Intro
Learn infection control basics, including prevention methods, hygiene practices, and disease transmission to maintain a healthy environment and prevent illnesses like nosocomial infections.
Infection control is a critical aspect of healthcare that plays a vital role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. It involves a set of practices and procedures designed to minimize the transmission of pathogens in healthcare settings. The importance of infection control cannot be overstated, as it helps to protect not only patients but also healthcare workers and the broader community from the risk of infection. Effective infection control measures can help to reduce the incidence of hospital-acquired infections, improve patient outcomes, and decrease the economic burden associated with treating infectious diseases.
Infection control is a multidisciplinary approach that requires the collaboration of healthcare professionals, including nurses, doctors, and other support staff. It involves a range of strategies, including hand hygiene, personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilization and disinfection, and surveillance and monitoring. By implementing these strategies, healthcare facilities can create a safe and healthy environment for patients, visitors, and staff. Moreover, infection control is not limited to healthcare settings; it is also essential in other environments, such as schools, childcare centers, and community settings, where people are at risk of contracting infectious diseases.
The basics of infection control are founded on the principles of epidemiology, microbiology, and infectious disease prevention. Understanding the modes of transmission, the types of microorganisms, and the risk factors associated with infection is crucial for developing effective infection control strategies. Furthermore, staying up-to-date with the latest guidelines, recommendations, and best practices is essential for ensuring that infection control measures are evidence-based and effective. By combining knowledge, skills, and resources, healthcare professionals can make a significant impact on reducing the burden of infectious diseases and promoting public health.
Infection Control Principles

Infection control principles are the foundation of a comprehensive infection control program. These principles are based on the understanding of how microorganisms are transmitted and how they can be controlled. The key principles of infection control include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilization and disinfection, and surveillance and monitoring. Hand hygiene is considered one of the most effective measures for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. It involves washing hands with soap and water or using an alcohol-based hand sanitizer. The use of PPE, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, is also essential for preventing the transmission of microorganisms.
Sterilization and disinfection are critical components of infection control, as they help to eliminate or reduce the number of microorganisms on surfaces and equipment. Sterilization involves the use of heat, steam, or chemicals to kill all forms of microbial life, while disinfection involves the use of chemicals to reduce the number of microorganisms to a safe level. Surveillance and monitoring are also essential for detecting and responding to outbreaks of infectious diseases. This involves collecting and analyzing data on infection rates, identifying trends and patterns, and implementing control measures to prevent the spread of infection.
Importance of Hand Hygiene
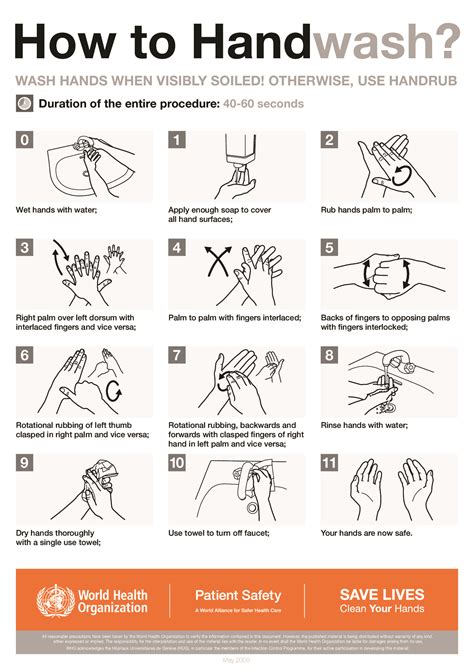
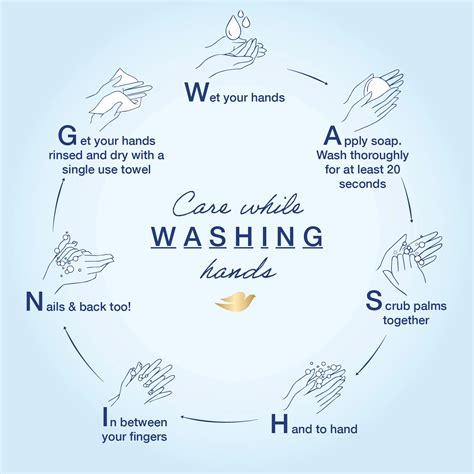
Hand hygiene is a critical component of infection control, as it helps to prevent the spread of microorganisms from one person to another. Hands are the most common vehicle for the transmission of infectious diseases, and poor hand hygiene is a major contributor to the spread of infection. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that healthcare workers perform hand hygiene at specific points of care, including before and after touching a patient, before and after performing a procedure, and after removing personal protective equipment (PPE).Infection Control Practices
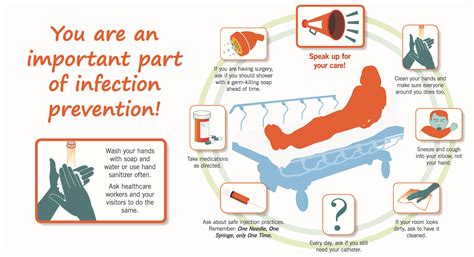
Infection control practices are the specific actions taken to prevent the spread of infectious diseases. These practices include the use of personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilization and disinfection, and surveillance and monitoring. The use of PPE, such as gloves, masks, and gowns, is essential for preventing the transmission of microorganisms. PPE helps to create a barrier between the healthcare worker and the patient, reducing the risk of transmission.
Sterilization and disinfection are critical components of infection control, as they help to eliminate or reduce the number of microorganisms on surfaces and equipment. Sterilization involves the use of heat, steam, or chemicals to kill all forms of microbial life, while disinfection involves the use of chemicals to reduce the number of microorganisms to a safe level. Surveillance and monitoring are also essential for detecting and responding to outbreaks of infectious diseases. This involves collecting and analyzing data on infection rates, identifying trends and patterns, and implementing control measures to prevent the spread of infection.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
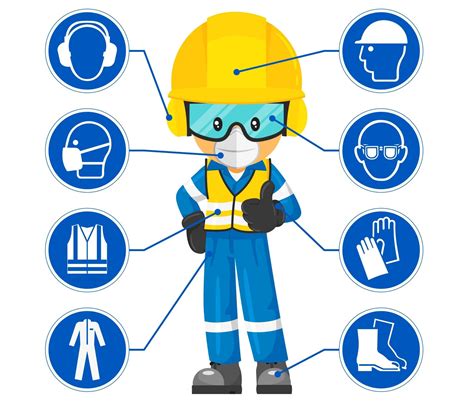
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is a critical component of infection control, as it helps to prevent the transmission of microorganisms from one person to another. PPE includes gloves, masks, gowns, and eye protection, and is used to create a barrier between the healthcare worker and the patient. The use of PPE is essential for preventing the transmission of infectious diseases, particularly in high-risk settings such as operating rooms and intensive care units.Infection Control in Healthcare Settings

Infection control in healthcare settings is critical for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Healthcare settings, such as hospitals and clinics, are high-risk environments where patients, visitors, and staff are at risk of contracting infectious diseases. Effective infection control measures, such as hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), sterilization and disinfection, and surveillance and monitoring, are essential for reducing the risk of transmission.
In addition to these measures, healthcare facilities must also have policies and procedures in place for managing outbreaks of infectious diseases. This includes identifying and isolating patients with infectious diseases, implementing control measures to prevent the spread of infection, and communicating with staff, patients, and visitors about the risks and prevention strategies. Healthcare facilities must also provide education and training to staff on infection control practices and procedures, and ensure that staff are competent and confident in their ability to prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Infection Control in Community Settings
Infection control in community settings, such as schools and childcare centers, is also essential for preventing the spread of infectious diseases. Community settings are high-risk environments where people are at risk of contracting infectious diseases, particularly respiratory and gastrointestinal infections. Effective infection control measures, such as hand hygiene, cleaning and disinfection, and surveillance and monitoring, are essential for reducing the risk of transmission.Gallery of Infection Control Images
Infection Control Image Gallery







Frequently Asked Questions
What is infection control?
+Infection control is a set of practices and procedures designed to minimize the transmission of pathogens in healthcare settings.
Why is hand hygiene important?
+Hand hygiene is important because it helps to prevent the spread of microorganisms from one person to another.
What is personal protective equipment (PPE)?
+Personal protective equipment (PPE) is equipment worn to minimize exposure to hazards, including microorganisms.
What is the importance of sterilization and disinfection?
+Sterilization and disinfection are critical components of infection control, as they help to eliminate or reduce the number of microorganisms on surfaces and equipment.
What is surveillance and monitoring in infection control?
+Surveillance and monitoring involve collecting and analyzing data on infection rates, identifying trends and patterns, and implementing control measures to prevent the spread of infection.
In conclusion, infection control is a critical aspect of healthcare that plays a vital role in preventing the spread of infectious diseases. By understanding the principles of infection control, implementing effective infection control practices, and staying up-to-date with the latest guidelines and recommendations, healthcare professionals can make a significant impact on reducing the burden of infectious diseases and promoting public health. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences on infection control in the comments section below. Additionally, we encourage you to share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about infection control. By working together, we can create a safer and healthier environment for everyone.
