Intro
Discover 5 essential tips for managing Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension in Newborns (PPHN), including diagnosis, treatment, and care strategies to improve infant health outcomes and reduce complications.
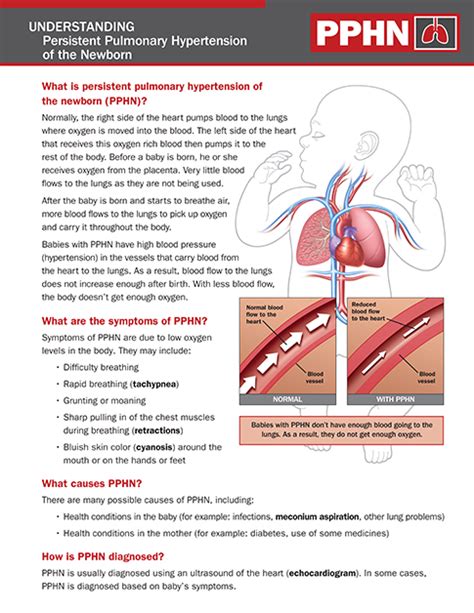
Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn (PPHN) is a serious condition that affects newborn babies, causing high blood pressure in the lungs and potentially leading to respiratory failure. Understanding the condition, its causes, symptoms, and management is crucial for healthcare providers and families. Here are five tips related to PPHN, aiming to provide insights into its management and the importance of early intervention.
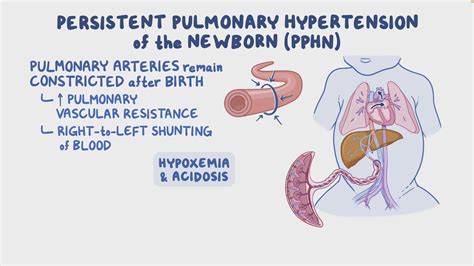
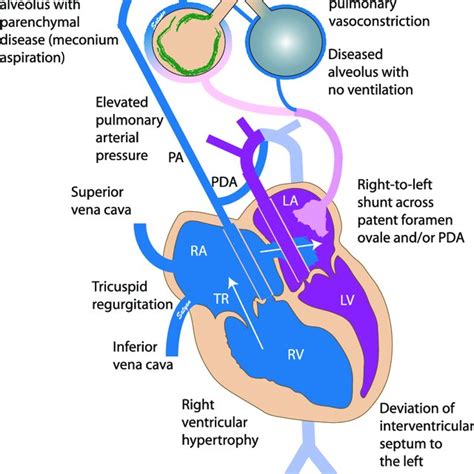
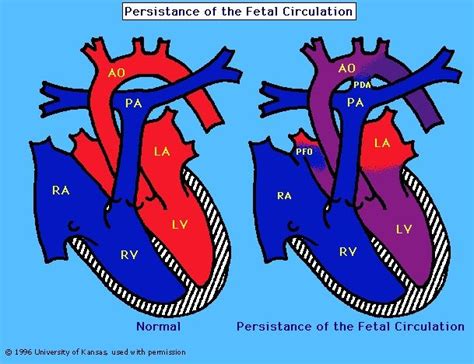
PPHN is a condition that occurs when the blood vessels in the lungs of a newborn baby fail to relax and expand, leading to high blood pressure. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention. The causes of PPHN can vary, including meconium aspiration syndrome, congenital heart disease, and maternal factors such as diabetes and hypertension. Recognizing the risk factors and symptoms early on is critical for effective management.
Understanding PPHN
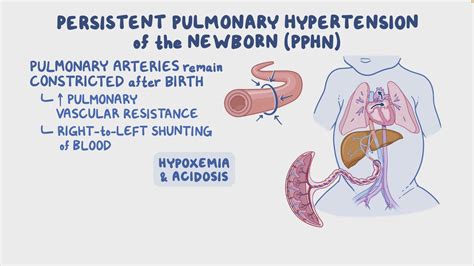
Causes and Risk Factors

Symptoms and Diagnosis
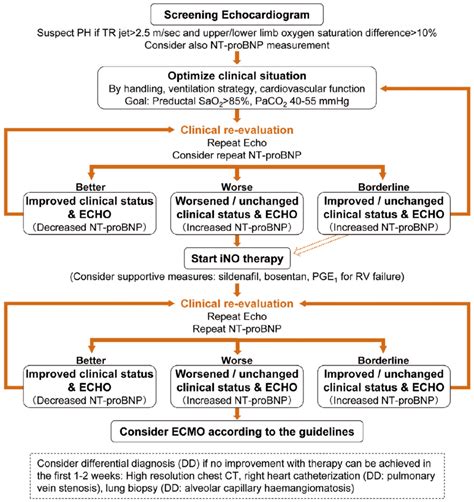
Treatment and Management
Prevention and Long-term Outcomes
Key Considerations for Families
For families with a newborn diagnosed with PPHN, it is essential to be aware of the condition, its management, and the potential long-term implications. This includes understanding the treatment options, recognizing the signs of complications, and being involved in the care plan. Support from healthcare providers, family, and friends can make a significant difference in navigating the challenges associated with PPHN.Future Directions in PPHN Research
Research into PPHN is ongoing, with a focus on better understanding the pathophysiology of the condition, developing more effective treatments, and improving outcomes. Advances in diagnostic techniques, therapeutic interventions, and preventive strategies hold promise for reducing the incidence and severity of PPHN. Collaboration between healthcare providers, researchers, and families is crucial for advancing our knowledge and improving the care for newborns with PPHN.PPHN Image Gallery
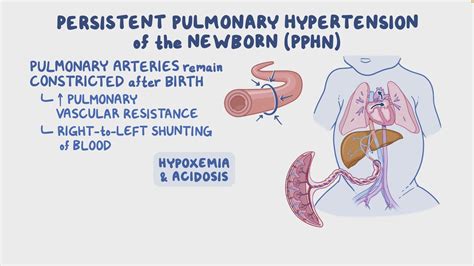
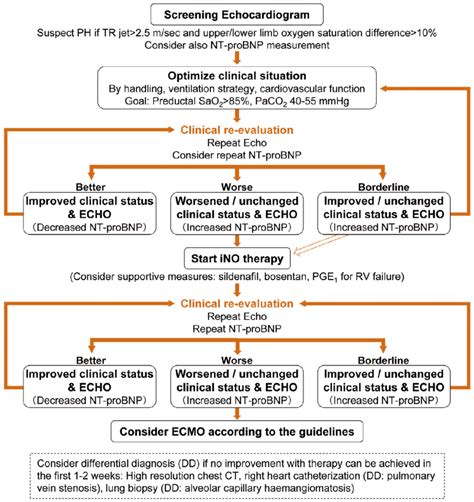

What are the primary symptoms of PPHN?
+The primary symptoms of PPHN include difficulty breathing, cyanosis, and signs of respiratory distress such as grunting and flaring of the nostrils.
How is PPHN diagnosed?
+PPHN is diagnosed through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests such as echocardiography, chest X-rays, and blood gas analyses.
What are the treatment options for PPHN?
+Treatment options for PPHN include oxygen therapy, mechanical ventilation, pharmacological interventions such as nitric oxide, and in severe cases, ECMO.
Can PPHN be prevented?
+While PPHN cannot be completely prevented, addressing underlying risk factors such as maternal health conditions and optimizing perinatal care can reduce its incidence.
What are the long-term outcomes for newborns with PPHN?
+Long-term outcomes for newborns with PPHN can vary, with some experiencing residual pulmonary hypertension or other respiratory complications, emphasizing the need for ongoing monitoring and follow-up care.
In conclusion, PPHN is a serious condition that requires prompt recognition and effective management to improve outcomes for affected newborns. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, healthcare providers and families can work together to address the challenges associated with PPHN. Ongoing research and advancements in diagnostic and therapeutic strategies hold promise for reducing the incidence and severity of PPHN, improving the quality of life for those affected. We invite readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and seek further information on this critical topic, fostering a community of support and knowledge for those impacted by PPHN.
