Intro
Discover the Famotidine Medication Template, a guide to understanding heartburn relief, acid reflux treatment, and stomach ulcer prevention with this H2 blocker medication, exploring dosage, side effects, and interactions for effective gastrointestinal health management.
The importance of understanding medications cannot be overstated, especially when it comes to managing and treating various health conditions. One such medication that has garnered significant attention in the medical community is famotidine, a histamine-2 (H2) blocker that reduces stomach acid production. For individuals suffering from conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, and peptic ulcers, famotidine offers a beacon of hope in alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life. As we delve into the world of famotidine, it's essential to grasp its benefits, working mechanisms, potential side effects, and usage guidelines to ensure safe and effective treatment.
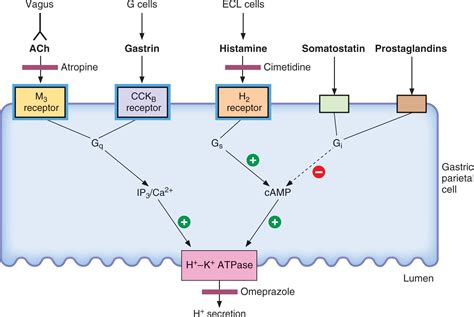
Famotidine's popularity stems from its efficacy in treating acid-related disorders. By inhibiting the action of histamine at the H2 receptors in the stomach lining, famotidine decreases gastric acid secretion, thereby reducing the risk of acid-related complications. This mechanism of action not only alleviates symptoms like heartburn and regurgitation but also facilitates the healing of esophageal and gastric mucosa damaged by excessive acid production. Moreover, famotidine's fast onset of action and prolonged duration of effect make it an attractive option for both short-term and long-term management of acid-related disorders.
The therapeutic benefits of famotidine extend beyond its primary use in treating acid-related conditions. Its ability to reduce stomach acid production also makes it useful in preventing stress-induced ulcers in critically ill patients and managing symptoms in those with dyspepsia. Furthermore, famotidine's safety profile, characterized by a low incidence of adverse effects, renders it a favorable choice for patients who require long-term acid suppression therapy. However, as with any medication, it's crucial to weigh the benefits against potential risks and consider individual patient factors, such as renal function and potential drug interactions, to optimize treatment outcomes.
Introduction to Famotidine

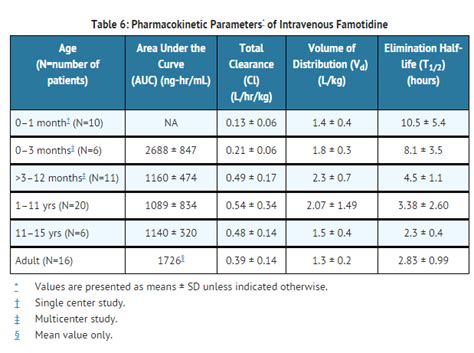
Famotidine, with its chemical name 3-[[2-(diaminomethylene)amino]-4-thiazolyl]methylthio]-N-sulfamoylpropanenitrile, is a competitive, reversible inhibitor of the action of histamine at the H2 receptor, a key player in regulating gastric acid secretion. This pharmacological property underlies its therapeutic efficacy in conditions characterized by excessive acid production. The drug's pharmacokinetic profile, including its rapid absorption, extensive distribution, and primarily renal excretion, contributes to its effectiveness and safety in clinical practice.
Pharmacological Properties of Famotidine
Key aspects of famotidine's pharmacology include: - **Rapid Onset of Action:** Famotidine begins to reduce gastric acid secretion within an hour of oral administration, peaking at about 1-3 hours. - **Prolonged Duration of Action:** Its effects last for approximately 10-12 hours, allowing for twice-daily dosing in many cases. - **High Bioavailability:** Oral bioavailability is about 40-45%, which is relatively high compared to other H2 blockers, ensuring effective plasma concentrations are achieved with oral administration. - **Extensive Distribution:** Famotidine is widely distributed throughout the body, including into gastric secretions, which is crucial for its mechanism of action. - **Primarily Renal Excretion:** The drug is mainly excreted unchanged in the urine, with a small fraction undergoing metabolic transformation, which is important for dosing adjustments in patients with renal impairment.Benefits of Famotidine

The benefits of famotidine are multifaceted, reflecting its efficacy in various clinical scenarios:
- Effective Symptom Relief: It provides rapid and sustained relief from symptoms of acid-related disorders, such as heartburn, regurgitation, and dyspepsia.
- Healing of Esophageal and Gastric Mucosa: By reducing acid exposure, famotidine facilitates the healing of damaged mucosa in conditions like esophagitis and peptic ulcers.
- Prevention of Acid-Related Complications: Its use can prevent complications such as bleeding, stricture formation, and Barrett's esophagus in patients with GERD.
- Safety Profile: Famotidine is generally well-tolerated, with a low incidence of serious adverse effects, making it suitable for long-term use.
Common Uses of Famotidine
Famotidine is commonly used for: - **Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD):** To reduce symptoms and prevent complications. - **Peptic Ulcer Disease:** Including gastric and duodenal ulcers, to promote healing and prevent recurrence. - **Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome:** A rare condition characterized by excessive gastric acid production, where famotidine helps control symptoms. - **Prevention of Stress-Induced Ulcers:** In critically ill patients, to reduce the risk of ulcer development and bleeding.Side Effects and Interactions

While famotidine is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects and interact with other medications:
- Common Side Effects: Include headache, dizziness, constipation, and diarrhea.
- Less Common but Serious Side Effects: Such as allergic reactions, seizures, and blood dyscrasias, which are rare but require immediate medical attention.
- Drug Interactions: Famotidine can interact with other medications, including warfarin, phenytoin, and ketoconazole, which may necessitate dose adjustments or close monitoring.
Precautions and Contraindications
- **Renal Impairment:** Dose adjustments are necessary in patients with significant renal impairment to avoid drug accumulation. - **Pregnancy and Breastfeeding:** Famotidine should be used with caution, as there is limited data on its safety in these populations. - **Allergic Reactions:** Patients with known hypersensitivity to famotidine or other H2 blockers should avoid its use.Dosing and Administration
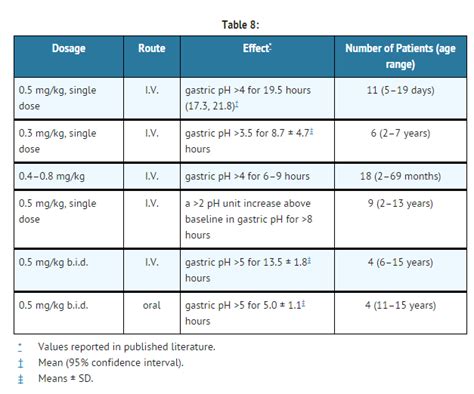
Famotidine dosing varies depending on the indication and patient factors:
- GERD and Peptic Ulcer Disease: Typically 20-40 mg twice daily.
- Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Higher doses may be required, often 20-160 mg every 6 hours.
- Prevention of Stress-Induced Ulcers: 20 mg every 12 hours.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of symptoms, renal function, and potential side effects is crucial during famotidine therapy. Follow-up appointments with healthcare providers can help adjust dosing as needed, manage side effects, and ensure the medication's efficacy in controlling the underlying condition.Gallery of Famotidine-Related Images
Famotidine Image Gallery



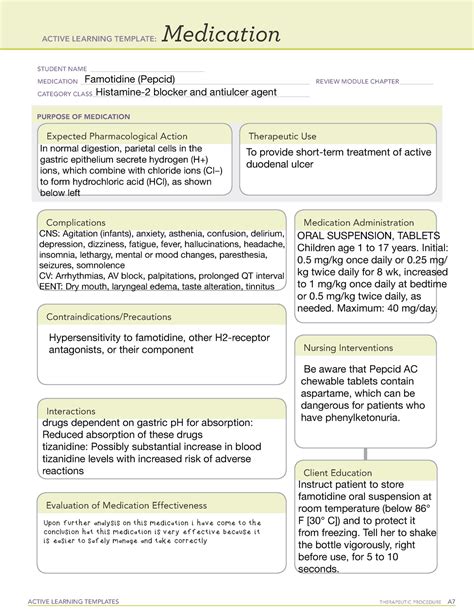
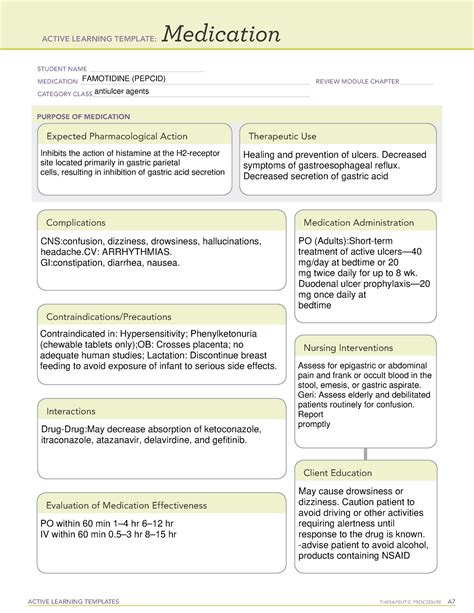

Frequently Asked Questions
What is famotidine used for?
+Famotidine is used to treat conditions like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome by reducing stomach acid production.
How does famotidine work?
+Famotidine works by blocking histamine H2 receptors in the stomach, which reduces gastric acid secretion.
What are the common side effects of famotidine?
+Can I take famotidine with other medications?
+Famotidine can interact with certain medications. It's essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you're taking before starting famotidine.
How long does it take for famotidine to start working?
+Famotidine starts to reduce gastric acid secretion within an hour of oral administration, with its peak effect occurring at about 1-3 hours.
As we conclude our exploration of famotidine, it's clear that this medication plays a vital role in managing acid-related disorders. Its efficacy, safety profile, and versatility make it a valuable asset in clinical practice. For individuals considering famotidine as part of their treatment plan, understanding its benefits, potential side effects, and proper usage is crucial. We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions about famotidine in the comments below, helping to create a community of informed individuals who can support and learn from each other. Additionally, feel free to share this article with others who may benefit from this comprehensive overview of famotidine, contributing to a broader discussion on effective management strategies for acid-related conditions.
