Intro
Unlock precise drilling with our 5 tap drill chart tips, featuring thread sizes, hole diameters, and drilling techniques for accurate tapping, threading, and hole-making processes.
The world of drilling and tapping can be complex, especially when it comes to selecting the right tap drill size for a specific project. A tap drill chart is an essential tool that helps individuals determine the correct drill bit size to use before tapping a hole. In this article, we will delve into the importance of using a tap drill chart and provide valuable tips on how to get the most out of it.
When working with metals, plastics, or other materials, it's crucial to have a precise hole size to ensure a secure and reliable thread. A tap drill chart serves as a guide, providing the necessary information to achieve the desired thread size and type. By using a tap drill chart, individuals can avoid common mistakes such as stripping threads, damaging the material, or creating holes that are too small or too large.
The use of a tap drill chart is not limited to professional machinists or engineers; it's also essential for DIY enthusiasts, woodworkers, and anyone who works with materials that require drilling and tapping. With a tap drill chart, individuals can ensure that their projects are completed efficiently and effectively, saving time and reducing the risk of errors.
Understanding Tap Drill Charts

Key Components of a Tap Drill Chart
A tap drill chart typically includes the following key components: * Thread size and type (e.g., metric, imperial, or ISO) * Drill bit size (in inches or millimeters) * Material type (e.g., steel, aluminum, or plastic) * Thread pitch (e.g., coarse or fine) * Tap size and type (e.g., straight or tapered)Tip 1: Choose the Right Material Type
Common Material Types
Some common material types that may be listed on a tap drill chart include: * Steel (e.g., stainless, carbon, or alloy) * Aluminum (e.g., 6061, 7075, or cast) * Plastic (e.g., ABS, PVC, or polycarbonate) * Wood (e.g., hardwood, softwood, or composite)Tip 2: Select the Correct Thread Size and Type
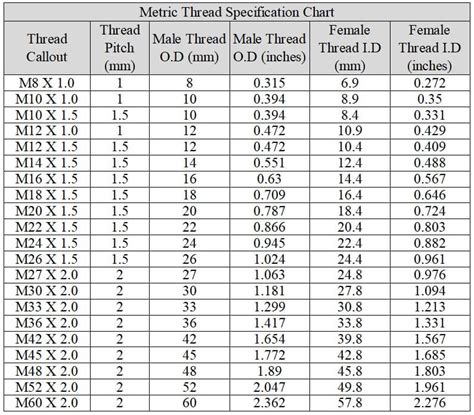
Common Thread Sizes and Types
Some common thread sizes and types that may be listed on a tap drill chart include: * Metric threads (e.g., M3, M5, or M10) * Imperial threads (e.g., #6, #8, or 1/4") * ISO threads (e.g., ISO 68, ISO 724, or ISO 1179)Tip 3: Consider the Thread Pitch
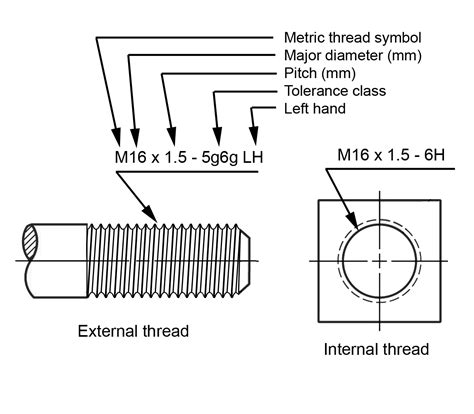
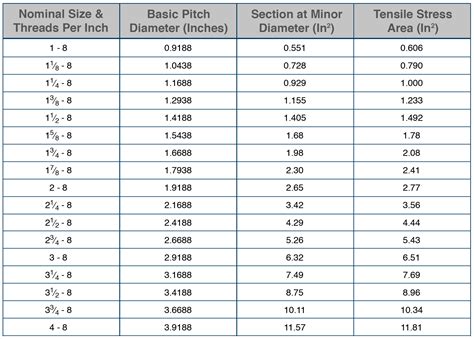
Common Thread Pitches
Some common thread pitches that may be listed on a tap drill chart include: * Coarse thread pitch (e.g., 1/4"-20 or M10 x 1.5) * Fine thread pitch (e.g., 1/4"-28 or M10 x 1.0)Tip 4: Use the Correct Tap Size and Type
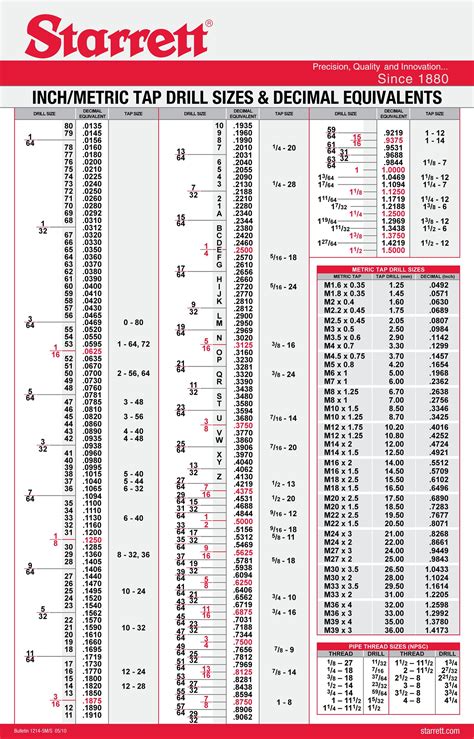
Common Tap Sizes and Types
Some common tap sizes and types that may be listed on a tap drill chart include: * Straight taps (e.g., 1/4"-20 or M10 x 1.5) * Tapered taps (e.g., 1/4"-20 or M10 x 1.0)Tip 5: Consult the Chart Carefully

Best Practices for Using a Tap Drill Chart
Some best practices for using a tap drill chart include: * Always consult the chart before drilling and tapping * Use the correct material type and thread size and type * Consider the thread pitch and tap size and type * Double-check the calculations to ensure accuracyTap Drill Chart Image Gallery
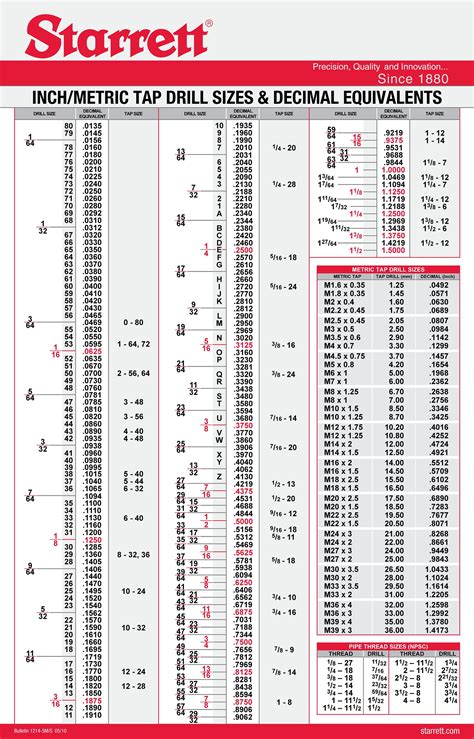




What is a tap drill chart?
+A tap drill chart is a table or graph that provides information on the recommended drill bit sizes for different thread sizes and types.
How do I read a tap drill chart?
+To read a tap drill chart, you need to consider the material type, thread size and type, thread pitch, and tap size and type.
What are the benefits of using a tap drill chart?
+The benefits of using a tap drill chart include increased accuracy, reduced errors, and improved efficiency in drilling and tapping operations.
Can I use a tap drill chart for different materials?
+Yes, a tap drill chart can be used for different materials, including steel, aluminum, plastic, and wood.
How often should I consult a tap drill chart?
+You should consult a tap drill chart every time you perform a drilling and tapping operation to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
In
