Intro
Discover the 5 Steps Roman Road, a biblical evangelism tool using scripture to share faith, incorporating salvation, gospel, and discipleship for effective witness.
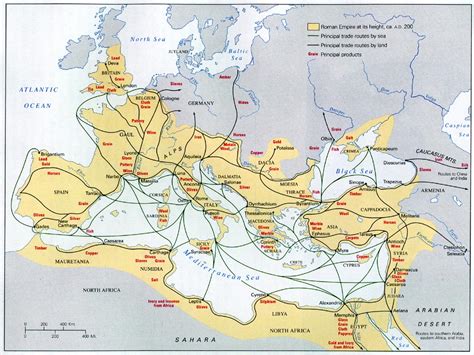
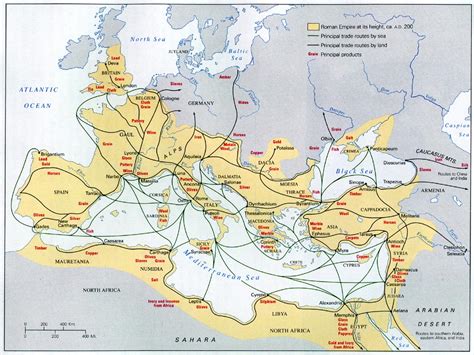
The Roman Road, also known as the Via Romana, was a network of roads built by the ancient Romans to connect their vast empire. These roads played a crucial role in the expansion and maintenance of the Roman Empire, facilitating the movement of goods, services, and people across the continent. In this article, we will explore the 5 steps involved in building a Roman Road, highlighting the engineering skills and techniques employed by the ancient Romans.
The construction of Roman Roads was a complex process that required careful planning, precise engineering, and meticulous execution. The Romans built over 250,000 miles of roads, which is a testament to their engineering prowess and logistical capabilities. The Roman Road network was not only a marvel of its time but also had a lasting impact on the development of modern transportation systems.
The Roman Road was more than just a means of transportation; it was a symbol of Roman power, engineering, and architecture. The roads were built to last, with some still existing today, and their construction involved a series of steps that ensured their durability and effectiveness.
Introduction to Roman Roads

The Roman Road network was a vital component of the Roman Empire, connecting cities, towns, and villages across the continent. The roads were built to facilitate trade, commerce, and the movement of people, goods, and services. The construction of Roman Roads involved a series of steps, from planning and surveying to building and maintenance.
Step 1: Planning and Surveying

The first step in building a Roman Road was planning and surveying. The Romans would identify the route, taking into account the terrain, climate, and existing infrastructure. They would use surveying tools, such as the groma, to determine the road's alignment and gradient. The groma was a simple yet effective tool that consisted of a vertical staff with a horizontal crossbar, allowing the surveyor to measure the road's alignment and ensure it was straight.
The Romans would also conduct a thorough analysis of the soil and geology, identifying potential hazards and challenges. They would use this information to determine the road's width, depth, and surface material. The planning and surveying stage was critical, as it ensured the road was built to last and could withstand the elements.
Key Considerations in Planning and Surveying
Some key considerations in planning and surveying a Roman Road included: * Terrain: The Romans would avoid building roads on steep slopes or in areas prone to landslides. * Climate: The Romans would take into account the local climate, building roads that could withstand extreme weather conditions. * Existing infrastructure: The Romans would often build roads that connected existing cities, towns, and villages.Step 2: Clearing and Grading
The second step in building a Roman Road was clearing and grading. The Romans would clear the land, removing any obstacles, such as trees, rocks, and other debris. They would then grade the land, ensuring the road was level and even. The Romans used a variety of tools, including pickaxes, shovels, and rakes, to clear and grade the land.
The clearing and grading stage was critical, as it ensured the road was built on a stable and even surface. The Romans would also use this stage to identify any potential hazards, such as underground water sources or unstable soil.
Tools Used in Clearing and Grading
Some tools used in clearing and grading a Roman Road included: * Pickaxes: Used to break up rocks and other hard surfaces. * Shovels: Used to remove soil and other debris. * Rakes: Used to level and even the surface.Step 3: Building the Roadbed
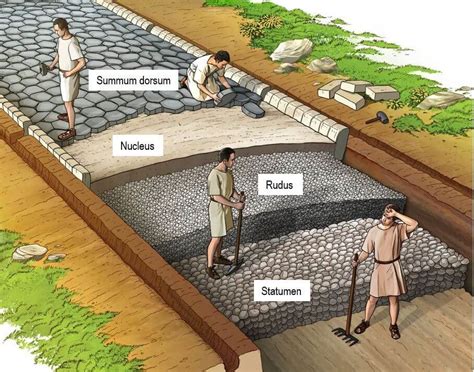
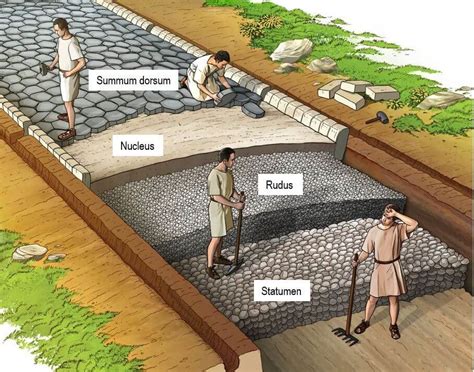
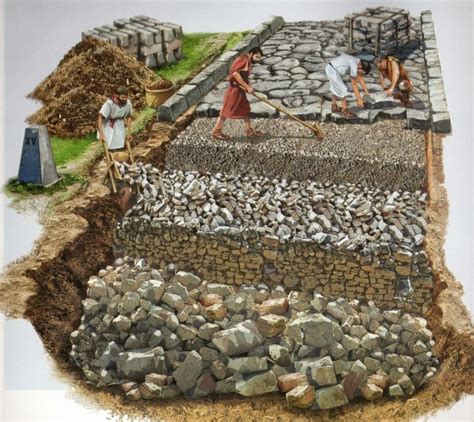
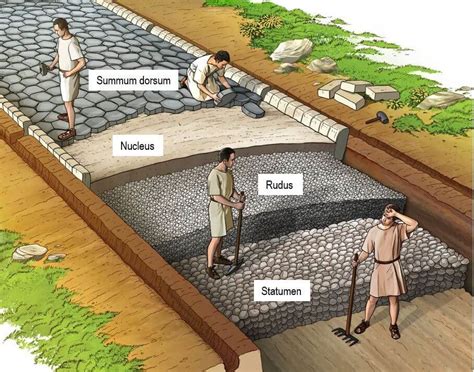
The third step in building a Roman Road was building the roadbed. The Romans would lay down a layer of large stones, known as the statumen, which provided a solid foundation for the road. They would then add a layer of smaller stones, known as the rudus, which helped to drain water and provide additional support.
The roadbed was critical, as it ensured the road was stable and could withstand heavy traffic. The Romans would also use this stage to add any additional features, such as drainage systems or culverts.
Components of the Roadbed
Some components of the roadbed included: * Statumen: A layer of large stones that provided a solid foundation for the road. * Rudus: A layer of smaller stones that helped to drain water and provide additional support. * Drainage systems: The Romans would often build drainage systems, such as culverts, to ensure water did not accumulate on the road.Step 4: Surfacing the Road

The fourth step in building a Roman Road was surfacing the road. The Romans would lay down a layer of small stones, known as the nucleus, which provided a smooth surface for travelers. They would then add a layer of gravel or sand, known as the summum, which helped to bind the stones together and provide additional traction.
The surfacing stage was critical, as it ensured the road was safe and durable. The Romans would also use this stage to add any additional features, such as milestones or road markers.
Components of the Surface
Some components of the surface included: * Nucleus: A layer of small stones that provided a smooth surface for travelers. * Summum: A layer of gravel or sand that helped to bind the stones together and provide additional traction. * Milestones: The Romans would often build milestones, which marked the distance and direction of the road.Step 5: Maintenance and Repair

The final step in building a Roman Road was maintenance and repair. The Romans would regularly inspect the road, identifying any damage or wear and tear. They would then repair the road, using a variety of techniques, such as repaving or resurfacing.
The maintenance and repair stage was critical, as it ensured the road remained safe and durable. The Romans would also use this stage to add any additional features, such as new drainage systems or road markers.
Techniques Used in Maintenance and Repair
Some techniques used in maintenance and repair included: * Repaving: The Romans would often repave the road, using new stones or gravel to provide a smooth surface. * Resurfacing: The Romans would often resurface the road, using new layers of stones or gravel to provide additional traction.Gallery of Roman Roads
Roman Roads Image Gallery







What were the main purposes of Roman Roads?
+The main purposes of Roman Roads were to facilitate trade, commerce, and the movement of people, goods, and services.
What were the key components of a Roman Road?
+The key components of a Roman Road included the statumen, rudus, nucleus, and summum.
How did the Romans maintain their roads?
+The Romans regularly inspected their roads, identifying any damage or wear and tear, and repaired them using a variety of techniques, such as repaving or resurfacing.
The construction of Roman Roads was a complex process that required careful planning, precise engineering, and meticulous execution. By following the 5 steps outlined in this article, the Romans were able to build a network of roads that played a crucial role in the expansion and maintenance of their empire. We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the engineering skills and techniques employed by the ancient Romans. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about Roman Roads, please do not hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
