Intro
Discover 5 ways to use Fishbone Diagrams, a powerful tool for root cause analysis, problem-solving, and decision-making, utilizing cause-and-effect, SWOT, and Six Sigma methodologies.
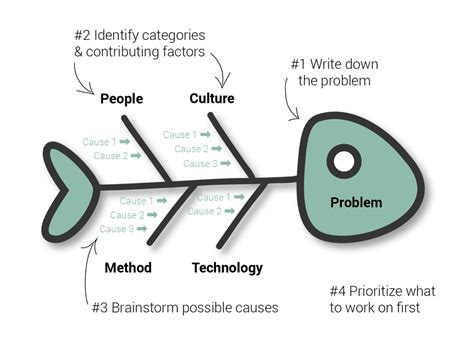
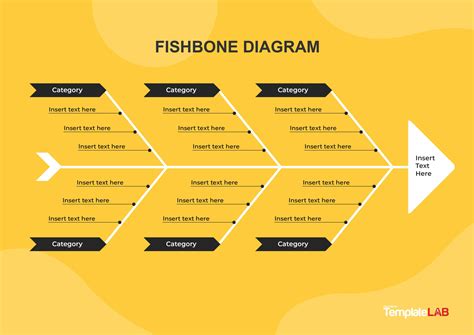
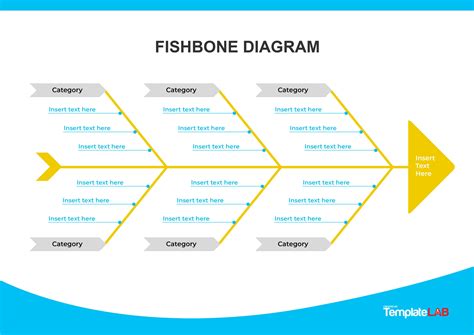
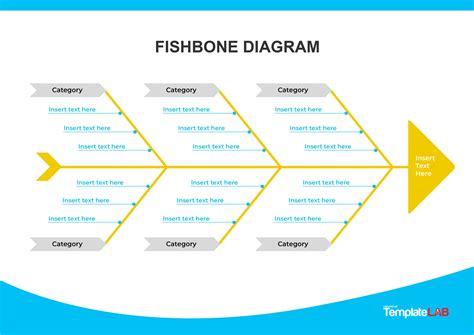
The fishbone diagram, also known as the Ishikawa diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a powerful tool used in various fields such as business, engineering, and quality management to identify and analyze the root causes of problems. It is called a fishbone diagram because of its resemblance to the skeleton of a fish, with the problem statement at the head and the various causes branching out like bones. This tool is highly effective in brainstorming sessions and problem-solving activities, helping teams to systematically identify, organize, and understand the relationships between different factors that contribute to a problem.
The fishbone diagram is named after its creator, Kaoru Ishikawa, a Japanese quality control expert who introduced it in the 1960s. Ishikawa recognized the importance of involving all employees in the quality control process and developed this tool as part of his broader quality management philosophy. The diagram is particularly useful because it encourages a structured approach to problem analysis, ensuring that all potential causes are considered before moving on to the solution phase.
One of the key benefits of using a fishbone diagram is its ability to facilitate a comprehensive and systematic analysis of problems. By categorizing the causes into major groups such as people, processes, materials, equipment, and environment, teams can ensure that all aspects of a problem are explored. This systematic approach helps in identifying not just the symptoms but the root causes of a problem, which is crucial for implementing effective and lasting solutions.
In addition to its analytical benefits, the fishbone diagram is also a valuable tool for enhancing teamwork and communication within organizations. It provides a visual framework that all team members can understand and contribute to, regardless of their technical expertise or departmental background. This inclusivity fosters a collaborative environment where everyone feels involved in the problem-solving process, leading to more innovative and well-rounded solutions.
The versatility of the fishbone diagram is another significant advantage. It can be applied to a wide range of problems and industries, from manufacturing and healthcare to education and service sectors. Whether the goal is to improve product quality, reduce operational costs, enhance customer satisfaction, or solve complex technical issues, the fishbone diagram offers a flexible and adaptable framework for analysis and improvement.
Introduction to Fishbone Diagrams
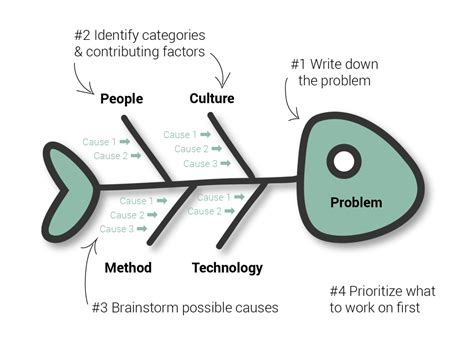
The introduction to fishbone diagrams typically involves understanding the basic structure and the steps involved in creating one. The process begins with defining the problem statement, which is placed at the head of the fishbone. Then, the major categories of causes (often referred to as the 6 Ms: Man, Machine, Material, Method, Measurement, and Mother Nature) are identified and drawn as branches off the main arrow. Team members then brainstorm and list all possible causes under these categories, creating a comprehensive map of potential factors contributing to the problem.
Benefits of Using Fishbone Diagrams
The benefits of using fishbone diagrams are multifaceted. They include the facilitation of systematic problem analysis, enhancement of teamwork and communication, and the ability to identify root causes rather than just symptoms. Additionally, fishbone diagrams are easy to understand and use, making them accessible to team members at all levels of an organization. They also promote a proactive approach to problem-solving, encouraging teams to address issues before they escalate.Creating a Fishbone Diagram
Creating a fishbone diagram involves several steps:
- Define the Problem: Clearly articulate the problem you want to solve. This will be the head of the fish.
- Identify the Categories: Determine the major categories of causes. These are usually the 6 Ms but can be tailored to fit the specific context of your problem.
- Brainstorm Causes: For each category, brainstorm as many potential causes as possible. These should be listed as branches off the main categories.
- Analyze Causes: Review the listed causes and analyze their potential impact on the problem.
- Identify Root Causes: Determine which causes are most likely contributing to the problem. This may involve further investigation or data collection.
Steps for Effective Use
For the effective use of fishbone diagrams, it's crucial to follow a structured approach: - **Engage the Team**: Involve all relevant team members in the brainstorming and analysis process to ensure a comprehensive view of the problem. - **Be Systematic**: Ensure that all categories are explored and that the analysis is thorough. - **Focus on Root Causes**: Prioritize identifying and addressing the root causes of the problem rather than just its symptoms. - **Iterate**: Be prepared to revisit and refine your analysis as new information becomes available.Applications of Fishbone Diagrams
Fishbone diagrams have a wide range of applications across different industries and sectors. They are particularly useful in quality management, where identifying and addressing the root causes of defects or issues is crucial. In healthcare, they can be used to analyze patient safety issues or operational inefficiencies. In manufacturing, they help in identifying causes of product defects or production bottlenecks. Their application is not limited to these areas; they can be used in any situation where a structured approach to problem analysis is beneficial.
Industry Examples
Examples of the use of fishbone diagrams can be seen in various industries: - **Manufacturing**: To identify the causes of product defects or quality issues. - **Healthcare**: To analyze patient safety incidents or operational inefficiencies. - **Service Sector**: To understand the causes of customer complaints or service delivery issues. - **Education**: To identify the reasons behind student underperformance or educational program inefficiencies.Challenges and Limitations
While fishbone diagrams are a powerful tool for problem analysis, they also have some challenges and limitations. One of the main challenges is ensuring that the team conducting the analysis is diverse and representative, to avoid missing critical causes. Another challenge is the potential for bias in the identification and analysis of causes. Additionally, the effectiveness of the fishbone diagram depends on the quality of the data and information available, which can sometimes be limited.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, it's essential to: - **Ensure Diverse Participation**: Involve team members from various backgrounds and expertise. - **Use Data-Driven Approaches**: Base the analysis on factual data and evidence. - **Regularly Review and Refine**: Continuously review the analysis and refine it as necessary to ensure it remains relevant and effective.Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, fishbone diagrams are a valuable tool for problem-solving and quality improvement. Their ability to facilitate systematic analysis, enhance teamwork, and identify root causes makes them indispensable in various industries. As organizations continue to face complex challenges, the use of fishbone diagrams will likely evolve, incorporating new technologies and methodologies to enhance their effectiveness. Future directions may include integrating fishbone diagrams with other quality management tools and techniques, such as lean manufacturing or Six Sigma, to create more comprehensive and powerful problem-solving frameworks.
Final Thoughts
The fishbone diagram is a timeless tool that has stood the test of time due to its simplicity, effectiveness, and versatility. Its application is not limited to specific industries or problems but can be adapted to suit a wide range of situations. As we move forward in an increasingly complex and interconnected world, tools like the fishbone diagram will remain essential for navigating challenges and achieving excellence in various fields.Fishbone Diagram Image Gallery
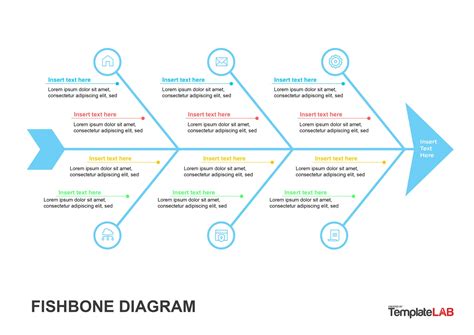
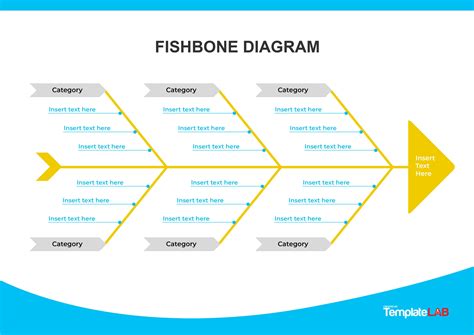
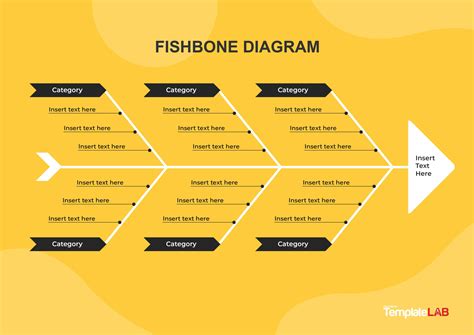
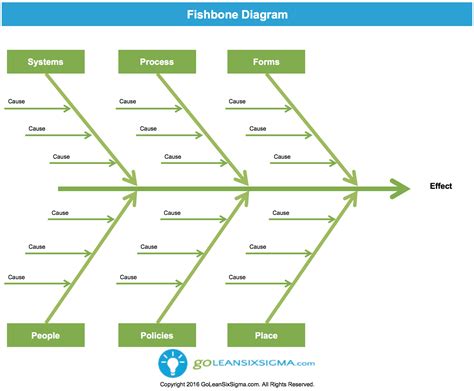
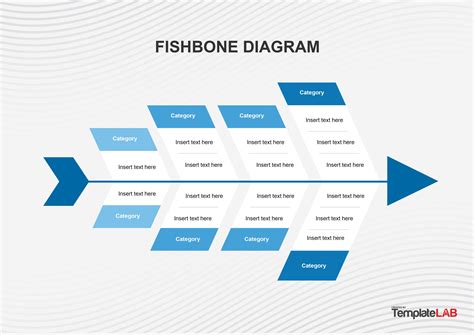
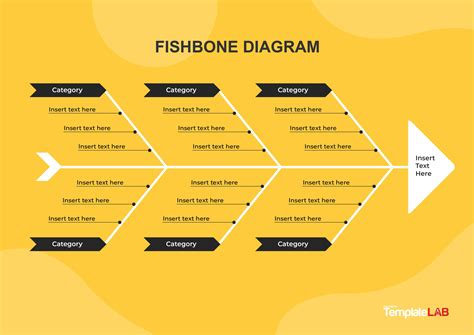
What is a Fishbone Diagram?
+A fishbone diagram, also known as an Ishikawa diagram, is a tool used to identify and analyze the root causes of problems.
How Do You Create a Fishbone Diagram?
+Creating a fishbone diagram involves defining the problem, identifying categories of causes, brainstorming potential causes, and analyzing these causes to identify the root causes of the problem.
What Are the Benefits of Using a Fishbone Diagram?
+The benefits include systematic problem analysis, enhancement of teamwork and communication, and the ability to identify root causes rather than just symptoms.
Can Fishbone Diagrams Be Used in Any Industry?
+Yes, fishbone diagrams are versatile and can be applied to a wide range of problems and industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, service sectors, and education.
How Do You Overcome the Challenges of Using a Fishbone Diagram?
+Overcoming challenges involves ensuring diverse participation, using data-driven approaches, and regularly reviewing and refining the analysis to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
We hope this comprehensive guide to fishbone diagrams has been informative and helpful. Whether you are a quality control specialist, a project manager, or simply someone looking to improve processes and solve problems effectively, understanding and applying the principles of fishbone diagrams can be a powerful tool in your arsenal. Don't hesitate to share your experiences or ask further questions in the comments below. Your input is invaluable in helping us create a community that learns and grows together.
