Intro
Maximize livestock productivity with expert 5 Grazing Lease Tips, including pasture management, rotational grazing, and lease agreement strategies for sustainable ranching and profitable farming practices.
Grazing lease agreements are a common practice among farmers and ranchers, allowing them to utilize land for livestock grazing while the landowner retains ownership. However, navigating these agreements can be complex, and it's essential to understand the terms and conditions to ensure a mutually beneficial arrangement. With the right approach, grazing leases can be a win-win for both parties, providing income for landowners and access to quality grazing land for farmers and ranchers. In this article, we will delve into the world of grazing leases, exploring the benefits, challenges, and best practices for creating successful agreements.
As the demand for sustainable and locally sourced food continues to grow, the importance of well-managed grazing leases cannot be overstated. By working together, landowners and farmers can promote environmentally friendly practices, improve soil health, and contribute to the local economy. Moreover, grazing leases offer a flexible and adaptable way to manage land, allowing for adjustments to be made in response to changing market conditions, weather patterns, and other factors. Whether you're a seasoned farmer or a newcomer to the world of agriculture, understanding the ins and outs of grazing leases is crucial for success.
The benefits of grazing leases are numerous, ranging from increased income for landowners to improved pasture management for farmers. By leasing land for grazing, farmers can expand their operations, reduce costs, and gain access to high-quality forage for their livestock. At the same time, landowners can earn a steady income, reduce their tax liability, and benefit from the environmental benefits of well-managed grazing practices. However, to reap these benefits, it's essential to create a well-structured grazing lease agreement that outlines the terms and conditions of the arrangement. This is where our 5 grazing lease tips come in, providing valuable insights and guidance for both landowners and farmers.
Understanding Grazing Lease Agreements

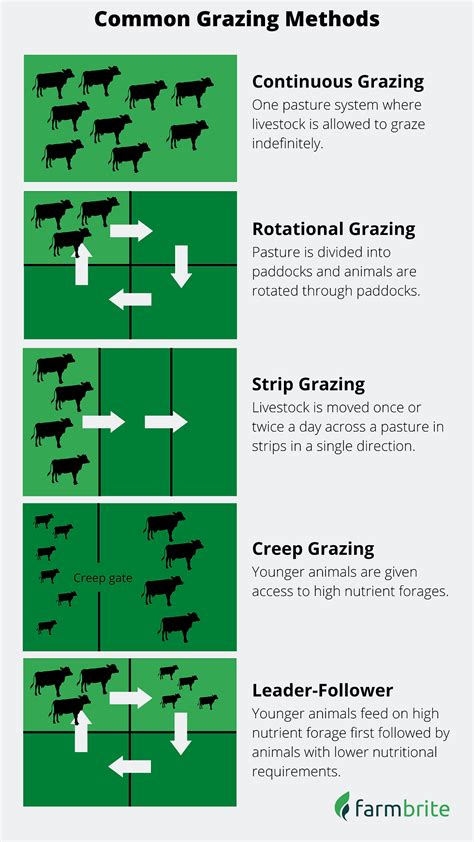
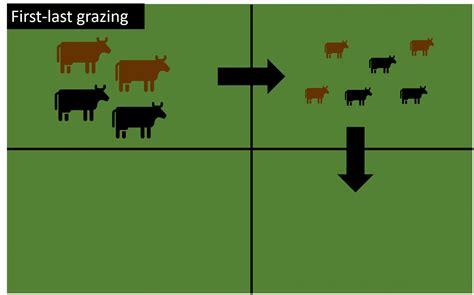
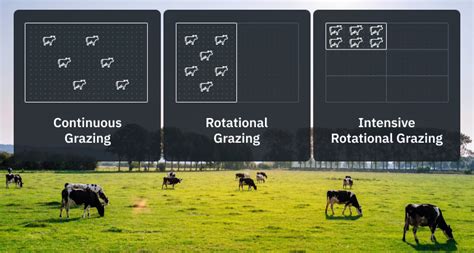
Types of Grazing Leases
The type of grazing lease chosen will depend on the specific needs and goals of both parties. Cash leases, for example, involve a fixed monthly or annual payment, while share leases require the farmer to pay a percentage of the gross income from the lease. Custom grazing leases, on the other hand, involve a customized agreement that takes into account the specific needs of the farmer and the landowner. By understanding the different types of grazing leases, landowners and farmers can create an agreement that meets their unique requirements and promotes a mutually beneficial relationship.Setting Clear Goals and Objectives

Conducting a Land Analysis
Conducting a land analysis is a critical step in setting clear goals and objectives. This involves assessing the quality of the soil, the type and quantity of forage, and the overall condition of the land. By conducting a thorough land analysis, landowners and farmers can determine the optimal use of the land, identify potential limitations, and develop strategies for improving the land's productivity. This may involve soil testing, forage sampling, and monitoring the land's condition over time.Establishing a Fair Rent Structure

Calculating a Fair Rent
Calculating a fair rent involves assessing the value of the land, the costs of maintaining the land, and the expected income from the lease. This may involve conducting a thorough analysis of the land's condition, assessing the quality and quantity of the forage, and determining the optimal stocking rate. By calculating a fair rent, landowners and farmers can ensure that the lease agreement is mutually beneficial and promotes a successful partnership.Managing Risk and Liability

Developing a Risk Management Plan
Developing a risk management plan involves identifying potential risks, assessing the likelihood and impact of these risks, and developing strategies for mitigating them. This may involve conducting a thorough analysis of the land, assessing the quality and quantity of the forage, and determining the optimal stocking rate. By developing a risk management plan, landowners and farmers can minimize their exposure to potential losses and ensure that the lease agreement is successful and sustainable.Monitoring and Evaluating the Lease

Conducting Regular Inspections
Conducting regular inspections is a critical component of monitoring and evaluating the lease. This involves assessing the condition of the land, evaluating the quality and quantity of the forage, and identifying potential issues or areas for improvement. By conducting regular inspections, landowners and farmers can ensure that the lease agreement is successful and sustainable, and make adjustments as needed to promote a mutually beneficial partnership.Grazing Lease Image Gallery







What is a grazing lease agreement?
+A grazing lease agreement is a legally binding contract between a landowner and a farmer or rancher, outlining the terms and conditions of the lease.
What are the benefits of a grazing lease agreement?
+The benefits of a grazing lease agreement include increased income for landowners, improved pasture management for farmers, and environmental benefits such as improved soil health and biodiversity.
How do I determine a fair rent for a grazing lease agreement?
+To determine a fair rent for a grazing lease agreement, you should consider factors such as the value of the land, the costs of maintaining the land, and the expected income from the lease.
What are the different types of grazing leases?
+The different types of grazing leases include cash leases, share leases, and custom grazing leases, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
How do I manage risk and liability in a grazing lease agreement?
+To manage risk and liability in a grazing lease agreement, you should identify potential risks, assess the likelihood and impact of these risks, and develop strategies for mitigating them, such as purchasing insurance and developing a contingency plan.
In conclusion, grazing lease agreements can be a valuable tool for landowners and farmers, providing a flexible and adaptable way to manage land and promote sustainable agriculture practices. By understanding the key components of a grazing lease agreement, including the type of lease, the duration, and the payment terms, landowners and farmers can create a successful and mutually beneficial partnership. Remember to set clear goals and objectives, establish a fair rent structure, manage risk and liability, and monitor and evaluate the lease to ensure its success. With these 5 grazing lease tips, you'll be well on your way to creating a successful and sustainable grazing lease agreement. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with grazing lease agreements in the comments below, and don't forget to share this article with your friends and colleagues who may be interested in learning more about this topic.
