Intro
Discover 7 low FODMAP foods, including gluten-free and lactose-free options, to manage IBS symptoms with a balanced diet and healthy digestion, reducing bloating and discomfort.
The importance of diet in managing digestive health cannot be overstated. For individuals suffering from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or other digestive issues, adopting a low FODMAP diet can be a game-changer. FODMAPs, which stand for Fermentable Oligo-, Di-, Mono-saccharides, and Polyols, are types of carbohydrates that can be difficult for some people to digest. By limiting or avoiding high FODMAP foods, individuals can alleviate symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and changes in bowel habits. In this article, we will delve into the world of low FODMAP foods, exploring the benefits, working mechanisms, and practical examples of incorporating these foods into your diet.
A low FODMAP diet is not just about cutting out problematic foods; it's also about introducing a variety of nutritious, low FODMAP options that can help regulate digestion and promote overall well-being. From fruits and vegetables to proteins and grains, there are numerous low FODMAP foods to choose from. By understanding which foods are low in FODMAPs, individuals can create a personalized diet that meets their unique needs and preferences. Whether you're looking to manage IBS symptoms or simply improve your digestive health, a low FODMAP diet can be a valuable tool in achieving your goals.
For those new to the concept of FODMAPs, it's essential to understand how these carbohydrates affect the body. When high FODMAP foods are consumed, they can draw water into the intestinal tract, leading to bloating and discomfort. Additionally, the fermentation of FODMAPs by gut bacteria can produce gas, further exacerbating symptoms. By limiting or avoiding high FODMAP foods, individuals can reduce the amount of undigested carbohydrates in the gut, thereby minimizing symptoms and promoting a healthier digestive system.
Introduction to Low FODMAP Foods
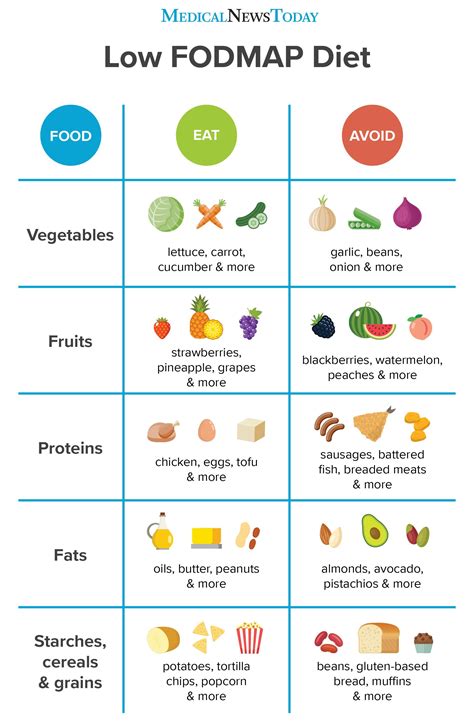
Low FODMAP foods are those that contain minimal amounts of fermentable carbohydrates. These foods can be categorized into several groups, including fruits, vegetables, proteins, grains, and dairy products. Some examples of low FODMAP foods include bananas, berries, cucumbers, carrots, chicken, turkey, rice, quinoa, and lactose-free milk. By focusing on these foods, individuals can create a balanced and nutritious diet that meets their dietary needs while minimizing digestive discomfort.
Benefits of a Low FODMAP Diet
The benefits of a low FODMAP diet are numerous and well-documented. By reducing or eliminating high FODMAP foods, individuals can experience significant improvements in digestive health, including: * Reduced bloating and abdominal pain * Improved bowel habits * Decreased gas and flatulence * Enhanced overall well-beingIn addition to these benefits, a low FODMAP diet can also help individuals identify specific food intolerances or sensitivities. By systematically introducing and eliminating different foods, individuals can pinpoint which foods trigger their symptoms, allowing for a more personalized and effective approach to managing digestive health.
Low FODMAP Fruits
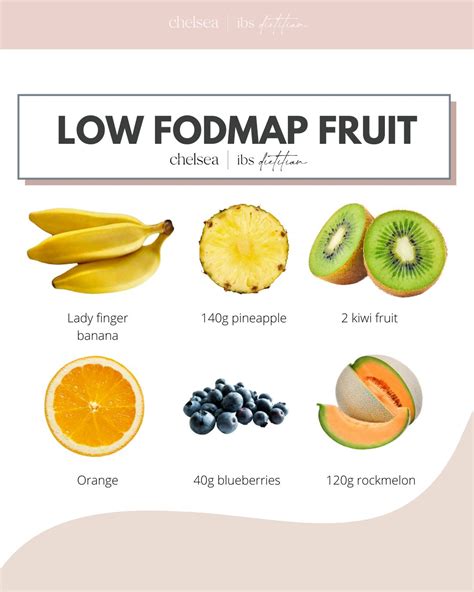
Fruits are a nutritious and delicious addition to a low FODMAP diet. Some examples of low FODMAP fruits include:
- Bananas
- Berries (such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries)
- Citrus fruits (such as oranges, grapefruits, and lemons)
- Avocados
- Pineapples
When consuming fruits, it's essential to be mindful of portion sizes, as even low FODMAP fruits can become high in FODMAPs if eaten in excess. A general rule of thumb is to limit fruit servings to 1/2 cup or 1 medium-sized fruit per serving.
Low FODMAP Vegetables
Vegetables are another crucial component of a low FODMAP diet. Some examples of low FODMAP vegetables include: * Cucumbers * Carrots * Bell peppers * Zucchini * Green beansLike fruits, vegetables should be consumed in moderation, with a focus on variety and portion control. A general rule of thumb is to limit vegetable servings to 1/2 cup or 1 medium-sized vegetable per serving.
Low FODMAP Proteins

Proteins are an essential part of a low FODMAP diet, providing the building blocks for muscle growth and repair. Some examples of low FODMAP proteins include:
- Chicken
- Turkey
- Fish (such as salmon, cod, and tilapia)
- Beef
- Pork
When consuming proteins, it's essential to choose lean cuts and avoid high FODMAP ingredients, such as onions and garlic, which are commonly used in marinades and sauces.
Low FODMAP Grains
Grains are a staple in many diets, providing fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Some examples of low FODMAP grains include: * Rice * Quinoa * Gluten-free bread * Gluten-free pasta * OatsWhen consuming grains, it's essential to choose gluten-free options and limit portion sizes, as even low FODMAP grains can become high in FODMAPs if eaten in excess.
Low FODMAP Dairy Products

Dairy products can be a challenging aspect of a low FODMAP diet, as many dairy products contain high amounts of lactose, a sugar that can be difficult for some individuals to digest. However, there are several low FODMAP dairy products available, including:
- Lactose-free milk
- Almond milk
- Coconut milk
- Hard cheeses (such as cheddar, Swiss, and parmesan)
- Yogurt (made with lactose-free milk)
When consuming dairy products, it's essential to choose lactose-free or low-lactose options and limit portion sizes, as even low FODMAP dairy products can become high in FODMAPs if eaten in excess.
Tips for Implementing a Low FODMAP Diet
Implementing a low FODMAP diet can be challenging, but there are several tips and strategies that can help. Some examples include: * Keeping a food diary to track symptoms and identify trigger foods * Working with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan * Gradually introducing new foods to minimize digestive discomfort * Cooking at home using low FODMAP ingredients * Reading food labels carefully to avoid high FODMAP ingredientsBy following these tips and strategies, individuals can successfully implement a low FODMAP diet and experience significant improvements in digestive health.
Gallery of Low FODMAP Foods
Low FODMAP Foods Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is a low FODMAP diet?
+A low FODMAP diet is a dietary approach that involves limiting or avoiding foods that contain high amounts of fermentable carbohydrates, such as fructose, lactose, and sorbitol.
What are the benefits of a low FODMAP diet?
+The benefits of a low FODMAP diet include reduced bloating and abdominal pain, improved bowel habits, and decreased gas and flatulence.
How do I implement a low FODMAP diet?
+To implement a low FODMAP diet, it's essential to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan, keep a food diary to track symptoms and identify trigger foods, and gradually introduce new foods to minimize digestive discomfort.
What are some examples of low FODMAP foods?
+Some examples of low FODMAP foods include bananas, berries, cucumbers, carrots, chicken, turkey, rice, quinoa, and lactose-free milk.
Can I still eat my favorite foods on a low FODMAP diet?
+While it may be challenging to completely eliminate favorite foods, it's possible to find low FODMAP alternatives or modify recipes to make them low FODMAP-friendly.
In conclusion, a low FODMAP diet can be a highly effective approach to managing digestive health and alleviating symptoms associated with IBS and other digestive disorders. By understanding which foods are low in FODMAPs and incorporating them into your diet, you can take the first step towards a healthier, happier you. Whether you're looking to reduce bloating and abdominal pain or simply improve your overall well-being, a low FODMAP diet is definitely worth considering. So why not give it a try? With the right guidance and support, you can unlock the benefits of a low FODMAP diet and start enjoying the digestive health you deserve. We invite you to share your experiences with low FODMAP diets, ask questions, and provide feedback in the comments section below. Together, let's explore the world of low FODMAP foods and discover the countless benefits they have to offer.
