Intro
Master Multiple Sclerosis care with our ATi template guide, covering symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and management, including relapsing-remitting MS, progressive MS, and disease-modifying therapies.
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic and often disabling autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system (CNS), which includes the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. The disease is characterized by the destruction of the myelin sheath, a protective layer that surrounds nerve fibers, leading to communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. In this article, we will delve into the world of MS, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies. Whether you are a healthcare professional, a person living with MS, or simply someone interested in learning more about this complex condition, this guide is designed to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of MS and its implications.
MS is a significant public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. According to the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, approximately 2.8 million people globally live with MS, with the disease being more common in women than men. The exact cause of MS remains unknown, but research suggests that it is a combination of genetic, environmental, and infectious factors that trigger the immune system to attack the myelin sheath. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of MS is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
The symptoms of MS can vary widely from person to person, depending on the location and severity of the damage to the CNS. Common symptoms include vision problems, muscle weakness, balance and coordination issues, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties. In some cases, people with MS may experience severe symptoms, such as paralysis, seizures, or speech problems. The unpredictable nature of MS can make it challenging for individuals to manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life. Therefore, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the disease and its treatment options to make informed decisions about care.
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis
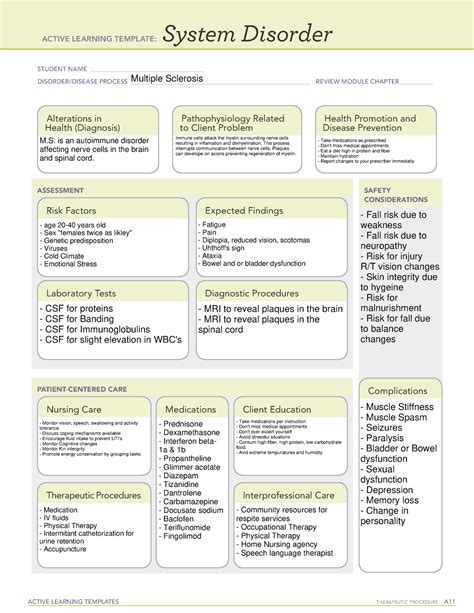
To comprehend the complexities of MS, it is vital to understand the different types of the disease. There are four main types of MS: relapsing-remitting MS (RRMS), secondary progressive MS (SPMS), primary progressive MS (PPMS), and progressive-relapsing MS (PRMS). Each type has distinct characteristics, and understanding the differences between them can help healthcare professionals develop personalized treatment plans. Additionally, recognizing the various stages of MS, including relapses, remissions, and progression, is critical for effective disease management.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact causes of MS are still not fully understood, but research has identified several risk factors that may contribute to the development of the disease. These include: * Genetic predisposition: Having a family history of MS increases the risk of developing the disease. * Environmental factors: Exposure to certain environmental toxins, such as pesticides and heavy metals, may trigger the onset of MS. * Infectious agents: Some research suggests that viral infections, such as Epstein-Barr virus, may play a role in the development of MS. * Vitamin D deficiency: Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to an increased risk of MS.Diagnosis and Treatment

Diagnosing MS can be challenging, as the symptoms are often similar to those of other conditions. A comprehensive diagnostic evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, is necessary to confirm the presence of MS. The most commonly used diagnostic criteria are the McDonald criteria, which involve a combination of clinical, radiological, and laboratory evidence.
Treatment for MS typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies. Disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) are the primary treatment for MS, aiming to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses, slow disease progression, and manage symptoms. Some common DMTs include:
- Interferon beta-1a (Avonex, Rebif)
- Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone)
- Fingolimod (Gilenya)
- Dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera)
- Teriflunomide (Aubagio)
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing MS. These include: * Maintaining a healthy diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce inflammation and promote overall health. * Staying physically active: Regular exercise, such as walking, swimming, or yoga, can help improve mobility, balance, and cognitive function. * Managing stress: Stress can exacerbate MS symptoms; engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or deep breathing, can help mitigate this effect. * Getting enough sleep: Adequate sleep is essential for overall health and can help reduce MS symptoms.Management Strategies

Effective management of MS requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies. Some additional strategies for managing MS include:
- Cognitive rehabilitation: This involves working with a therapist to improve cognitive function, such as memory, attention, and processing speed.
- Physical therapy: A physical therapist can help improve mobility, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and injuries.
- Occupational therapy: An occupational therapist can assist with daily activities, such as bathing, dressing, and cooking, to promote independence and self-care.
- Support groups: Joining a support group can provide emotional support, education, and connection with others who are living with MS.
Alternative Therapies
Some people with MS may find alternative therapies, such as acupuncture, massage, or herbal supplements, helpful in managing their symptoms. However, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new therapies, as some may interact with medications or have adverse effects.Current Research and Future Directions

Research into MS is ongoing, with scientists exploring new treatments, diagnostic tools, and management strategies. Some promising areas of research include:
- Stem cell therapy: This involves using stem cells to repair damaged tissue in the CNS.
- Gene therapy: This involves using genes to modify the immune system and reduce inflammation.
- Nanotechnology: This involves using tiny particles to deliver medications directly to the CNS.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the progress made in understanding and managing MS, there are still significant challenges to be addressed. These include: * Improving diagnosis and treatment options for progressive forms of MS. * Developing more effective and targeted therapies for specific symptoms and disease stages. * Enhancing patient education and support to promote self-management and empowerment.Multiple Sclerosis Image Gallery
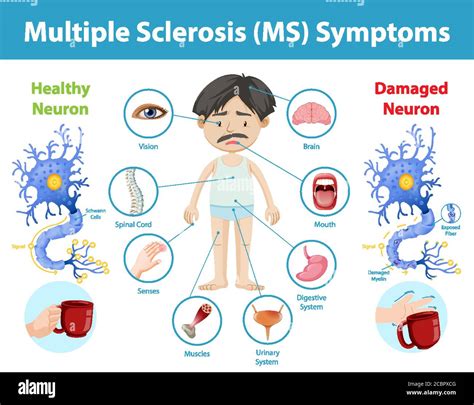
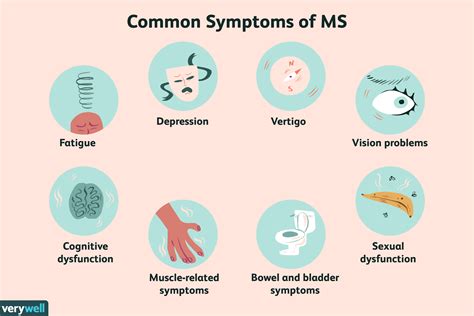








What are the early signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis?
+The early signs and symptoms of multiple sclerosis can vary widely, but common symptoms include vision problems, muscle weakness, balance and coordination issues, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties.
How is multiple sclerosis diagnosed?
+Multiple sclerosis is diagnosed through a comprehensive evaluation, including medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, such as MRI scans.
What are the treatment options for multiple sclerosis?
+Treatment options for multiple sclerosis include disease-modifying therapies, such as interferon beta-1a and glatiramer acetate, as well as lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet and staying physically active.
Can multiple sclerosis be cured?
+Currently, there is no cure for multiple sclerosis, but research is ongoing to develop new treatments and therapies that can help manage the disease and improve patient outcomes.
How can I manage my multiple sclerosis symptoms?
+Managing multiple sclerosis symptoms requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating medical treatment, lifestyle modifications, and alternative therapies, such as cognitive rehabilitation and physical therapy.
In conclusion, multiple sclerosis is a complex and multifaceted disease that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies for MS, individuals can take control of their health and improve their quality of life. We encourage readers to share their experiences, ask questions, and seek support from healthcare professionals and support groups to navigate the challenges of living with MS. Together, we can work towards a better understanding of this disease and improve patient outcomes.
