Intro
Explore grief, loss, and palliative care strategies with ATIs, addressing emotional support, bereavement, and end-of-life needs, promoting compassionate care and healing.
Grief and loss are universal human experiences that can have a profound impact on an individual's physical, emotional, and psychological well-being. Palliative care, a specialized field of healthcare, plays a vital role in supporting patients and their families as they navigate the complex and often challenging journey of serious illness, death, and bereavement. The American Academy of Hospice and Palliative Medicine (AAHPM) and the Association of Professional Chaplains (APC) emphasize the importance of addressing grief and loss in palliative care, highlighting the need for a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to care.
Palliative care is a patient-centered approach that focuses on alleviating the suffering, pain, and stress associated with serious illness, rather than curing the underlying disease. This approach recognizes that patients and their families have unique needs, preferences, and values that must be respected and addressed throughout the care process. The National Consensus Project for Quality Palliative Care (NCP) outlines eight domains of palliative care, including physical, emotional, social, and spiritual aspects of care, all of which are essential in addressing grief and loss.
The experience of grief and loss can be intense and overwhelming, affecting not only the patient but also their loved ones. The grieving process can be influenced by various factors, including the nature of the loss, the relationship with the deceased, and the individual's coping mechanisms and support systems. Palliative care teams, comprising physicians, nurses, social workers, chaplains, and other healthcare professionals, work together to provide emotional, spiritual, and practical support to patients and their families, helping them navigate the grieving process and find meaning and purpose in the face of loss.
Introduction to Grief and Loss

Types of Grief
Palliative care teams must be aware of the different types of grief that patients and their families may experience, including: * Anticipatory grief: occurs before a loss, often in the context of a terminal illness * Complicated grief: a prolonged and intense grieving process that can interfere with daily life * Disenfranchised grief: experienced by individuals who are not recognized as grieving, such as non-traditional family members or friends * Collective grief: shared by a community or group, often in response to a traumatic eventPalliative Care and Grief Support

Bereavement Care
Bereavement care is an essential component of palliative care, recognizing that the grieving process can be intense and prolonged. Palliative care teams must be prepared to provide bereavement support, including: * Assessment of grief and bereavement needs * Development of individualized bereavement plans * Provision of emotional, spiritual, and practical support * Facilitation of connections with community resources and support groupsAddressing Grief and Loss in Palliative Care

Challenges and Opportunities
Palliative care teams face several challenges in addressing grief and loss, including: * Limited resources and funding * Lack of training and education in grief and bereavement care * Cultural and linguistic barriers * Stigma and taboo surrounding death and dying However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth, including: * Development of new models of care that prioritize grief and bereavement support * Integration of grief and bereavement care into existing healthcare systems * Increased recognition of the importance of palliative care in addressing grief and lossFuture Directions in Grief and Loss Palliative Care

Implications for Practice and Policy
The implications of grief and loss palliative care are far-reaching, with potential impacts on practice, policy, and research. Palliative care teams must be aware of the latest developments and research in grief and bereavement care, incorporating this knowledge into their practice and advocating for policies that support the provision of high-quality grief and bereavement care.Grief and Loss Image Gallery

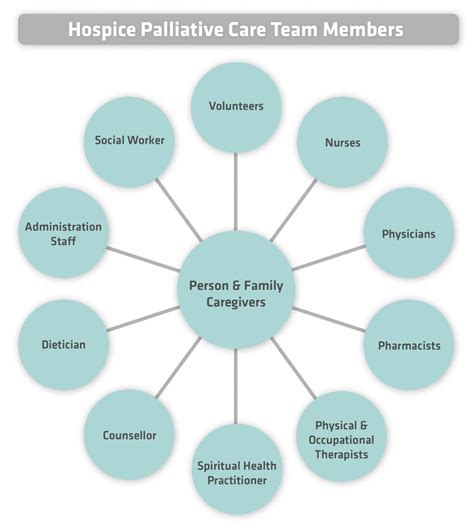




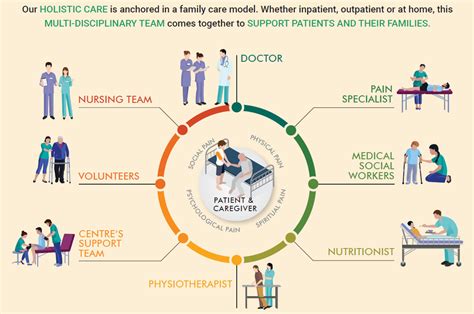



What is grief and loss in palliative care?
+Grief and loss in palliative care refer to the emotional, spiritual, and practical support provided to patients and their families as they navigate the complex and often challenging journey of serious illness, death, and bereavement.
What are the types of grief that patients and their families may experience?
+Patients and their families may experience various types of grief, including anticipatory grief, complicated grief, disenfranchised grief, and collective grief.
What is bereavement care in palliative care?
+Bereavement care in palliative care refers to the ongoing support and guidance provided to patients and their families after a loss, including counseling, support groups, and memorial services.
How can palliative care teams address grief and loss?
+Palliative care teams can address grief and loss by conducting regular assessments of grief and bereavement needs, developing individualized care plans, providing education and support, and facilitating connections with community resources and support groups.
What are the future directions in grief and loss palliative care?
+Future directions in grief and loss palliative care may include increased emphasis on bereavement care and support, development of new therapies and interventions for grief and bereavement, integration of technology and digital media into grief and bereavement care, and expanded recognition of the role of palliative care in addressing grief and loss across the lifespan.
In conclusion, grief and loss are essential components of palliative care, requiring a comprehensive and multidisciplinary approach to care. Palliative care teams must be proactive in addressing grief and loss, recognizing the unique needs and experiences of patients and their families. By providing emotional, spiritual, and practical support, palliative care teams can help patients and their families navigate the complex and often challenging journey of serious illness, death, and bereavement. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences on this topic, and to explore the resources and support available for those affected by grief and loss.
