Intro
Discover expert 5 Vancomycin Tips for safe usage, dosing, and side effect management, including antibiotic resistance, infection treatment, and patient care guidelines.
Vancomycin is an antibiotic that has been widely used to treat serious bacterial infections, particularly those caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is a crucial medication in the arsenal against antibiotic-resistant bacteria. Understanding how to use vancomycin effectively and safely is essential for healthcare professionals and patients alike. Here are some key points to consider when dealing with vancomycin, aiming to enhance its efficacy and minimize its side effects.
The importance of vancomycin in modern medicine cannot be overstated. It is one of the few antibiotics that can effectively treat infections caused by MRSA and other gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to many other antibiotics. However, its use must be carefully managed due to potential side effects and the risk of promoting further antibiotic resistance. Healthcare providers must balance the benefits of vancomycin with its potential drawbacks, ensuring that it is used judiciously and only when necessary.
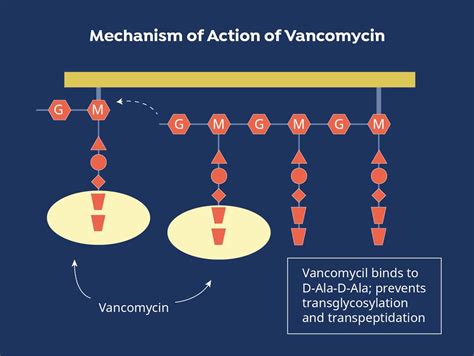
Vancomycin's mechanism of action involves inhibiting cell wall synthesis in bacteria, which ultimately leads to the death of the bacterial cells. This makes it highly effective against gram-positive bacteria, including MRSA. However, its effectiveness can be compromised if not administered correctly or if the patient has factors that alter its distribution and elimination from the body. Monitoring vancomycin levels and adjusting doses based on patient-specific factors such as kidney function and weight is crucial for achieving optimal therapeutic effects while minimizing toxicity.
Introduction to Vancomycin
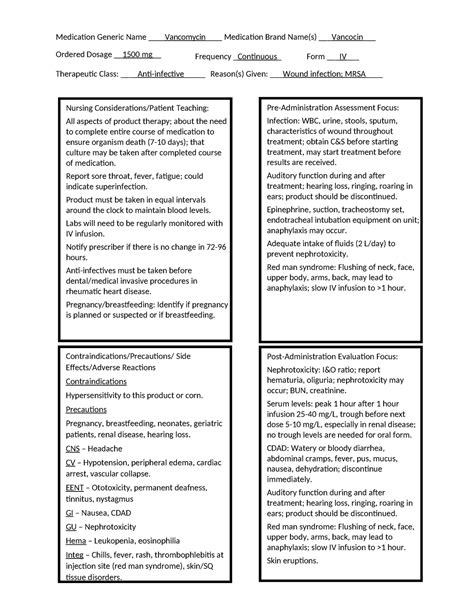
Vancomycin is typically administered intravenously for systemic infections, and its dosing must be carefully calculated. The standard dosing regimen may need to be adjusted for patients with renal impairment, as vancomycin is primarily excreted by the kidneys. Nephrotoxicity is a significant concern with vancomycin use, especially when used in combination with other nephrotoxic agents. Monitoring renal function and vancomycin trough levels can help mitigate this risk.
Benefits of Vancomycin
The benefits of vancomycin are numerous, including its broad spectrum of activity against gram-positive bacteria, its effectiveness in treating serious and life-threatening infections, and its role as a salvage therapy when other antibiotics have failed. However, these benefits must be weighed against potential risks such as nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and the risk of Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) infection.Administration and Monitoring

Proper administration and monitoring of vancomycin are critical to its safe and effective use. This includes ensuring the correct dose is given, monitoring for signs of toxicity, and adjusting doses as necessary based on trough levels and patient response. Healthcare providers should also be vigilant for signs of adverse effects, such as renal dysfunction or hearing loss, and intervene promptly if these occur.
Side Effects and Toxicity
Vancomycin can cause several side effects, ranging from mild to severe. Common side effects include infusion-related reactions such as "red man syndrome," which can be mitigated by slowing the infusion rate. More serious side effects include nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity, which can be irreversible and require immediate cessation of the drug. The risk of these adverse effects underscores the importance of careful patient selection, dose adjustment, and monitoring.Vancomycin Resistance

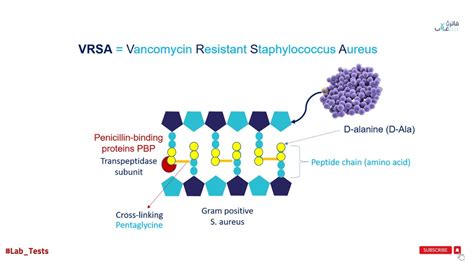
The emergence of vancomycin-resistant bacteria is a growing concern. This resistance can develop through several mechanisms, including thickening of the bacterial cell wall, which reduces vancomycin's ability to bind, and alterations in the cell wall precursors that vancomycin targets. The development of resistance highlights the need for stewardship programs that promote the judicious use of vancomycin and other antibiotics, to preserve their effectiveness for future generations.
Stewardship and Future Directions
Antibiotic stewardship programs are essential for ensuring that vancomycin and other antibiotics are used appropriately. These programs involve a multidisciplinary approach to optimize antibiotic use, improve patient outcomes, and reduce the risk of resistance. Future directions in vancomycin use may include the development of new dosing strategies, the use of vancomycin in combination with other antibiotics to enhance its effectiveness, and research into new antibiotics that can combat resistant bacteria.Practical Considerations

Practically, the use of vancomycin requires careful consideration of several factors, including the patient's renal function, weight, and the severity of the infection. Doses must be adjusted accordingly, and trough levels must be monitored to ensure therapeutic levels are achieved without exceeding toxic thresholds. Additionally, patients should be educated on the potential side effects and the importance of completing the full treatment course to minimize the risk of resistance.
Patient Education
Patient education is a critical component of vancomycin therapy. Patients should understand the reasons for vancomycin use, the potential side effects, and the importance of adherence to the prescribed regimen. They should also be informed about signs of toxicity or adverse effects that require immediate medical attention. Empowering patients with knowledge can improve outcomes and enhance safety.Gallery of Vancomycin-Related Images
Vancomycin Image Gallery





Frequently Asked Questions
What is vancomycin used for?
+Vancomycin is used to treat serious bacterial infections, particularly those caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
How is vancomycin administered?
+Vancomycin is typically administered intravenously for systemic infections.
What are the potential side effects of vancomycin?
+Potential side effects include nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and infusion-related reactions. Monitoring and dose adjustment can help mitigate these risks.
Why is vancomycin stewardship important?
+Vancomycin stewardship is crucial for promoting the judicious use of vancomycin, reducing the risk of resistance, and preserving its effectiveness for treating serious infections.
How can patients contribute to safe vancomycin use?
+Patients can contribute by adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen, reporting any side effects promptly, and understanding the importance of completing the full treatment course.
In conclusion, vancomycin is a valuable antibiotic in the treatment of serious bacterial infections, particularly those caused by MRSA. Its use requires careful consideration of dosing, monitoring, and potential side effects. By understanding the benefits and risks of vancomycin and promoting its judicious use, we can ensure its continued effectiveness in combating bacterial infections. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with vancomycin, and to consider the importance of antibiotic stewardship in preserving the efficacy of this and other critical antibiotics for future generations.
