Intro
Master 5 division chart tips to improve math skills, featuring division tables, charts, and worksheets with long division methods and examples.
Division is a fundamental concept in mathematics that can be challenging for students to grasp, especially when it comes to creating division charts. A division chart, also known as a division table, is a visual tool used to help students understand the relationship between numbers and their quotients. In this article, we will explore the importance of division charts and provide five valuable tips to help students create and use them effectively.
Division charts are essential for students to develop a strong foundation in mathematics, as they help build problem-solving skills, improve mental math abilities, and enhance overall math fluency. By using division charts, students can quickly identify patterns and relationships between numbers, making it easier to solve complex math problems. Moreover, division charts can be used to introduce students to more advanced math concepts, such as fractions, decimals, and percentages.
The use of division charts can also help students develop critical thinking skills, as they learn to analyze and interpret data, identify errors, and make connections between different math concepts. Additionally, division charts can be used to support different learning styles, making them an excellent tool for teachers to differentiate instruction and cater to the diverse needs of their students. Whether you are a student, teacher, or parent, understanding how to create and use division charts effectively can make a significant difference in math education.
Introduction to Division Charts

To create a division chart, students can start by listing the numbers they want to include in the chart, usually ranging from 0 to 10 or 12. They can then draw a grid, with the dividend listed on the top row and the divisor listed on the left column. The next step is to fill in the quotients, using the division symbol (÷) to indicate the operation. For example, if the dividend is 12 and the divisor is 3, the quotient would be 4, since 12 ÷ 3 = 4.
Tip 1: Start with Simple Division Charts
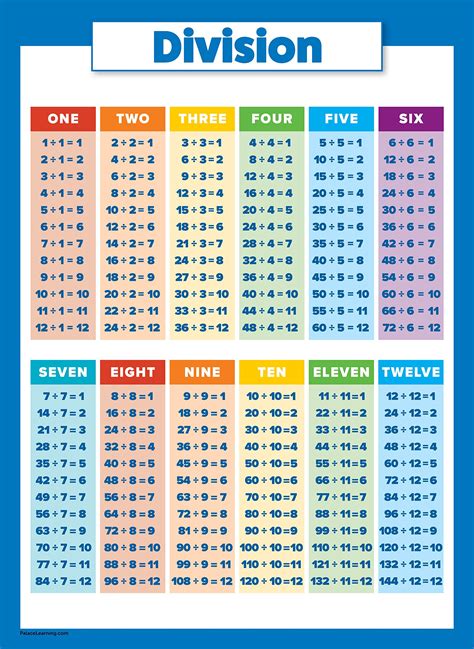
To create a simple division chart, students can start by listing the numbers 0 to 10 on the top row and the numbers 1 to 10 on the left column. They can then fill in the quotients, using the division symbol (÷) to indicate the operation. For example, if the dividend is 6 and the divisor is 2, the quotient would be 3, since 6 ÷ 2 = 3.
Tip 2: Use Visual Aids to Support Learning

For example, teachers can use base-ten blocks to demonstrate the concept of division, where students can see the physical representation of the dividend being divided into equal groups. This visual representation can help students understand the concept of division and develop a stronger foundation in math.
Tip 3: Practice with Real-World Applications

For instance, if a student is baking cookies and needs to divide a batch of 24 cookies among 4 friends, they can use a division chart to determine how many cookies each friend will get. This real-world application can help students see the value and importance of division charts in solving everyday problems.
Tip 4: Use Technology to Enhance Learning
For example, teachers can use online resources such as math games or interactive division charts to provide students with a fun and engaging way to practice division charts. These digital tools can also provide immediate feedback and assessment, helping teachers to track student progress and identify areas where students need additional support.
Tip 5: Make it Fun and Engaging

For instance, teachers can create a division chart scavenger hunt where students have to find and solve division problems around the classroom or school. This interactive activity can help students develop problem-solving skills, build teamwork, and make learning division charts a fun and enjoyable experience.
Gallery of Division Chart Examples
Division Chart Image Gallery

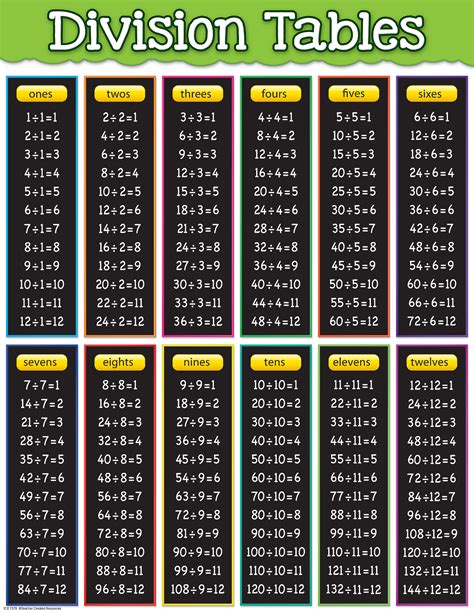


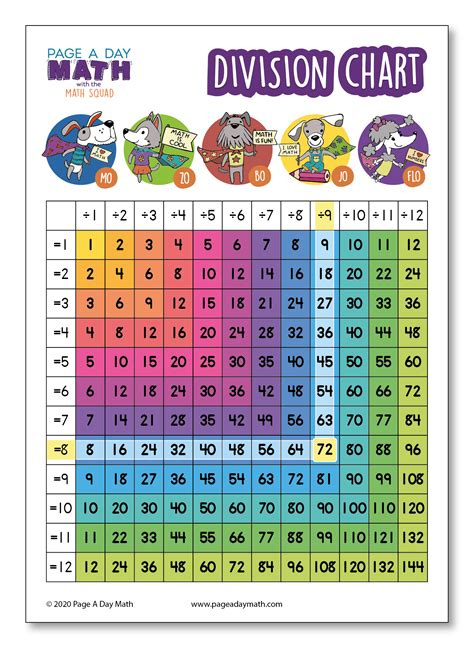

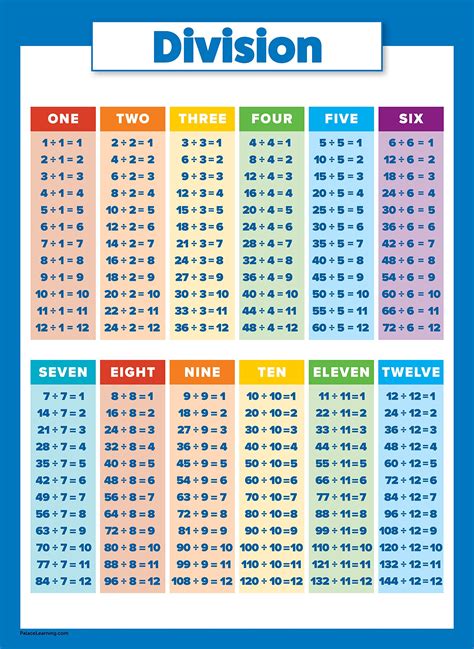
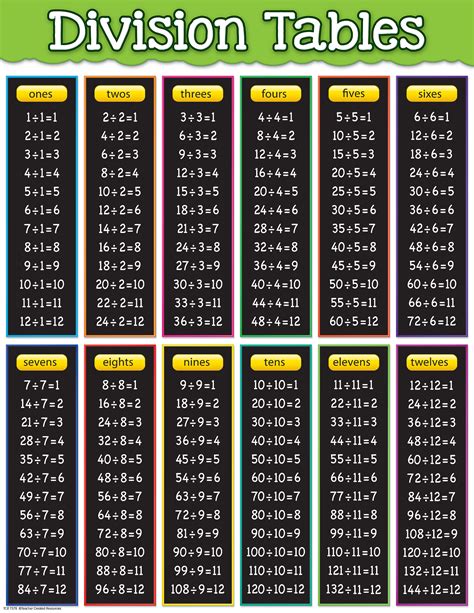

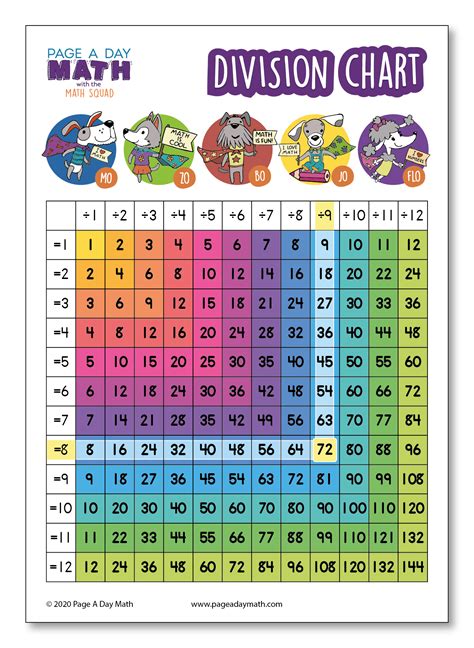
What is a division chart?
+A division chart is a table that displays the quotients of a set of numbers, typically ranging from 0 to 10 or 12.
How do I create a division chart?
+To create a division chart, start by listing the numbers you want to include in the chart, usually ranging from 0 to 10 or 12. Draw a grid, with the dividend listed on the top row and the divisor listed on the left column. Fill in the quotients, using the division symbol (÷) to indicate the operation.
What are the benefits of using division charts?
+The benefits of using division charts include developing problem-solving skills, improving mental math abilities, and enhancing overall math fluency. Division charts can also help students identify patterns and relationships between numbers, making it easier to solve complex math problems.
How can I make division charts fun and engaging for students?
+There are many ways to make division charts fun and engaging for students, such as creating division chart scavenger hunts, playing division games, or using music and movement to practice division facts. Teachers can also use visual aids, such as diagrams, charts, and graphs, to support student learning and make division charts more interactive.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when creating division charts?
+Some common mistakes to avoid when creating division charts include not listing the numbers correctly, not filling in the quotients accurately, and not using the division symbol (÷) consistently. Teachers should also ensure that students understand the concept of division and can apply it to real-world problems.
In conclusion, division charts are a valuable tool for students to develop a strong foundation in mathematics. By following the five tips outlined in this article, teachers can help students create and use division charts effectively, making math more engaging, interactive, and fun. Whether you are a student, teacher, or parent, we encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with division charts in the comments below. Don't forget to share this article with others who may benefit from learning about division charts, and stay tuned for more math-related topics and tips!
