Intro
Learn effective Pressure Injury Wound Management Ati techniques, including wound assessment, staging, and treatment, to prevent pressure ulcers and promote wound healing, with strategies for offloading pressure and managing tissue damage.
Pressure injury wound management is a critical aspect of healthcare, particularly for individuals with limited mobility or those who are bedridden for extended periods. The development of pressure injuries, also known as pressure ulcers or bedsores, can lead to severe health complications, increased healthcare costs, and a decreased quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the importance of pressure injury wound management, its benefits, working mechanisms, steps, and other key information related to the topic.
Pressure injuries are localized damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of pressure, or pressure in combination with shear and/or friction. The management of pressure injuries requires a comprehensive approach, involving the assessment of the patient's overall health, the identification of risk factors, and the implementation of effective prevention and treatment strategies. The Assessment Technologies Institute (ATI) has developed guidelines and resources to support healthcare professionals in providing high-quality care for individuals with pressure injuries.
Understanding Pressure Injuries

Assessment and Prevention

Pressure Redistribution
Pressure redistribution is a critical aspect of pressure injury prevention and treatment. This involves the use of support surfaces, such as mattresses and cushions, to reduce pressure on vulnerable areas. Other strategies, such as regular repositioning and the use of protective devices, can also help to redistribute pressure and prevent pressure injuries.Wound Management
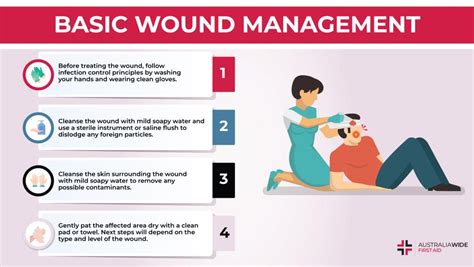
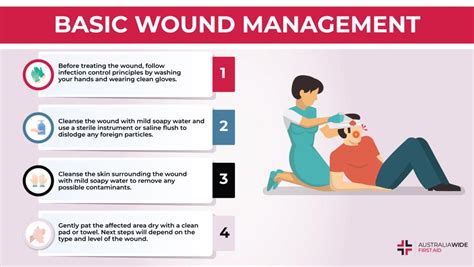
Debridement and Wound Cleansing
Debridement and wound cleansing are critical aspects of wound management. Debridement involves the removal of dead tissue, bacteria, and other debris from the wound, promoting the growth of healthy tissue. Wound cleansing involves the use of saline solution or other cleansers to remove bacteria, debris, and other contaminants from the wound.ATI Guidelines and Resources
ATI Assessment Tools
ATI assessment tools are designed to support healthcare professionals in assessing the risk of pressure injuries and developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. These tools include the Braden Scale for Predicting Pressure Sore Risk and the Norton Scale for Predicting Pressure Sore Risk.Benefits of Pressure Injury Wound Management
Improved Patient Outcomes
The effective management of pressure injuries can lead to improved patient outcomes, including faster wound healing, reduced pain, and improved mobility. Pressure injury wound management can also promote the prevention of pressure injuries, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient safety.Working Mechanisms of Pressure Injury Wound Management

Steps in Pressure Injury Wound Management
The steps in pressure injury wound management include: * Assessing the patient's overall health and identifying risk factors * Developing a treatment plan and implementing evidence-based interventions * Promoting wound healing and managing pain * Preventing infection and promoting self-management * Involving the patient and their family in the care processPractical Examples and Statistical Data

Statistical Data
Statistical data on pressure injuries and wound management include: * The prevalence of pressure injuries in healthcare settings is estimated to be around 10-20% * The cost of treating pressure injuries is estimated to be around $10-20 billion annually * The implementation of pressure injury prevention programs can reduce the incidence of pressure injuries by 50-70%Pressure Injury Wound Management Image Gallery


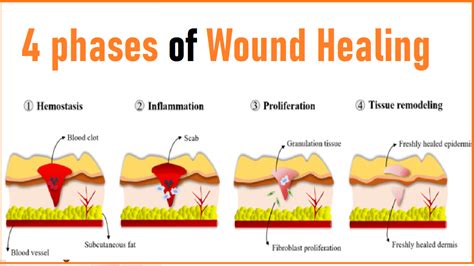
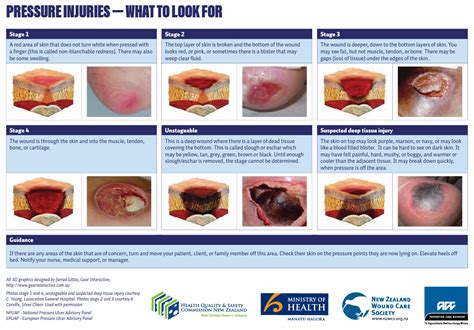





What is a pressure injury?
+A pressure injury is a localized damage to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occurs over a bony prominence as a result of pressure, or pressure in combination with shear and/or friction.
How can pressure injuries be prevented?
+Pressure injuries can be prevented by assessing the patient's overall health, identifying risk factors, and implementing effective prevention strategies, such as regular repositioning, the use of support surfaces, and the application of protective devices.
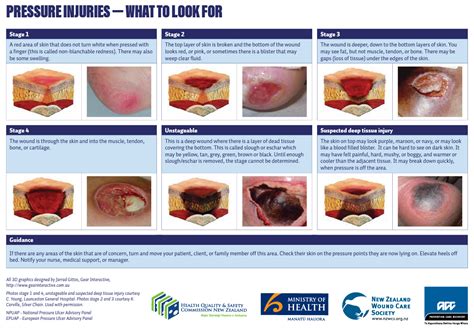
What are the stages of pressure injuries?
+Pressure injuries can be categorized into four stages, each with distinct characteristics and treatment requirements. Stage 1 pressure injuries are the earliest stage, where the skin is intact but may appear red or discolored. Stage 2 pressure injuries involve the breakdown of the skin, resulting in a shallow open sore. Stage 3 pressure injuries are more severe, with the sore extending into the tissue beneath the skin. Stage 4 pressure injuries are the most severe, with the sore extending into the muscle, bone, or other supporting structures.
In summary, pressure injury wound management is a critical aspect of healthcare, requiring a comprehensive approach to assessment, prevention, and treatment. The effective management of pressure injuries can have numerous benefits, including improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs, and enhanced quality of life. By understanding the importance of pressure injury wound management and implementing evidence-based strategies, healthcare professionals can promote the prevention and treatment of pressure injuries, improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on pressure injury wound management, and to explore the resources and guidelines provided by the Assessment Technologies Institute (ATI) to support healthcare professionals in providing high-quality care for individuals with pressure injuries.
