding Warfarin Therapy

Importance of Regular Monitoring
Regular monitoring of INR levels is crucial to ensure that the blood is within the therapeutic range. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to schedule regular blood tests and to adjust their warfarin dose as needed. Additionally, patients should be aware of the factors that can affect warfarin levels, such as changes in diet, medications, and lifestyle, and inform their healthcare provider of any changes.Dietary Considerations

Interactions with Other Medications
Warfarin can interact with other medications, including over-the-counter medications and herbal supplements. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of all medications they are taking, including vitamins and supplements, to minimize the risk of interactions. Some medications, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, can increase the risk of bleeding when taken with warfarin, while others, such as certain antibiotics, can affect warfarin levels.Lifestyle Modifications

Travel Considerations
Traveling can be challenging for patients taking warfarin, as it may require adjustments to their medication regimen and monitoring schedule. Patients should inform their healthcare provider of their travel plans and work with them to develop a plan to manage their warfarin therapy while away. This may include scheduling blood tests at a local laboratory or adjusting their medication dose to account for changes in time zones or altitude.Warfarin and Pregnancy

Warfarin and Breastfeeding
Warfarin is generally considered safe during breastfeeding, as it is not excreted in significant amounts in breast milk. However, patients should inform their healthcare provider if they are breastfeeding, as they may need to monitor their infant's INR levels and adjust their warfarin dose accordingly.Warfarin Alternatives

Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, warfarin is a commonly prescribed anticoagulant medication that requires careful management to minimize the risk of complications. Patients should work closely with their healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, including regular monitoring of INR levels, dietary considerations, and lifestyle modifications. By following these tips and being aware of the potential risks and benefits associated with warfarin therapy, patients can minimize the risk of complications and achieve optimal treatment outcomes.Warfarin Image Gallery




What is warfarin and how does it work?
+Warfarin is an anticoagulant medication that works by inhibiting the production of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors in the liver, thereby reducing the risk of thrombosis and embolism.
What are the potential risks and benefits of warfarin therapy?
+The potential risks of warfarin therapy include bleeding, which can be life-threatening in severe cases, while the benefits include the prevention and treatment of blood clots.
How often should I have my INR levels checked?
+The frequency of INR level checks depends on individual factors, such as the reason for warfarin therapy and the patient's medical history, but typically ranges from weekly to monthly.
Can I take warfarin during pregnancy or breastfeeding?
+Warfarin can be teratogenic and should be avoided during pregnancy, while it is generally considered safe during breastfeeding, but patients should inform their healthcare provider if they are breastfeeding.
What are the alternatives to warfarin?
+Warfarin alternatives, such as direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), are available for patients who are unable to take warfarin or who require a more convenient medication regimen.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of warfarin therapy and its management. If you have any further questions or concerns, please do not hesitate to comment below or share this article with others who may benefit from this information. Additionally, we encourage you to take specific actions, such as consulting with your healthcare provider or seeking additional resources, to ensure safe and effective treatment with warfarin.
