Intro
Discover 5 ways iron deficiency affects health, from fatigue to hair loss, and learn about anemia symptoms, iron-rich foods, and supplementation to boost energy and overall well-being.
Iron deficiency is a common nutritional disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body does not have enough iron to produce adequate amounts of hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to different parts of the body. Iron deficiency can lead to a range of health problems, including fatigue, weakness, and impaired cognitive function. In this article, we will explore five ways iron deficiency can affect the body and what can be done to prevent or treat it.
Iron deficiency is often caused by a lack of iron in the diet, particularly in people who follow a vegetarian or vegan diet. It can also be caused by certain medical conditions, such as celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis, which can impair the body's ability to absorb iron from food. Additionally, iron deficiency can be caused by heavy menstrual periods, pregnancy, and childbirth, which can lead to a significant loss of iron.
Impact of Iron Deficiency on the Body
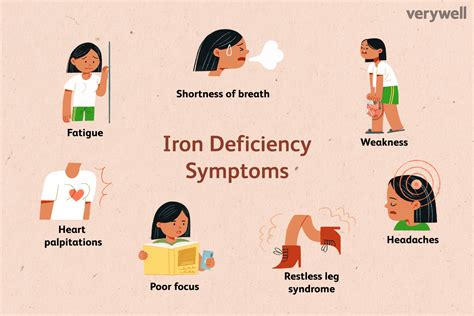
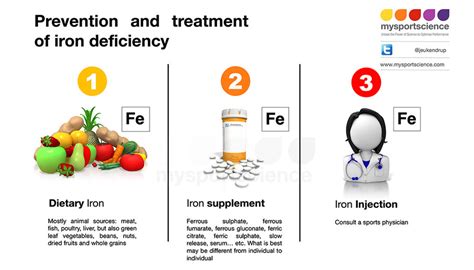
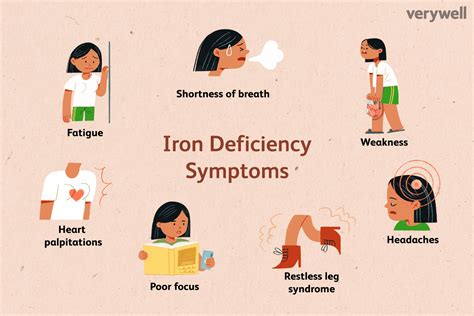
Iron Deficiency and Fatigue
Iron deficiency is a common cause of fatigue, which can range from mild to severe. When the body does not have enough iron, it cannot produce enough hemoglobin, which can lead to a decrease in oxygen delivery to the body's tissues. This can cause feelings of tiredness, weakness, and lethargy, making it difficult to perform daily activities.Causes of Iron Deficiency
Treatment Options for Iron Deficiency
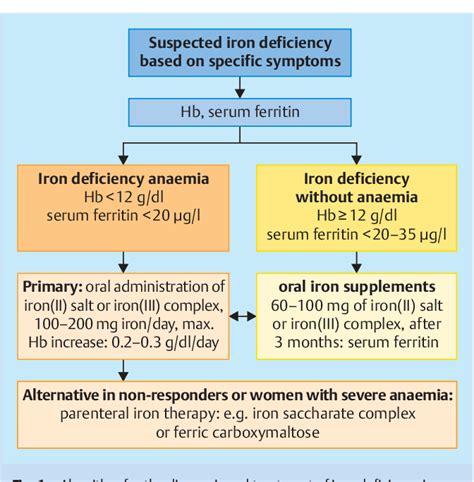
Treatment for iron deficiency typically involves taking iron supplements or increasing iron intake through dietary changes. Iron supplements are available in various forms, including ferrous sulfate, ferrous gluconate, and ferric citrate. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking iron supplements, as they can interact with other medications and cause side effects.Dietary Changes to Prevent Iron Deficiency

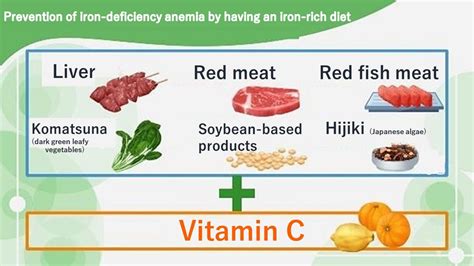
Iron-Rich Foods
Some of the richest sources of iron include: * Red meat: beef, lamb, and pork * Poultry: chicken and turkey * Fish: shellfish, sardines, and anchovies * Beans: kidney beans, black beans, and chickpeas * Lentils: green and brown lentils * Fortified cereals: iron-fortified breakfast cerealsPrevention of Iron Deficiency
Risk Factors for Iron Deficiency
Some of the risk factors for iron deficiency include: * Female sex: women are at a higher risk of iron deficiency due to menstrual blood loss * Vegetarian or vegan diet: people who follow a plant-based diet are at a higher risk of iron deficiency * Pregnancy and childbirth: pregnancy and childbirth can lead to a significant loss of iron * Certain medical conditions: celiac disease, Crohn's disease, and ulcerative colitis can impair iron absorptionComplications of Iron Deficiency
Diagnosis of Iron Deficiency
Diagnosing iron deficiency typically involves a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests. Some of the laboratory tests used to diagnose iron deficiency include: * Complete blood count (CBC): a test that measures the levels of different blood cells, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets * Serum iron test: a test that measures the level of iron in the blood * Ferritin test: a test that measures the level of ferritin, a protein that stores iron in the bodyIron Deficiency Image Gallery








What are the symptoms of iron deficiency?
+The symptoms of iron deficiency include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, and dizziness.
What are the causes of iron deficiency?
+The causes of iron deficiency include a lack of iron in the diet, certain medical conditions, and heavy menstrual periods.
How can iron deficiency be prevented?
+Iron deficiency can be prevented by eating iron-rich foods, consuming vitamin C-rich foods, and avoiding tea and coffee with meals.
What are the complications of iron deficiency?
+The complications of iron deficiency include anemia, poor cognitive function, weakened immune system, and poor pregnancy outcomes.
How is iron deficiency diagnosed?
+Iron deficiency is diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests, including complete blood count, serum iron test, and ferritin test.
In conclusion, iron deficiency is a common nutritional disorder that can have significant consequences on the body. It is essential to be aware of the symptoms, causes, and complications of iron deficiency and take steps to prevent it. By making dietary changes, taking iron supplements, and avoiding certain foods, individuals can reduce their risk of iron deficiency and maintain optimal health. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be suffering from iron deficiency, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Share this article with your friends and family to raise awareness about the importance of iron in our bodies. Leave a comment below if you have any questions or concerns about iron deficiency.
