Intro
Discover the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) role in email delivery, routing, and protocol management, including SMTP, email servers, and message transfer.
The mail transfer agent (MTA) is a crucial component of the email infrastructure, responsible for routing and delivering emails between different mail servers. In today's digital age, email has become an essential means of communication, and the MTA plays a vital role in ensuring that emails are delivered efficiently and securely. In this article, we will delve into the world of MTAs, exploring their importance, functionality, and key characteristics.
The MTA is a software application that runs on a mail server, acting as a relay between the sender's and recipient's mail servers. Its primary function is to forward emails from the sender's server to the recipient's server, using a complex network of protocols and routing tables. The MTA is responsible for resolving the recipient's email address, determining the best route for delivery, and handling any errors or bounce messages that may occur during transmission.
The importance of MTAs cannot be overstated, as they enable the seamless exchange of emails between different email providers, organizations, and individuals. Without MTAs, email communication would be severely limited, and the internet as we know it would be vastly different. In addition to their functional role, MTAs also play a critical part in maintaining email security, filtering out spam and malicious content, and ensuring that emails are delivered to the intended recipient.
How Mail Transfer Agents Work

MTAs use a variety of protocols to communicate with other mail servers, including the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), the Post Office Protocol (POP), and the Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP). When an email is sent, the MTA on the sender's server establishes a connection with the recipient's server using SMTP, and then forwards the email to the recipient's inbox. The MTA also performs a series of checks to ensure that the email is valid, including verifying the sender's and recipient's email addresses, checking for spam and viruses, and applying any filters or rules that may be in place.
Key Components of a Mail Transfer Agent
The key components of an MTA include the mail queue, the routing table, and the protocol stack. The mail queue is a temporary storage area where emails are held until they can be delivered to the recipient's server. The routing table is a database that contains information about the best route for delivering emails to different domains and mail servers. The protocol stack refers to the set of protocols that the MTA uses to communicate with other mail servers, including SMTP, POP, and IMAP.Types of Mail Transfer Agents

There are several types of MTAs, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common types of MTAs include open-source MTAs, such as Postfix and Sendmail, and commercial MTAs, such as Microsoft Exchange and IBM Notes. Open-source MTAs are highly customizable and can be modified to meet the specific needs of an organization, while commercial MTAs offer a high level of support and integration with other software applications.
Benefits of Using a Mail Transfer Agent
The benefits of using an MTA include improved email delivery rates, enhanced security, and increased flexibility. MTAs can help to reduce spam and malicious content, improve email routing and delivery, and provide a high level of customization and control. Additionally, MTAs can help to improve email performance, reduce latency, and increase the overall efficiency of email communication.Mail Transfer Agent Configuration and Setup
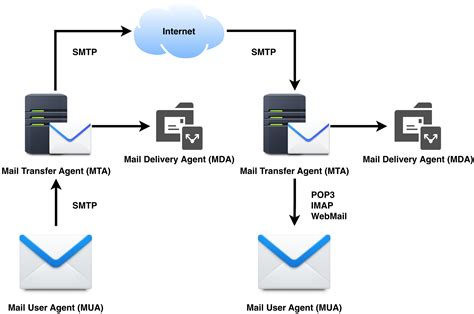
Configuring and setting up an MTA can be a complex process, requiring a high level of technical expertise. The setup process typically involves installing the MTA software, configuring the mail queue and routing table, and setting up the protocol stack. Additionally, the MTA must be configured to work with other email applications and services, such as email clients and spam filters.
Common Mail Transfer Agent Configuration Options
Some common MTA configuration options include setting up email authentication, configuring spam filters, and establishing email routing rules. Email authentication involves verifying the identity of the sender and recipient, while spam filters help to reduce unwanted email. Email routing rules determine how emails are routed between different mail servers and domains.Mail Transfer Agent Security Considerations
MTA security is a critical concern, as email communication can be vulnerable to spam, viruses, and other types of malicious content. To ensure MTA security, it is essential to configure the MTA to use secure protocols, such as TLS and SSL, and to implement robust spam filtering and email authentication measures. Additionally, the MTA should be regularly updated and patched to prevent vulnerabilities and exploits.
Best Practices for Mail Transfer Agent Security
Some best practices for MTA security include using strong passwords and authentication, implementing email encryption, and configuring the MTA to use secure protocols. Additionally, the MTA should be configured to reject suspicious emails and to implement rate limiting to prevent spam and denial-of-service attacks.Mail Transfer Agent Troubleshooting and Maintenance

Troubleshooting and maintaining an MTA can be a complex process, requiring a high level of technical expertise. Common issues that may arise include email delivery problems, spam and virus infections, and configuration errors. To troubleshoot and maintain an MTA, it is essential to have a thorough understanding of the MTA's configuration and setup, as well as the underlying email protocols and infrastructure.
Common Mail Transfer Agent Troubleshooting Techniques
Some common MTA troubleshooting techniques include checking the mail queue and routing table, verifying email authentication and spam filtering, and analyzing email headers and logs. Additionally, the MTA should be regularly updated and patched to prevent vulnerabilities and exploits.Mail Transfer Agent Image Gallery
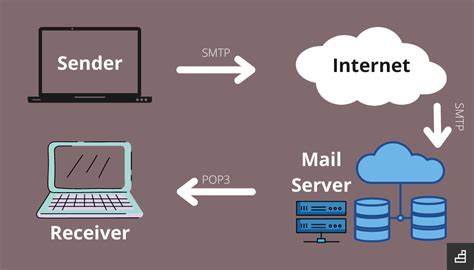




What is a mail transfer agent?
+A mail transfer agent is a software application that routes and delivers emails between different mail servers.
How does a mail transfer agent work?
+A mail transfer agent uses a variety of protocols to communicate with other mail servers, including SMTP, POP, and IMAP.
What are the benefits of using a mail transfer agent?
+The benefits of using a mail transfer agent include improved email delivery rates, enhanced security, and increased flexibility.
How do I configure and set up a mail transfer agent?
+Configuring and setting up a mail transfer agent typically involves installing the MTA software, configuring the mail queue and routing table, and setting up the protocol stack.
What are some common mail transfer agent security considerations?
+Some common mail transfer agent security considerations include using secure protocols, implementing spam filtering and email authentication, and regularly updating and patching the MTA.
In summary, mail transfer agents play a critical role in the email infrastructure, enabling the seamless exchange of emails between different email providers, organizations, and individuals. By understanding how MTAs work, configuring and setting them up correctly, and ensuring their security, we can improve email delivery rates, reduce spam and malicious content, and increase the overall efficiency of email communication. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of mail transfer agents and their importance in the world of email. If you have any further questions or would like to learn more about MTAs, please don't hesitate to comment or share this article with others.
