Intro
Discover the ultimate Diabetes Insipidus Guide, covering symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for central, nephrogenic, and gestational types, with expert insights on management and care.
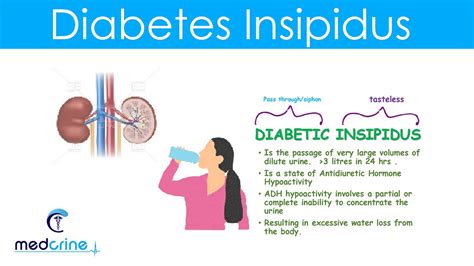
Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that affects the body's ability to regulate fluids. It is characterized by excessive thirst and the production of large amounts of diluted urine. Despite its name, diabetes insipidus is not related to diabetes mellitus, which is a condition that affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar levels. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of diabetes insipidus, as well as provide guidance on how to manage the condition.
The importance of understanding diabetes insipidus cannot be overstated. If left untreated, the condition can lead to serious complications, such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and even kidney damage. Furthermore, diabetes insipidus can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making everyday activities a challenge. By learning more about the condition, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms, prevent complications, and improve their overall health.
Diabetes insipidus is often misunderstood, and many people are unaware of its symptoms and consequences. However, with the right knowledge and treatment, it is possible to manage the condition effectively. Whether you are experiencing symptoms of diabetes insipidus or are simply interested in learning more about the condition, this article aims to provide a comprehensive guide to help you understand and navigate the complexities of diabetes insipidus.
What is Diabetes Insipidus?

Types of Diabetes Insipidus
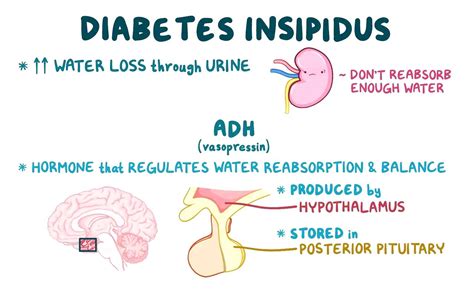
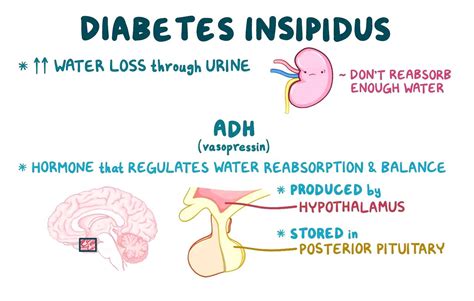
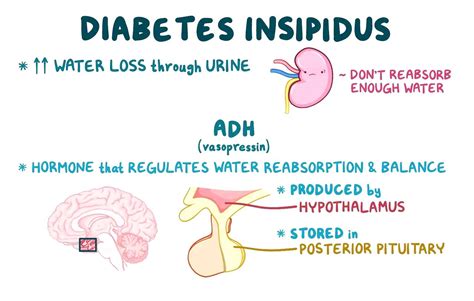
The four main types of diabetes insipidus are: * Central diabetes insipidus: This type is caused by a lack of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which is produced by the hypothalamus and released by the posterior pituitary gland. * Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus: This type is caused by the kidneys' inability to respond to ADH, resulting in an inability to concentrate urine. * Dipsogenic diabetes insipidus: This type is caused by a defect in the thirst mechanism, leading to excessive water intake and production of diluted urine. * Gestational diabetes insipidus: This type occurs during pregnancy and is caused by an imbalance of hormones.Causes and Risk Factors

Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing diabetes insipidus, including: * Family history * Age * Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or hypokalemia * Use of certain medications, such as lithium or demeclocyclineSymptoms
Complications
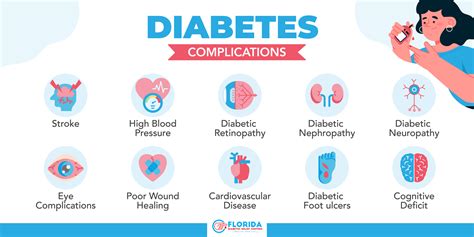
If left untreated, diabetes insipidus can lead to serious complications, including: * Dehydration * Electrolyte imbalances * Kidney damage * Heat stroke * SeizuresDiagnosis

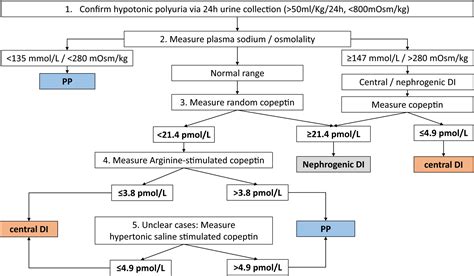
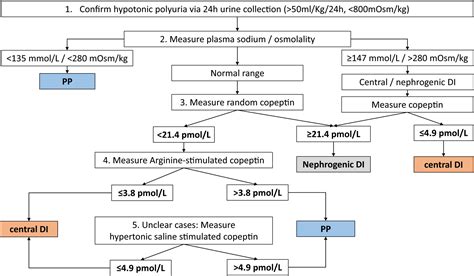
Water Deprivation Test
The water deprivation test is a diagnostic test used to confirm the presence of diabetes insipidus. The test involves: * Withholding water for a period of time (usually 12-24 hours) * Measuring urine output and osmolality * Administering ADH or desmopressin to see if urine concentration improvesTreatment
Lifestyle Modifications
Making lifestyle modifications can help manage the symptoms of diabetes insipidus. These modifications may include: * Drinking plenty of water to stay hydrated * Avoiding caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate symptoms * Eating a balanced diet to maintain electrolyte levels * Getting regular exercise to improve overall healthDiabetes Insipidus Image Gallery



What is the main cause of diabetes insipidus?
+The main cause of diabetes insipidus is a lack of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or the kidneys' inability to respond to ADH.
What are the symptoms of diabetes insipidus?
+The symptoms of diabetes insipidus include excessive thirst, production of large amounts of diluted urine, nocturia, polyuria, fatigue, headaches, dry skin, and dizziness.
How is diabetes insipidus diagnosed?
+Diabetes insipidus is diagnosed based on a combination of medical history, physical examination, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and the water deprivation test.
What are the treatment options for diabetes insipidus?
+Treatment options for diabetes insipidus include hormone replacement therapy, medications to reduce urine production, medications to increase urine concentration, and lifestyle modifications.
Can diabetes insipidus be prevented?
+While diabetes insipidus cannot be prevented, making lifestyle modifications and managing underlying medical conditions can help reduce the risk of developing the condition.
In conclusion, diabetes insipidus is a rare and complex condition that requires proper diagnosis and treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. If you suspect that you or a loved one may have diabetes insipidus, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment. Additionally, making lifestyle modifications, such as increasing water intake and avoiding caffeine and alcohol, can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. We encourage you to share this article with others who may be affected by diabetes insipidus and to take an active role in managing your health.
