Intro
Discover Ebt Vs Wic differences, including eligibility, benefits, and food assistance programs, to understand government aid for low-income families, nutrition support, and welfare services.
The world of government assistance programs can be complex and overwhelming, especially for those who are new to the system. Two programs that are often mentioned together are EBT (Electronic Benefits Transfer) and WIC (Women, Infants, and Children). While they share some similarities, they are distinct programs with different goals, eligibility requirements, and benefits. In this article, we will delve into the differences between EBT and WIC, exploring their purposes, eligibility criteria, and the benefits they provide.
The importance of understanding these programs cannot be overstated. For many individuals and families, EBT and WIC are lifelines that provide essential support during difficult times. By grasping the nuances of each program, participants can navigate the system more effectively, ensuring they receive the assistance they need. Moreover, this knowledge can help policymakers and administrators refine these programs, making them more efficient and responsive to the needs of their constituents.
As we explore the differences between EBT and WIC, it becomes clear that these programs are designed to address specific aspects of food insecurity and nutritional health. EBT, for instance, is a broader program that encompasses various benefits, including food assistance, while WIC is focused on the nutritional needs of a particular demographic. This distinction is crucial, as it reflects the diverse challenges faced by different segments of the population. By recognizing these differences, we can better appreciate the complexity of the issues at hand and the importance of tailored solutions.
Introduction to EBT

One of the key benefits of EBT is its flexibility. Recipients can use their EBT cards at a wide range of stores, from grocery supermarkets to farmers' markets. This flexibility is particularly important for individuals with limited mobility or those living in areas with limited access to traditional grocery stores. Moreover, EBT cards can be used to purchase a variety of food items, including fresh produce, meat, dairy products, and canned goods.
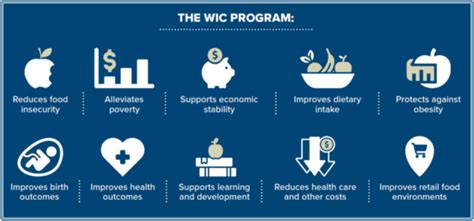
Introduction to WIC
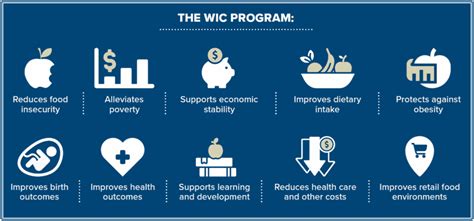
WIC is unique in its focus on the nutritional needs of a specific demographic. The program recognizes that pregnant women, infants, and young children have distinct dietary requirements that are essential for healthy growth and development. By providing access to nutrient-rich foods, WIC helps to support the health and well-being of these vulnerable populations. Moreover, WIC's emphasis on nutrition education and healthcare referrals reflects a broader commitment to promoting holistic health and wellness.
Eligibility Criteria for EBT and WIC
The eligibility criteria for EBT and WIC differ significantly. EBT eligibility is typically based on income and family size, with varying thresholds depending on the state and the specific program. For example, SNAP eligibility is usually limited to households with incomes at or below 130% of the federal poverty level. In contrast, WIC eligibility is based on a combination of income, nutritional risk, and categorical eligibility (e.g., pregnancy, breastfeeding, or having a child under the age of five).To be eligible for WIC, applicants must meet specific income guidelines, which vary by state. In general, WIC eligibility is limited to households with incomes at or below 185% of the federal poverty level. Additionally, applicants must be at nutritional risk, which can be determined through a health screening or a dietary assessment. This dual eligibility criteria reflects WIC's focus on supporting the nutritional health of vulnerable populations.
Benefits and Services Provided by EBT and WIC

Some of the key benefits provided by EBT include:
- Access to a wide range of food items, including fresh produce, meat, dairy products, and canned goods
- Flexibility in using EBT cards at participating retailers, including grocery stores, farmers' markets, and online retailers
- Support for household expenses, such as rent, utilities, and childcare
In contrast, WIC benefits are more specialized, with a focus on supporting the nutritional health of pregnant women, infants, and young children. Some of the key benefits provided by WIC include:
- Access to nutrient-rich foods, such as milk, cheese, eggs, and fresh produce
- Nutrition education and counseling to support healthy eating habits and meal planning
- Healthcare referrals to support prenatal care, postpartum care, and pediatric care
Application Process for EBT and WIC
The application process for EBT and WIC varies depending on the state and the specific program. In general, applicants can apply for EBT and WIC benefits through their local social services department or online through a state-specific portal.To apply for EBT, applicants typically need to provide documentation of their income, family size, and expenses. This may include pay stubs, tax returns, and proof of residency. Once the application is submitted, it will be reviewed and processed by the relevant authorities.
To apply for WIC, applicants typically need to provide documentation of their income, nutritional risk, and categorical eligibility. This may include proof of pregnancy, breastfeeding, or having a child under the age of five, as well as a health screening or dietary assessment. Once the application is submitted, it will be reviewed and processed by the relevant authorities.
Gallery of EBT and WIC Images
EBT and WIC Image Gallery









Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between EBT and WIC?
+EBT and WIC are two distinct government assistance programs. EBT provides a broader range of benefits, including food assistance, while WIC is focused on supporting the nutritional health of pregnant women, infants, and young children.
How do I apply for EBT and WIC benefits?
+To apply for EBT and WIC benefits, you can contact your local social services department or visit the relevant website for your state. You will need to provide documentation of your income, family size, and expenses, as well as proof of nutritional risk and categorical eligibility for WIC.
What are the eligibility criteria for EBT and WIC?
+The eligibility criteria for EBT and WIC vary depending on the state and the specific program. Generally, EBT eligibility is based on income and family size, while WIC eligibility is based on a combination of income, nutritional risk, and categorical eligibility.
Can I use my EBT card at any store?
+No, you can only use your EBT card at participating retailers that accept EBT payments. This may include grocery stores, farmers' markets, and online retailers.
How long does it take to process my EBT and WIC application?
+The processing time for EBT and WIC applications varies depending on the state and the specific program. Generally, it can take several weeks to several months to process an application.
In conclusion, EBT and WIC are two vital government assistance programs that provide essential support to individuals and families in need. While they share some similarities, they are distinct programs with different goals, eligibility requirements, and benefits. By understanding the differences between EBT and WIC, participants can navigate the system more effectively, ensuring they receive the assistance they need. We encourage readers to share their experiences and insights about EBT and WIC, and to explore the resources and links provided throughout this article for more information. Together, we can work towards creating a more comprehensive and supportive social safety net that addresses the diverse needs of our communities.
