Intro
Master Humalog dosing with 5 expert sliding scale tips, optimizing insulin therapy, and managing blood sugar levels with precision, flexibility, and control.
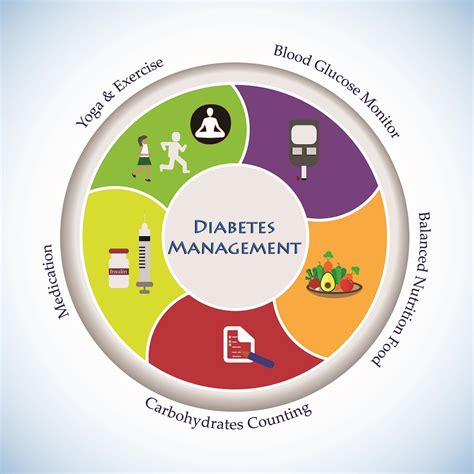
Humalog, a fast-acting insulin, is often used in conjunction with a sliding scale regimen to manage blood glucose levels in individuals with diabetes. The sliding scale approach involves adjusting the dose of insulin based on the current blood glucose reading, with the goal of maintaining glucose levels within a target range. Here are some key points to consider when using a Humalog sliding scale:
Humalog is designed to start working quickly, typically within 15 minutes of injection, and its effects last for about 2 to 4 hours. This rapid onset and relatively short duration of action make it an ideal choice for managing mealtime glucose spikes. However, to get the most out of a Humalog sliding scale, it's crucial to understand how to adjust doses effectively based on blood glucose readings.
When implementing a Humalog sliding scale, it's essential to consider factors such as the individual's sensitivity to insulin, their diet, physical activity levels, and any other medications they might be taking. The scale is typically tailored to the individual, with specific dose adjustments for different blood glucose levels. For example, if the blood glucose is significantly elevated before a meal, a larger dose of Humalog might be administered to bring levels back down.
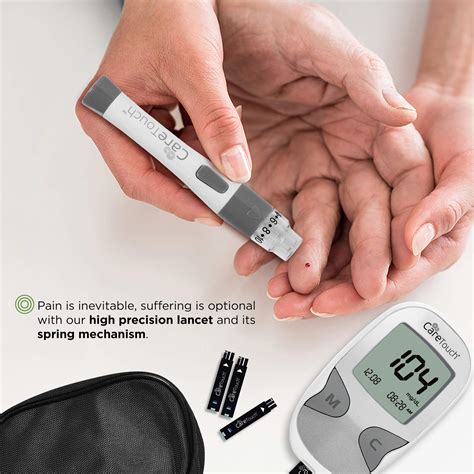
One of the critical aspects of managing diabetes with a Humalog sliding scale is monitoring blood glucose levels regularly. This involves checking glucose levels at various times throughout the day, especially before meals and at bedtime, to get a comprehensive picture of how glucose levels are responding to the insulin therapy. Regular monitoring also helps in identifying patterns or times of the day when glucose levels tend to be higher or lower, allowing for more precise adjustments to the sliding scale.
Another important consideration is the risk of hypoglycemia, which can occur if too much insulin is administered relative to the current glucose level and anticipated glucose intake from meals. Therefore, it's vital to educate individuals on the symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as shakiness, dizziness, sweating, hunger, irritability, confusion, or feeling jittery, and how to treat it promptly with fast-acting carbohydrates.
Understanding how different factors such as stress, illness, and changes in diet or exercise routines can affect blood glucose levels is also crucial. These factors can sometimes necessitate temporary adjustments to the Humalog sliding scale to maintain glucose control. For instance, during periods of increased physical activity, less insulin might be required to avoid hypoglycemia, while during times of illness, more insulin might be needed due to the body's increased glucose production in response to stress.
Introduction to Humalog Sliding Scale
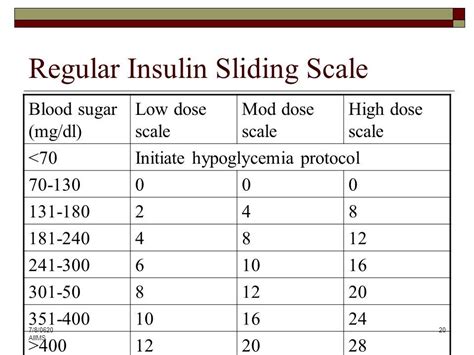
Benefits of Humalog in Sliding Scale Regimens
The use of Humalog in a sliding scale regimen offers several benefits, including improved postprandial glucose control, reduced risk of hypoglycemia when used appropriately, and the flexibility to adjust insulin doses based on changing circumstances such as variations in meal size or timing, and changes in physical activity levels. Additionally, Humalog's rapid onset of action makes it particularly useful for managing the glucose spikes that occur after meals, which are a significant challenge in diabetes management.Implementing a Humalog Sliding Scale
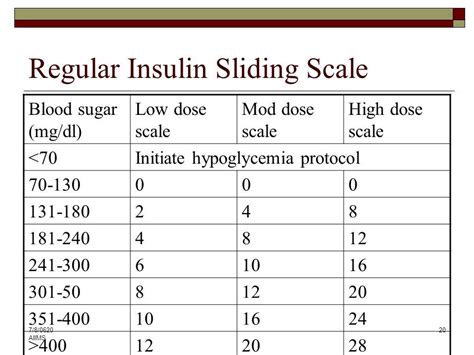
Key Considerations for Effective Use
For the effective use of a Humalog sliding scale, several key considerations must be taken into account. These include the individual's insulin sensitivity, the carbohydrate content of meals, the timing and intensity of physical activity, and any other health conditions or medications that may affect glucose levels or insulin action. Additionally, education on how to use the sliding scale, how to monitor blood glucose levels, and how to recognize and treat hypoglycemia is crucial for individuals using this approach.Monitoring and Adjusting the Sliding Scale
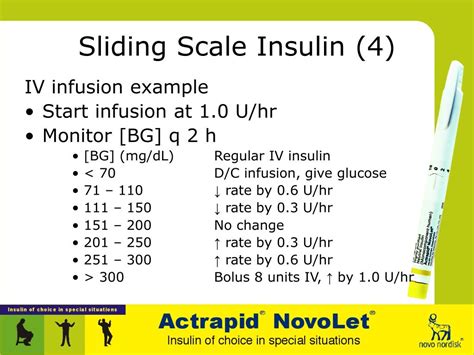
Common Challenges and Solutions
Common challenges encountered when using a Humalog sliding scale include difficulty in achieving consistent glucose control, managing the risk of hypoglycemia, and dealing with the impact of variable factors such as meal sizes and physical activity levels. Solutions to these challenges include closely monitoring glucose levels and adjusting the sliding scale as needed, educating individuals on the importance of consistent meal times and carbohydrate intake, and encouraging regular physical activity while adjusting insulin doses accordingly.Advanced Strategies for Optimizing Humalog Sliding Scales
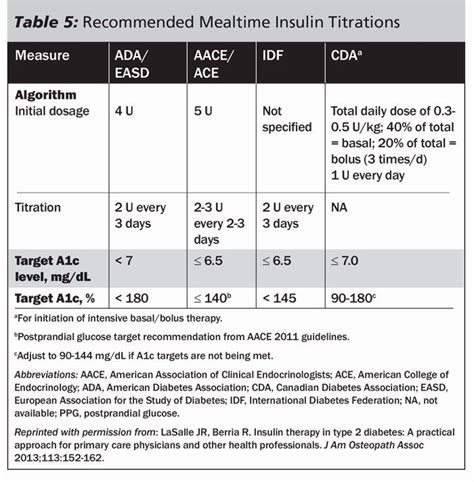
Future Directions in Diabetes Management
The future of diabetes management is likely to involve even more sophisticated technologies and therapies, including closed-loop insulin delivery systems, artificial pancreas devices, and new classes of glucose-lowering medications. These advancements hold promise for improving the ease and effectiveness of diabetes management, potentially reducing the burden on individuals with diabetes and their healthcare providers.Gallery of Humalog Sliding Scale Images








What is the purpose of a Humalog sliding scale in diabetes management?
+The purpose of a Humalog sliding scale is to provide a personalized approach to insulin dosing, allowing for adjustments based on current blood glucose levels, meals, and other factors to achieve optimal glucose control.
How often should blood glucose levels be monitored when using a Humalog sliding scale?
+Blood glucose levels should be monitored regularly, ideally before meals, at bedtime, and occasionally after meals, to assess the effectiveness of the current insulin regimen and make necessary adjustments to the sliding scale.
What are the common challenges faced when implementing a Humalog sliding scale, and how can they be addressed?
+Common challenges include achieving consistent glucose control, managing hypoglycemia risk, and dealing with variable factors like meal sizes and physical activity. These can be addressed through close monitoring, education on consistent carbohydrate intake and physical activity, and regular review and adjustment of the sliding scale.
In conclusion, a Humalog sliding scale can be a valuable tool in the management of diabetes, offering the flexibility to adjust insulin doses based on current glucose levels and other factors. By understanding how to implement and adjust the sliding scale effectively, individuals with diabetes can achieve better glucose control, reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. Remember, managing diabetes is a continuous process that requires ongoing education, support, and adjustments to therapy as needed. By working closely with healthcare providers and staying informed about the latest advancements in diabetes care, individuals can lead active, healthy lives despite their diagnosis. We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions about using Humalog sliding scales in the comments below, and consider sharing this article with others who may benefit from this information.
