The Ultimate Guide To Understanding Volatility Index And Its Role In Financial Markets
Mar 20 2025
Volatility Index (VIX), often referred to as the "Fear Index," plays a pivotal role in financial markets by measuring market expectations of near-term volatility based on option prices. It serves as a critical tool for investors, traders, and analysts to assess the level of risk, fear, or stress in the market. Understanding the VIX is essential for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of financial trading and risk management.
As the financial landscape becomes increasingly interconnected, the importance of volatility as a metric cannot be overstated. The VIX is not just a number; it reflects the collective sentiment of market participants and provides valuable insights into potential market movements. By delving into the mechanics of the VIX, we can better understand how it influences trading decisions and portfolio strategies.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the concept of the Volatility Index, its significance in financial markets, and how it can be utilized effectively. Whether you're a seasoned investor or a newcomer to the world of finance, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to harness the power of the VIX for better decision-making.
Read also:Kim Fields Net Worth A Comprehensive Guide To Her Wealth Career And Achievements
Table of Contents
- What is the Volatility Index (VIX)?
- History of the Volatility Index
- How Does the VIX Work?
- The VIX and Market Sentiment
- Using the VIX in Trading Strategies
- Volatility Index Products
- The Role of VIX in Risk Management
- VIX as an Indicator for Market Trends
- The VIX and Global Financial Markets
- Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of the VIX
What is the Volatility Index (VIX)?
The Volatility Index, commonly known as the VIX, is a real-time market index that represents the market's expectation of 30-day forward-looking volatility. Developed by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE), the VIX is derived from the prices of S&P 500 index options, providing a measure of expected market fluctuations over the next month.
This index is a key indicator of investor sentiment and market volatility. A high VIX reading indicates increased uncertainty and fear in the market, while a low reading suggests calmness and stability. Understanding the VIX helps investors anticipate market shifts and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Key Features of the VIX
- Reflects the implied volatility of the S&P 500 index options.
- Serves as a barometer of market sentiment and risk perception.
- Trades in real-time, offering a dynamic view of market expectations.
History of the Volatility Index
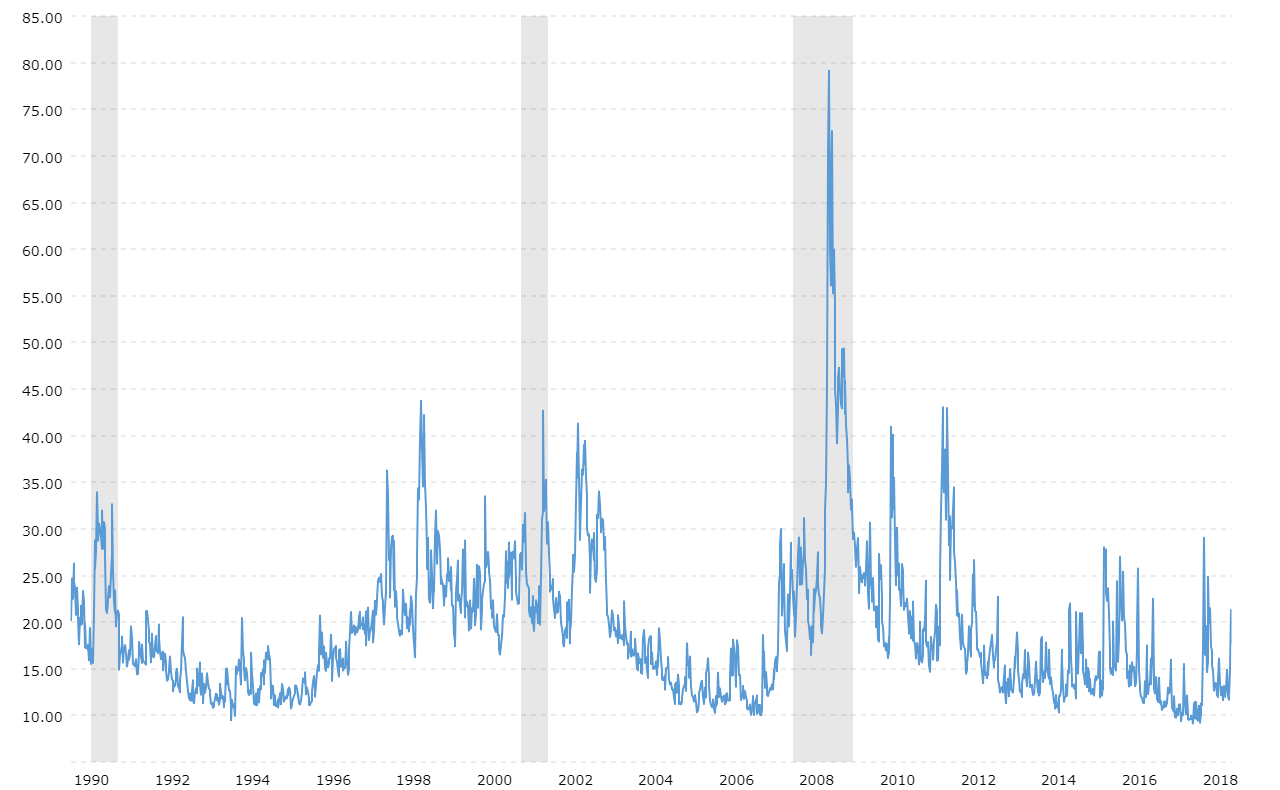
The VIX was introduced in 1993 by the CBOE as a way to quantify market volatility. Initially, it was based on the S&P 100 index options but later evolved to incorporate the broader S&P 500 index. Over the years, the VIX has become a cornerstone of financial analysis and trading strategies.
Historically, significant market events such as the 2008 financial crisis and the 2020 pandemic have seen sharp spikes in the VIX, highlighting its role as a gauge of market stress. By examining historical VIX data, investors can gain insights into past market conditions and potential future trends.
How Does the VIX Work?
The VIX operates by analyzing the prices of S&P 500 index options across a range of strike prices and expiration dates. These prices reflect the market's expectation of future volatility, which is then translated into a single numerical value. The higher the VIX reading, the greater the anticipated volatility.
Traders and analysts use the VIX to identify potential buying or selling opportunities. For instance, a rising VIX may signal an impending market downturn, prompting investors to adopt more defensive positions.
Read also:Afroman Lawsuit Understanding The Legal Battle And Its Implications
VIX Calculation Methodology
- Utilizes a wide range of S&P 500 index options to calculate implied volatility.
- Incorporates both near-term and next-term options for a comprehensive view.
- Adjusts for time decay to provide a consistent 30-day forward-looking measure.
The VIX and Market Sentiment
The VIX is often referred to as the "Fear Index" because it closely tracks investor sentiment. When market participants are anxious or uncertain, the VIX tends to rise, reflecting heightened volatility expectations. Conversely, during periods of calm, the VIX typically declines.
Understanding the relationship between the VIX and market sentiment can help investors gauge the overall mood of the market and make informed decisions. By monitoring the VIX, traders can anticipate shifts in market direction and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Using the VIX in Trading Strategies
Investors and traders employ the VIX in various strategies to manage risk and enhance returns. One common approach is to use VIX futures and options to hedge against market volatility. By purchasing VIX options, investors can protect their portfolios from unexpected market swings.
Additionally, the VIX can be used as a contrarian indicator. For example, when the VIX reaches extreme levels, it may signal an opportunity to buy or sell assets based on the assumption that the market is overreacting.
Volatility Index Products
- VIX futures: Allow traders to speculate on future volatility levels.
- VIX options: Provide a way to hedge against volatility or profit from directional bets.
- ETPs linked to the VIX: Offer investors exposure to volatility through exchange-traded products.
The Role of VIX in Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial aspect of investing, and the VIX plays a significant role in this process. By providing a forward-looking measure of volatility, the VIX helps investors assess the level of risk in their portfolios. This information can be used to adjust asset allocations, implement hedging strategies, and manage downside risk.
Moreover, the VIX can serve as an early warning system for potential market disruptions. By monitoring changes in the VIX, investors can identify emerging risks and take proactive measures to protect their investments.
VIX as an Indicator for Market Trends
- Signals potential market turning points based on shifts in volatility.
- Provides insights into investor sentiment and market expectations.
- Helps identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market.
The VIX and Global Financial Markets
While the VIX is primarily focused on the U.S. market, its implications extend to global financial markets. As the world's largest economy, the U.S. often sets the tone for global market trends. Therefore, changes in the VIX can have ripple effects across international markets.
Investors in global markets use the VIX as a barometer of global economic health. A rising VIX may indicate increased uncertainty and risk, prompting investors to reassess their exposure to international assets.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of the VIX
In conclusion, the Volatility Index (VIX) is an indispensable tool for anyone involved in financial markets. By providing a forward-looking measure of market volatility, the VIX helps investors navigate the complexities of trading and risk management. Understanding the VIX and its role in shaping market sentiment can lead to better decision-making and improved investment outcomes.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with the VIX in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into financial markets and investment strategies. Together, let's unlock the potential of the VIX and enhance our financial acumen.
Data Source: Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE)