Intro
Discover the ultimate Glycemic Load Chart Printable Guide, featuring glycemic index, blood sugar control, and carbohydrate management for a healthy diet, with easy-to-use food charts and nutrition tips.
The concept of glycemic load has become increasingly important in the world of nutrition and health. It's a measure that takes into account the amount of carbohydrates in a food and how quickly they raise blood sugar levels. Understanding glycemic load is crucial for managing conditions like diabetes, as well as for maintaining overall health and wellness. In this article, we'll delve into the world of glycemic load, exploring its benefits, how it works, and providing a comprehensive guide to help you make informed choices about the foods you eat.
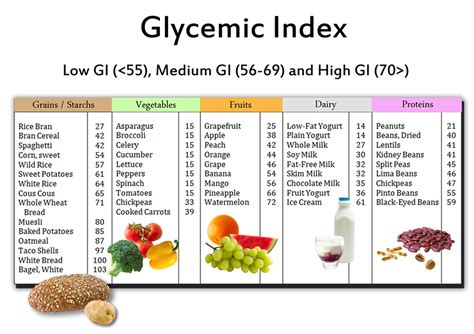
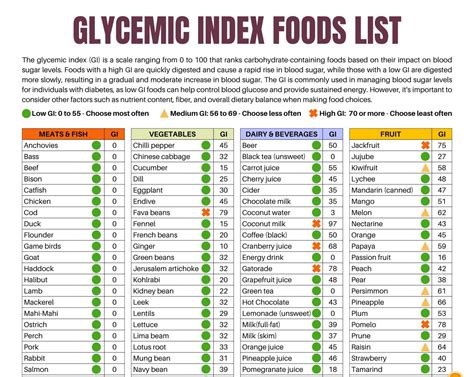
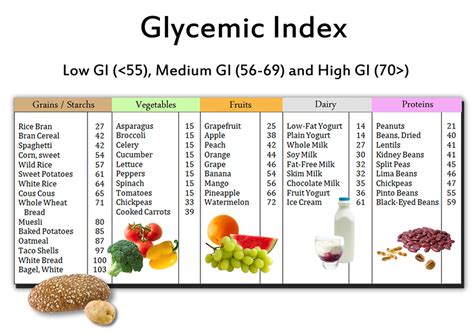
Glycemic load is a more nuanced approach to understanding the impact of carbohydrates on blood sugar levels compared to the glycemic index, which only considers the type of carbohydrate in a food. The glycemic index ranks foods on a scale from 0 to 100 based on how much they raise blood sugar levels after consumption. However, it doesn't account for the serving size of the food, which can be misleading. For instance, a food with a high glycemic index might have a minimal impact on blood sugar if the serving size is small. This is where the glycemic load comes into play, offering a more accurate picture by multiplying the glycemic index of a food by the amount of carbohydrate it contains and then dividing by 100.
The importance of understanding glycemic load cannot be overstated, especially for individuals with diabetes or those who are trying to manage their weight. Foods with a high glycemic load can cause a spike in blood sugar levels, followed by a crash, which can lead to feelings of hunger and lethargy. Over time, consuming high glycemic load foods regularly can contribute to insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes. On the other hand, choosing foods with a low glycemic load can help regulate blood sugar levels, provide sustained energy, and support overall health.
Glycemic Load Benefits
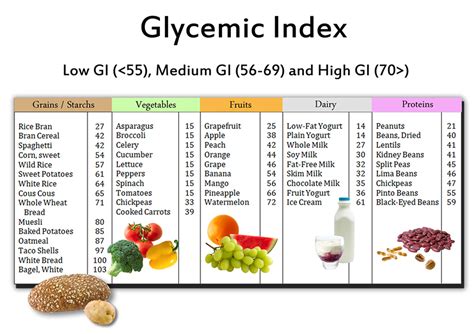
How Glycemic Load Works
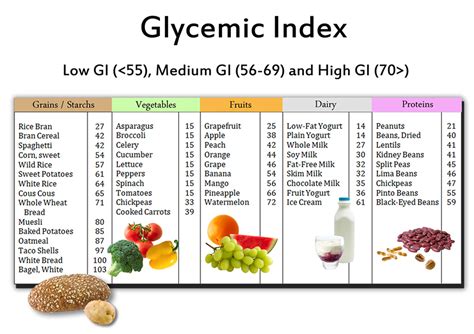
Calculating Glycemic Load
Calculating the glycemic load of a food can be a bit complex, but it can be simplified by using a glycemic load chart. The formula for calculating glycemic load is: (Glycemic Index x Carbohydrates per serving) / 100. For example, if a food has a glycemic index of 50 and contains 30 grams of carbohydrates per serving, its glycemic load would be (50 x 30) / 100 = 15. A glycemic load of 10 or less is considered low, 11-19 is medium, and 20 or more is high.Glycemic Load Chart
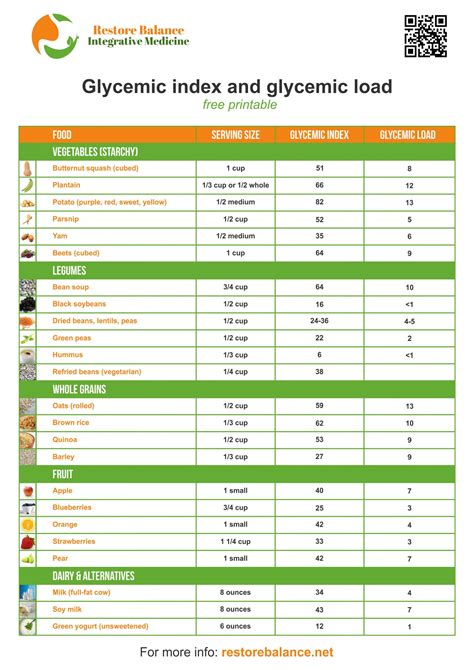
Printable Glycemic Load Guide
Having a printable glycemic load guide can be incredibly useful for daily meal planning and grocery shopping. It provides a quick reference to the glycemic load of common foods, allowing you to make informed decisions about what you eat. This guide can be printed out and kept in the kitchen or even on your phone for easy access when you're out shopping for groceries. It's a practical tool that can help you navigate the complex world of nutrition and make choices that support your health goals.Managing Glycemic Load in Daily Life
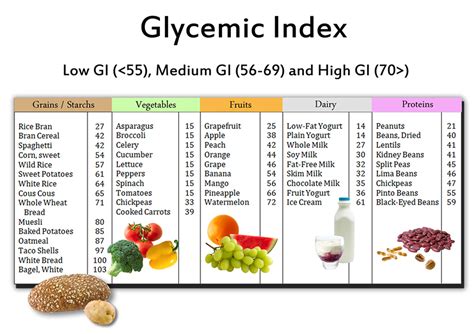
Practical Tips for Low Glycemic Load Diet
- **Eat More Vegetables:** Vegetables are not only low in carbohydrates but also rich in fiber, which slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, thereby reducing their glycemic load. - **Choose Whole Grains:** Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread have a lower glycemic load compared to refined grains. - **Incorporate Legumes:** Legumes are rich in protein, fiber, and complex carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for a low glycemic load diet. - **Limit Sugary Foods:** Sugary foods and drinks have a high glycemic load and should be consumed in moderation.Glycemic Load and Weight Management
Benefits for Athletes and Individuals with Active Lifestyles
For athletes and individuals with active lifestyles, managing glycemic load can be particularly beneficial. It can help in optimizing energy levels, enhancing endurance, and supporting recovery after exercise. Foods with a low to moderate glycemic load are ideal for pre-workout meals as they provide a steady release of glucose, while post-workout, a combination of protein and carbohydrates can help in recovery.Glycemic Load Image Gallery







What is the difference between glycemic index and glycemic load?
+The glycemic index ranks foods based on how much they raise blood sugar levels, while the glycemic load takes into account the amount of carbohydrates in a serving of food, providing a more accurate measure of a food's impact on blood sugar.
How can I use a glycemic load chart in my daily life?
+A glycemic load chart can be used as a guide for making healthier food choices. It can help you identify which foods are likely to cause a spike in blood sugar levels and which ones will provide sustained energy.
What are some examples of low glycemic load foods?
+Examples of low glycemic load foods include most vegetables, legumes, nuts, and whole grains like brown rice and quinoa. These foods are rich in fiber and complex carbohydrates, which digest slowly and have a minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
In conclusion, understanding and managing glycemic load is a powerful tool for achieving and maintaining good health. By making informed choices about the foods we eat and incorporating low glycemic load options into our diets, we can better regulate our blood sugar levels, support weight management, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases. We invite you to share your experiences with managing glycemic load and your favorite low glycemic load recipes in the comments below. Additionally, if you found this article informative and helpful, please consider sharing it with others who might benefit from this knowledge. Together, we can support each other in our journey towards healthier living.
