Intro
Discover Soviet military ranks, from Private to Marshal, and understand the hierarchical structure, insignia, and responsibilities of each position, including officer, enlisted, and general ranks.
The Soviet military, also known as the Red Army, was one of the largest and most complex military forces in history. With a rich history spanning over seven decades, the Soviet military played a significant role in shaping world events, particularly during World War II and the Cold War. Understanding the Soviet military ranks is essential to grasping the structure and hierarchy of the Red Army. In this article, we will delve into the world of Soviet military ranks, exploring their history, significance, and evolution over time.
The Soviet military rank system was established in the early 20th century, shortly after the Russian Revolution. The system was designed to reflect the Marxist-Leninist ideology of the Soviet Union, emphasizing the importance of collective leadership and the suppression of individualism. The ranks were divided into several categories, including enlisted personnel, non-commissioned officers, and commissioned officers. Each category had its own set of ranks, with distinct responsibilities and privileges.
As the Soviet military expanded and evolved, so did its rank system. New ranks were introduced, and existing ones were modified to reflect changes in the military's structure and doctrine. The Soviet military rank system was known for its complexity, with numerous ranks and sub-ranks, each with its own unique insignia and uniform. Despite its complexity, the Soviet military rank system played a crucial role in maintaining discipline and order within the Red Army.
Introduction to Soviet Military Ranks

The Soviet military rank system was divided into several categories, including enlisted personnel, non-commissioned officers, and commissioned officers. Enlisted personnel, also known as privates, made up the bulk of the Red Army. They were responsible for carrying out basic tasks, such as guard duty, maintenance, and combat operations. Non-commissioned officers, on the other hand, held leadership positions, overseeing enlisted personnel and coordinating unit operations. Commissioned officers, the highest ranking category, were responsible for commanding units, developing strategy, and making key decisions.
Enlisted Personnel Ranks

Enlisted personnel ranks in the Soviet military included:
- Private (Ryadovoy)
- Junior Sergeant (Mladshiy Serzhant)
- Sergeant (Serzhant)
- Senior Sergeant (Starshiy Serzhant)
- Master Sergeant (Starshina)
These ranks were responsible for carrying out basic tasks, such as guard duty, maintenance, and combat operations. Enlisted personnel were the backbone of the Red Army, making up the bulk of the military's personnel.
Non-Commissioned Officer Ranks
Non-commissioned officer ranks in the Soviet military included:
- Junior Lieutenant (Mladshiy Leytenant)
- Lieutenant (Leytenant)
- Senior Lieutenant (Starshiy Leytenant)
- Captain (Kapitan)
- Major (Mayor)
These ranks held leadership positions, overseeing enlisted personnel and coordinating unit operations. Non-commissioned officers played a crucial role in maintaining discipline and order within the Red Army.
Commissioned Officer Ranks

Commissioned officer ranks in the Soviet military included:
- Lieutenant Colonel (Podpolkovnik)
- Colonel (Polkovnik)
- Major General (General-Major)
- Lieutenant General (General-Leytenant)
- General of the Army (General Armii)
These ranks were responsible for commanding units, developing strategy, and making key decisions. Commissioned officers were the highest ranking category in the Soviet military, holding significant power and influence.
Admiral Ranks

The Soviet Navy also had its own set of ranks, including:
- Midshipman (Michman)
- Sub-Lieutenant (Mladshiy Leytenant)
- Lieutenant (Leytenant)
- Senior Lieutenant (Starshiy Leytenant)
- Captain-Lieutenant (Kapitan-Leytenant)
These ranks were responsible for commanding naval vessels, developing naval strategy, and coordinating maritime operations.
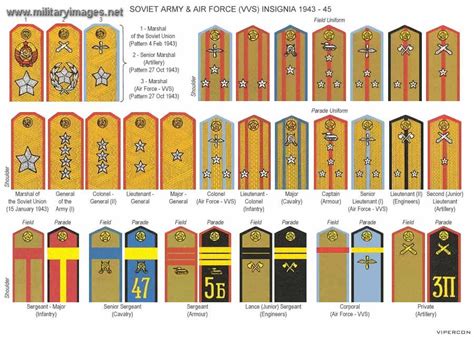
Marshal Ranks

The Soviet military also had a set of marshal ranks, which were the highest ranking positions in the Red Army. These ranks included:
- Marshal of the Soviet Union (Marshal Sovetskogo Soyuza)
- Chief Marshal of the Soviet Union (Glavnyy Marshal Sovetskogo Soyuza)
- Marshal of a Branch (Marshal Roda Voysk)
These ranks were responsible for commanding entire branches of the military, developing national strategy, and advising the Soviet government on military matters.
Gallery of Soviet Military Ranks
Soviet Military Ranks Image Gallery
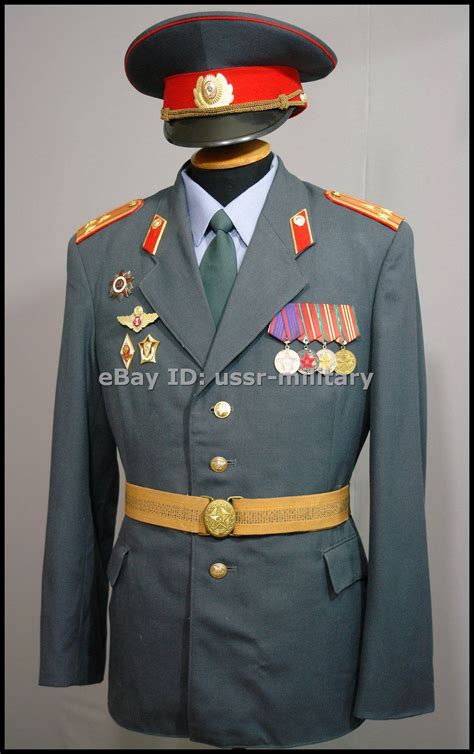









What was the highest ranking position in the Soviet military?
+The highest ranking position in the Soviet military was Marshal of the Soviet Union.
What was the difference between a lieutenant and a senior lieutenant in the Soviet military?
+A senior lieutenant was a higher ranking position than a lieutenant, with more responsibilities and authority.
What was the role of the Soviet Navy in the Soviet military?
+The Soviet Navy played a crucial role in the Soviet military, responsible for maritime operations, naval strategy, and defending the Soviet Union's coastal borders.
How did the Soviet military rank system change over time?
+The Soviet military rank system underwent several changes over time, with new ranks introduced and existing ones modified to reflect changes in the military's structure and doctrine.
What was the significance of the Soviet military rank system?
+The Soviet military rank system played a crucial role in maintaining discipline and order within the Red Army, as well as reflecting the Marxist-Leninist ideology of the Soviet Union.
In conclusion, the Soviet military rank system was a complex and multifaceted structure that played a crucial role in the Red Army's operations and ideology. Understanding the Soviet military ranks is essential to grasping the history and significance of the Soviet military, as well as its impact on world events. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the Soviet military rank system, and we encourage you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments below. Whether you're a history buff, a military enthusiast, or simply interested in learning more about the Soviet Union, we invite you to explore the fascinating world of Soviet military ranks and discover the rich history and significance behind them.
