Intro
Boost efficiency with 5 key manufacturing KPIs, including productivity, quality, and lead time metrics, to optimize production and drive business growth through data-driven decision making and performance monitoring.
The manufacturing industry is a complex and multifaceted sector that requires careful monitoring and evaluation to ensure optimal performance. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) play a crucial role in this process, providing manufacturers with valuable insights into their operations and helping them make informed decisions. In this article, we will explore five essential manufacturing KPIs that can help manufacturers improve their efficiency, productivity, and overall competitiveness.
Manufacturing is a critical component of many economies around the world, providing employment opportunities, driving innovation, and contributing to economic growth. However, the industry is also facing numerous challenges, including rising costs, increasing competition, and growing environmental concerns. To remain competitive, manufacturers must be able to measure and evaluate their performance regularly, identifying areas for improvement and implementing strategies to address these challenges. This is where manufacturing KPIs come in – providing manufacturers with a powerful tool to optimize their operations and achieve their goals.
The use of KPIs in manufacturing is not a new concept, but it has become increasingly important in recent years. With the rise of Industry 4.0 and the Internet of Things (IoT), manufacturers have access to vast amounts of data and information, which can be used to inform their decision-making processes. By tracking and analyzing KPIs, manufacturers can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, identify trends and patterns, and make data-driven decisions to drive improvement. Whether it's improving efficiency, reducing waste, or enhancing product quality, KPIs provide manufacturers with a clear roadmap for success.
Overview of Manufacturing KPIs

Manufacturing KPIs are metrics used to measure and evaluate the performance of manufacturing operations. These KPIs can be broadly categorized into several areas, including productivity, quality, safety, and efficiency. By tracking and analyzing these KPIs, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize their operations, and achieve their goals. Some common examples of manufacturing KPIs include overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), defect rate, and inventory turnover.
Types of Manufacturing KPIs
Manufacturing KPIs can be classified into several types, including: * Productivity KPIs: These KPIs measure the efficiency and effectiveness of manufacturing operations, including metrics such as labor productivity and machine utilization. * Quality KPIs: These KPIs measure the quality of products and processes, including metrics such as defect rate and customer satisfaction. * Safety KPIs: These KPIs measure the safety of manufacturing operations, including metrics such as accident rate and injury frequency. * Efficiency KPIs: These KPIs measure the efficiency of manufacturing operations, including metrics such as energy consumption and waste reduction.1. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)

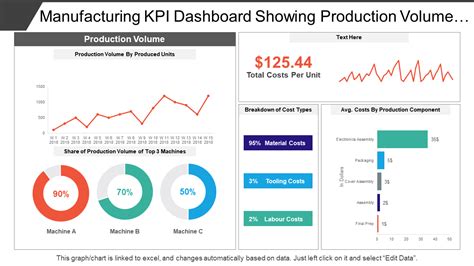
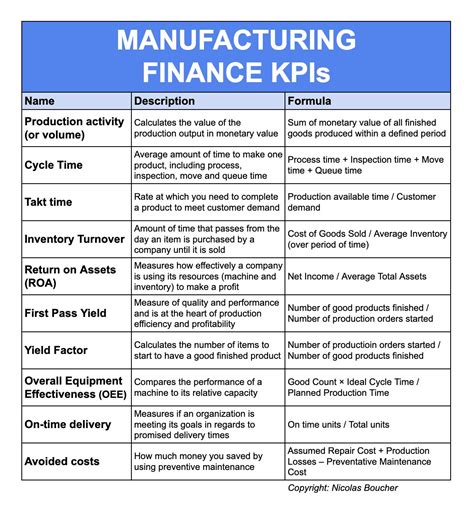
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a widely used KPI in manufacturing that measures the efficiency and effectiveness of equipment and machinery. OEE takes into account three key factors: availability, performance, and quality. Availability refers to the amount of time that equipment is available for production, while performance measures the speed at which equipment operates. Quality, on the other hand, measures the percentage of products that meet quality standards. By tracking OEE, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize equipment performance, and reduce downtime.
OEE is calculated using the following formula: OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality Where: Availability = (Operating time / Total time) x 100 Performance = (Ideal cycle time / Actual cycle time) x 100 Quality = (Good products / Total products) x 100
Benefits of OEE
The benefits of tracking OEE include: * Improved equipment performance and efficiency * Reduced downtime and increased productivity * Enhanced product quality and reduced waste * Better decision-making and resource allocation2. Defect Rate
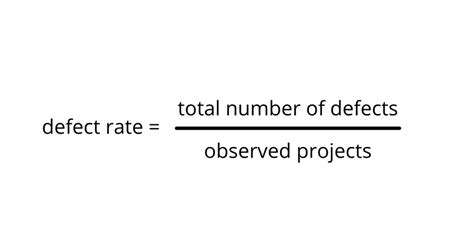
Defect rate is a KPI that measures the percentage of products that do not meet quality standards. This KPI is critical in manufacturing, as it directly impacts product quality, customer satisfaction, and revenue. By tracking defect rate, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize quality control processes, and reduce waste.
Defect rate is calculated using the following formula: Defect rate = (Number of defective products / Total number of products) x 100
Benefits of Defect Rate
The benefits of tracking defect rate include: * Improved product quality and reduced waste * Enhanced customer satisfaction and loyalty * Reduced costs associated with rework and scrap * Better decision-making and resource allocation3. Inventory Turnover
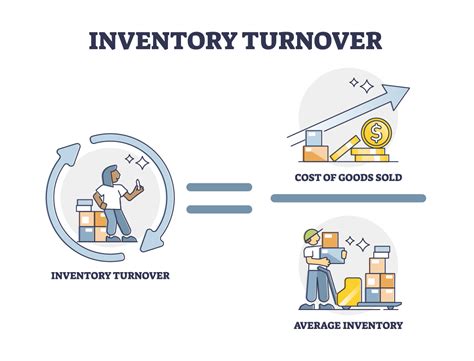
Inventory turnover is a KPI that measures the number of times that inventory is sold and replaced within a given period. This KPI is critical in manufacturing, as it directly impacts cash flow, working capital, and supply chain efficiency. By tracking inventory turnover, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize inventory management processes, and reduce costs.
Inventory turnover is calculated using the following formula: Inventory turnover = Cost of goods sold / Average inventory
Benefits of Inventory Turnover
The benefits of tracking inventory turnover include: * Improved cash flow and reduced working capital * Enhanced supply chain efficiency and reduced lead times * Reduced costs associated with inventory storage and handling * Better decision-making and resource allocation4. Lead Time
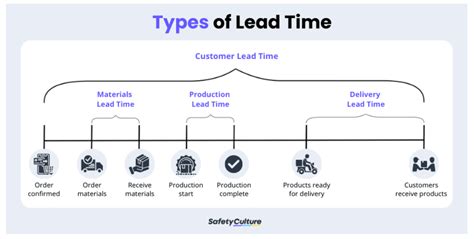
Lead time is a KPI that measures the time it takes to produce and deliver a product from raw materials to finished goods. This KPI is critical in manufacturing, as it directly impacts customer satisfaction, revenue, and competitiveness. By tracking lead time, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize production processes, and reduce delivery times.
Lead time is calculated using the following formula: Lead time = Time from order receipt to shipment
Benefits of Lead Time
The benefits of tracking lead time include: * Improved customer satisfaction and loyalty * Enhanced competitiveness and revenue growth * Reduced costs associated with inventory storage and handling * Better decision-making and resource allocation5. Overall Labor Effectiveness (OLE)

Overall Labor Effectiveness (OLE) is a KPI that measures the efficiency and effectiveness of labor in manufacturing operations. OLE takes into account two key factors: labor productivity and labor quality. Labor productivity measures the amount of work produced per hour, while labor quality measures the percentage of products that meet quality standards. By tracking OLE, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, optimize labor performance, and reduce costs.
OLE is calculated using the following formula: OLE = Labor productivity x Labor quality Where: Labor productivity = (Units produced / Labor hours) x 100 Labor quality = (Good products / Total products) x 100
Benefits of OLE
The benefits of tracking OLE include: * Improved labor performance and efficiency * Enhanced product quality and reduced waste * Reduced costs associated with labor and training * Better decision-making and resource allocationManufacturing KPIs Image Gallery


What is the purpose of manufacturing KPIs?
+The purpose of manufacturing KPIs is to measure and evaluate the performance of manufacturing operations, identify areas for improvement, and optimize processes to achieve goals and objectives.
How do I choose the right manufacturing KPIs for my business?
+To choose the right manufacturing KPIs for your business, you should consider your goals and objectives, industry benchmarks, and the specific needs of your operations. It's also important to select KPIs that are measurable, relevant, and actionable.
How often should I track and analyze my manufacturing KPIs?
+You should track and analyze your manufacturing KPIs regularly, ideally on a daily or weekly basis. This will allow you to identify trends and patterns, make data-driven decisions, and take corrective action to address any issues or concerns.
What are some common challenges associated with implementing manufacturing KPIs?
+Some common challenges associated with implementing manufacturing KPIs include data quality issues, lack of standardization, and inadequate training and support. It's also important to ensure that KPIs are aligned with business goals and objectives, and that they are regularly reviewed and updated.
How can I use manufacturing KPIs to improve my business?
+You can use manufacturing KPIs to improve your business by identifying areas for improvement, optimizing processes, and making data-driven decisions. KPIs can also help you to reduce costs, improve quality, and increase efficiency, ultimately leading to improved profitability and competitiveness.
In conclusion, manufacturing KPIs are a powerful tool for manufacturers to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve their goals. By tracking and analyzing KPIs such as OEE, defect rate, inventory turnover, lead time, and OLE, manufacturers can identify areas for improvement, reduce waste, and enhance product quality. We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with manufacturing KPIs in the comments section below. Additionally, if you found this article helpful, please share it with your network to help spread the knowledge.
