Dengue Fever: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding, Preventing, And Treating The Disease
Mar 20 2025
Dengue fever is a growing global health concern that affects millions of people each year. This mosquito-borne illness has become a significant threat in tropical and subtropical regions worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment of dengue fever is crucial for safeguarding public health.
Dengue fever has been described as one of the fastest-growing viral diseases globally. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the number of dengue cases has increased dramatically over the past few decades. This alarming trend makes it essential for individuals to be informed about the disease and take preventive measures.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of dengue fever, providing detailed insights into its causes, transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. By the end of this guide, you will have a thorough understanding of dengue fever and how to protect yourself and your loved ones from this potentially life-threatening illness.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Joe Alwyn And Taylor Swifts Love Story
Table of Contents
- What is Dengue Fever?
- Causes of Dengue Fever
- Symptoms of Dengue Fever
- Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
- Treatment Options for Dengue Fever
- Prevention Strategies
- Dengue Fever Statistics
- Impact on Public Health
- Travel and Dengue Fever
- Conclusion
What is Dengue Fever?
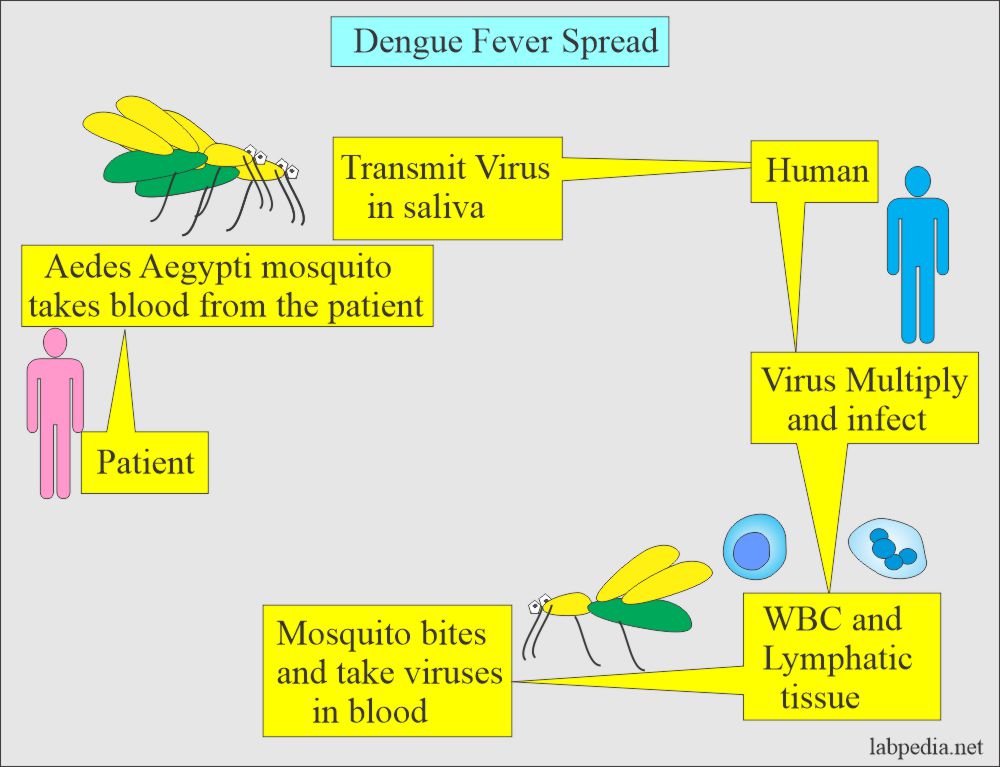
Dengue fever is a viral infection transmitted by the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. It is caused by four closely related dengue viruses (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4). The disease is endemic in more than 100 countries, primarily in tropical and subtropical regions. While most cases of dengue fever are mild, some individuals may develop severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever, which can be life-threatening.
This section will explore the basic characteristics of dengue fever, its prevalence, and its significance as a public health issue. We will also discuss the role of the Aedes mosquito in spreading the disease.
History of Dengue Fever
The history of dengue fever dates back centuries, with early records of the disease appearing in China around 265 AD. Over the years, dengue fever has evolved into a global health crisis, particularly in urban and semi-urban areas. The resurgence of the disease in the mid-20th century was attributed to rapid urbanization, globalization, and climate change.
Causes of Dengue Fever
The primary cause of dengue fever is the dengue virus, which is transmitted through the bite of an infected Aedes mosquito. These mosquitoes thrive in environments with stagnant water, making urban areas with poor sanitation and inadequate water management particularly vulnerable to outbreaks.
There are several factors that contribute to the spread of dengue fever, including:
- Poor waste management
- Inadequate mosquito control measures
- Climate change
- Increased international travel
How the Virus Spreads
When a mosquito bites an infected person, it becomes a carrier of the dengue virus. The virus then multiplies within the mosquito and is transmitted to another person when the mosquito bites again. This cycle of transmission makes dengue fever difficult to control, especially in densely populated areas.
Read also:Subhashree Sahu New Video Unveiling The Latest Trend And Insights
Symptoms of Dengue Fever
The symptoms of dengue fever typically appear within 4 to 10 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito. The disease presents with a range of symptoms, from mild flu-like symptoms to severe complications. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for timely medical intervention.
Common symptoms of dengue fever include:
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Pain behind the eyes
- Muscle and joint pain
- Rash
- Nausea and vomiting
Differences Between Mild and Severe Dengue
Severe dengue, also known as dengue hemorrhagic fever, can lead to bleeding, plasma leakage, and organ failure. Recognizing the warning signs of severe dengue is vital for preventing complications. Symptoms such as persistent vomiting, difficulty breathing, and abdominal pain indicate the need for immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis of Dengue Fever
Diagnosing dengue fever involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests. Healthcare providers assess the patient's symptoms, travel history, and exposure to mosquitoes to determine the likelihood of infection. Laboratory tests, such as blood tests, can confirm the presence of the dengue virus or antibodies.
Common diagnostic methods include:
- NS1 antigen test
- IgM and IgG antibody tests
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) test
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of dengue fever is critical for effective treatment and management. Delayed diagnosis can lead to severe complications, particularly in cases of severe dengue. Healthcare providers must remain vigilant in identifying dengue fever, especially in regions where the disease is endemic.
Treatment Options for Dengue Fever
There is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue fever. Management of the disease focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing complications. Patients with mild dengue fever can recover with proper rest, hydration, and pain relief. However, severe cases require hospitalization and intensive care.
Treatment strategies include:
- Hydration through oral or intravenous fluids
- Pain relief using acetaminophen
- Close monitoring of vital signs
Preventing Complications
Preventing complications is a key aspect of treating dengue fever. Patients should avoid aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as these can increase the risk of bleeding. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential for monitoring recovery and addressing any lingering symptoms.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing dengue fever involves a combination of personal protection measures and community-wide efforts to control mosquito populations. Individuals can reduce their risk of infection by avoiding mosquito bites and eliminating breeding grounds for mosquitoes.
Effective prevention strategies include:
- Using insect repellent
- Wearing long-sleeved clothing
- Installing window screens and mosquito nets
- Eliminating stagnant water around the home
Community-Based Initiatives
Community-based initiatives play a crucial role in controlling the spread of dengue fever. Governments and health organizations often launch awareness campaigns to educate the public about mosquito control measures. Collaborative efforts between local communities and health authorities are essential for reducing the incidence of dengue fever.
Dengue Fever Statistics
Dengue fever statistics highlight the growing burden of the disease on global health. According to the WHO, an estimated 390 million dengue infections occur annually, with approximately 96 million cases resulting in clinical illness. The disease is most prevalent in Southeast Asia, the Americas, and the Western Pacific region.
Key statistics include:
- More than 100 countries are affected by dengue fever
- Approximately 70% of dengue cases occur in Asia
- The economic impact of dengue fever is estimated to be billions of dollars annually
Trends in Dengue Incidence
Recent trends indicate a steady increase in dengue fever cases worldwide. Climate change, urbanization, and globalization have contributed to the spread of the disease. Public health experts warn that without effective intervention, the incidence of dengue fever could continue to rise in the coming years.
Impact on Public Health
Dengue fever has a significant impact on public health, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. The disease places a heavy burden on healthcare systems, leading to increased hospital admissions and healthcare costs. Additionally, dengue outbreaks can disrupt economic activities and negatively affect tourism.
Efforts to mitigate the impact of dengue fever include:
- Developing vaccines
- Improving mosquito control programs
- Enhancing surveillance systems
Role of Vaccines
Vaccines offer a promising solution for reducing the incidence of dengue fever. The first dengue vaccine, Dengvaxia, was approved in 2015 and has been used in several countries. However, its effectiveness is limited to individuals who have previously been infected with the dengue virus. Ongoing research aims to develop more effective and widely applicable vaccines.
Travel and Dengue Fever
Travelers to dengue-endemic regions should take precautions to protect themselves from mosquito bites. Understanding the risks associated with dengue fever in specific destinations can help travelers make informed decisions about their travel plans. Travel health advisories provide valuable information on dengue outbreaks and preventive measures.
Travel-related prevention tips include:
- Using insect repellent containing DEET or picaridin
- Staying in air-conditioned or screened accommodations
- Wearing protective clothing
Travel Health Advisories
Travel health advisories issued by organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the WHO provide up-to-date information on dengue fever outbreaks. Travelers should consult these advisories before visiting dengue-endemic regions to ensure their safety and well-being.
Conclusion
Dengue fever remains a significant global health challenge, affecting millions of people each year. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of the disease is crucial for reducing its impact on public health. By implementing effective mosquito control measures and promoting awareness, we can work towards minimizing the spread of dengue fever.
We encourage readers to share this article and spread awareness about dengue fever. For further reading, explore our other articles on infectious diseases and public health. Together, we can make a difference in combating this growing global health concern.