Intro
Discover 5 essential Periodic Table tips, including element classification, symbol decoding, and group trends, to master chemistry and understand atomic structures, electron configurations, and periodic trends.
Understanding the periodic table is crucial for anyone interested in chemistry, physics, or biology. The periodic table is a tabular display of the known chemical elements, organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number (number of protons in the atom's nucleus) and are grouped into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Here are some essential tips to help you navigate and understand the periodic table better.
The periodic table can seem overwhelming at first glance, with its complex arrangement of elements and numerous symbols. However, once you grasp the underlying principles and patterns, it becomes a powerful tool for predicting the properties and behavior of elements. For instance, elements in the same group exhibit similar chemical properties due to the same number of electrons in their outer shell, which is crucial for understanding chemical reactions and bonding.
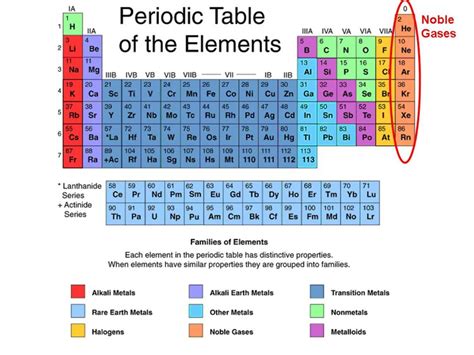
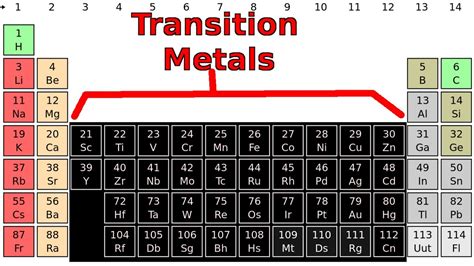
As you delve deeper into the world of chemistry, you'll find that the periodic table is not just a static chart but a dynamic tool that helps in understanding the relationships between elements. It's divided into metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, with metals being on the left side and nonmetals on the right, and metalloids forming a staircase line that demarcates metals from nonmetals. This division is crucial for understanding the physical and chemical properties of elements.
Understanding the Periodic Table Structure
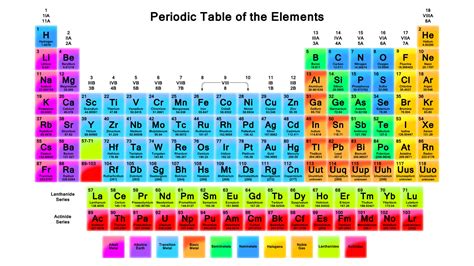
The periodic table is structured in a way that elements with similar properties recur at regular intervals. This is due to the periodic nature of electron configuration, where elements in the same group have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell. Understanding this structure is key to predicting chemical behavior and identifying trends in physical properties such as atomic radius, electronegativity, and electron affinity.
Groups and Periods
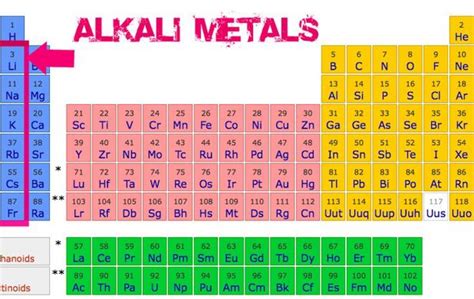
The periodic table is divided into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows). Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of electrons in their outermost shell. This leads to similar chemical behavior, such as the reactivity of alkali metals in Group 1. On the other hand, elements in the same period show trends in atomic radius, electronegativity, and electron affinity as you move from left to right across a period.Identifying Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids

Metals are typically found on the left side and center of the periodic table. They are usually shiny, malleable, and good conductors of electricity. Nonmetals are located on the right side of the periodic table and tend to be brittle, not shiny, and poor conductors of electricity. Metalloids, which exhibit some properties of metals and some of nonmetals, are found on the border between metals and nonmetals, forming a staircase line from boron (B) to astatine (At).
Periodic Trends
Understanding periodic trends is essential for predicting the properties of elements. Key trends include atomic radius, which generally decreases from left to right across a period and increases down a group; electronegativity, which increases from left to right across a period and decreases down a group; and electron affinity, which shows a more complex trend but generally increases across a period.Using the Periodic Table to Predict Chemical Behavior

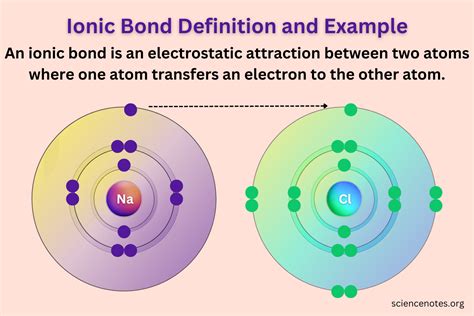
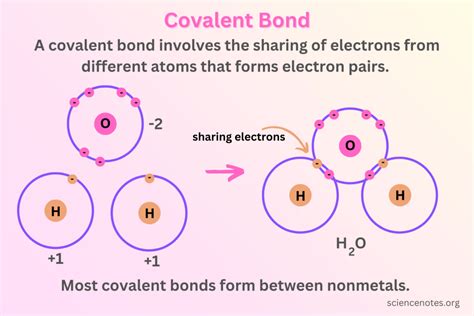
The periodic table can be used to predict how elements will react with each other. For example, elements in Group 1 (alkali metals) and Group 17 (halogens) readily form ions with a +1 and -1 charge, respectively, making their compounds highly reactive. The table also helps in understanding the types of bonds that can form between elements, such as ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds, based on their positions in the table.
Chemical Reactivity
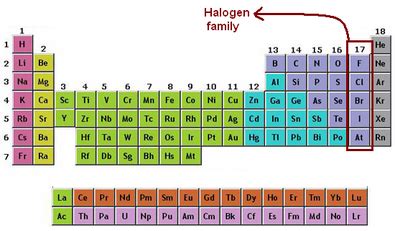
Chemical reactivity is closely related to the position of an element in the periodic table. Highly reactive elements like fluorine (F) and oxygen (O) are found in the upper right corner of the periodic table, while less reactive elements like neon (Ne) and argon (Ar) are located below them. The noble gases, in the far right column, are unreactive due to their full outer energy level.Learning the Elements
Learning the elements can seem daunting, but there are several strategies to make it more manageable. Starting with the most common elements and learning their positions, symbols, and basic properties can provide a solid foundation. Using mnemonics or songs to remember the order of elements, especially in the first few periods, can also be helpful.
Mnemonics and Memory Aids
Mnemonics are memory aids that associate new information with something already familiar, like a word, phrase, or image. For the periodic table, mnemonics can help remember the order of elements or the elements in a particular group. For example, "Happy Henry Likes Beer But Can't Obtain Fizzy Nachos" can help recall the first letter of elements in a specific order.Practical Applications of the Periodic Table

The periodic table has numerous practical applications in fields such as chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering. It is used in the development of new materials, prediction of chemical reactions, and understanding of biological processes. The table also plays a crucial role in environmental science, helping to understand and mitigate the effects of pollutants.
Environmental Science
In environmental science, the periodic table is used to understand the cycling of elements through ecosystems and the impact of human activities on the environment. For example, understanding the properties of carbon (C) and its compounds is essential for studying climate change and the carbon cycle.Gallery of Periodic Table Elements
Periodic Table Elements Image Gallery

What is the periodic table used for?
+The periodic table is used to predict the properties and behavior of elements, understand chemical reactions, and identify trends in physical properties.
How are elements organized in the periodic table?
+Elements are organized by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties, into rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
What are the main categories of elements in the periodic table?
+The main categories are metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, with metals being on the left side, nonmetals on the right, and metalloids forming a staircase line that demarcates metals from nonmetals.
How can the periodic table help in predicting chemical behavior?
+The periodic table can predict how elements will react with each other based on their positions, helping to understand the formation of ions, ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds, and the reactivity of elements.
What are some practical applications of the periodic table?
+The periodic table has applications in chemistry, physics, biology, engineering, and environmental science, including the development of new materials, prediction of chemical reactions, and understanding biological processes.
As we conclude our exploration of the periodic table and its many facets, it's clear that this tool is indispensable for anyone interested in the sciences. Whether you're a student looking to grasp the fundamentals of chemistry or a professional seeking to apply the principles of the periodic table in real-world scenarios, understanding the periodic table is essential. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, or questions about the periodic table in the comments below. How do you use the periodic table in your studies or work? What aspects of the periodic table do you find most fascinating or challenging? By engaging with the periodic table and its many applications, we can deepen our understanding of the world around us and unlock new discoveries and innovations.
