Intro
Discover the comprehensive Cbc Diagnostic Procedure Template, featuring detailed blood test analysis, medical diagnosis, and treatment planning, utilizing laboratory results and clinical guidelines for accurate patient care and disease management.
The Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a fundamental diagnostic tool used in medical practices to evaluate a patient's overall health and detect a wide range of conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders. It is a test that measures various components of the blood, providing valuable insights into the body's physiological and pathological states. Understanding the CBC diagnostic procedure is crucial for both healthcare professionals and patients, as it helps in making informed decisions about treatments and further diagnostic tests.
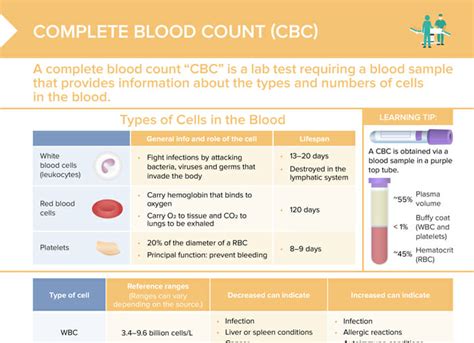
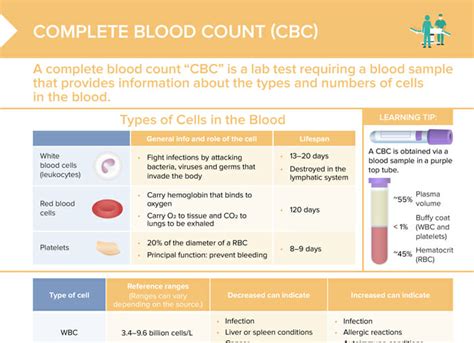
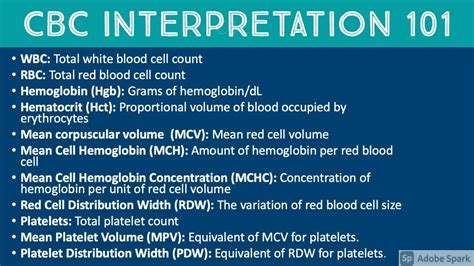
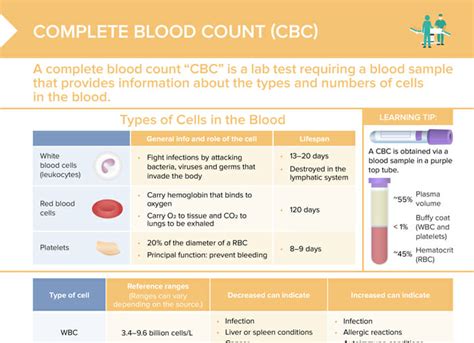
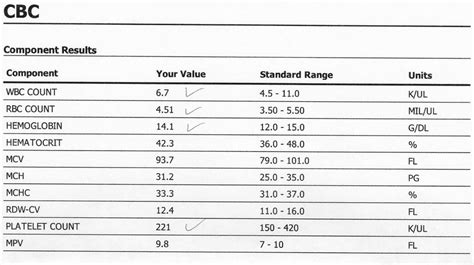
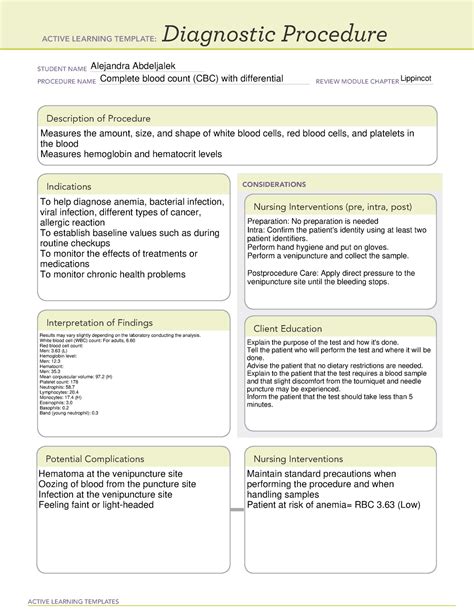
The CBC test is often the first step in a diagnostic process, offering a broad view of a patient's health status. It is commonly ordered as part of a routine check-up, before surgery, or when a patient presents with symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or signs of infection. The test includes several parameters that are measured and analyzed, including the red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV), among others.
Introduction to CBC Diagnostic Procedure
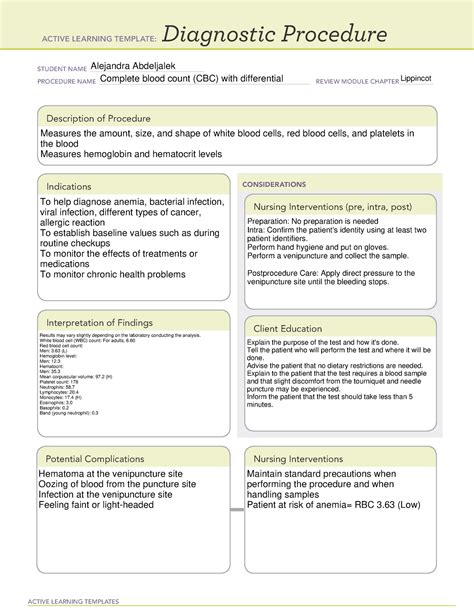
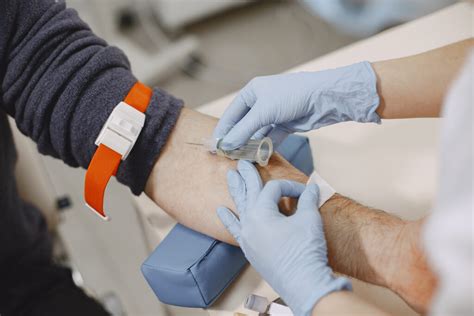
The CBC diagnostic procedure starts with the collection of a blood sample, typically from a vein in the arm. The blood is drawn into a tube that contains an anticoagulant to prevent the blood from clotting. This process is minimally invasive and usually takes only a few minutes. Once the blood sample is collected, it is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
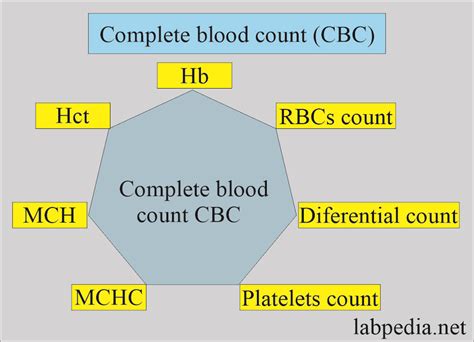
Components of CBC
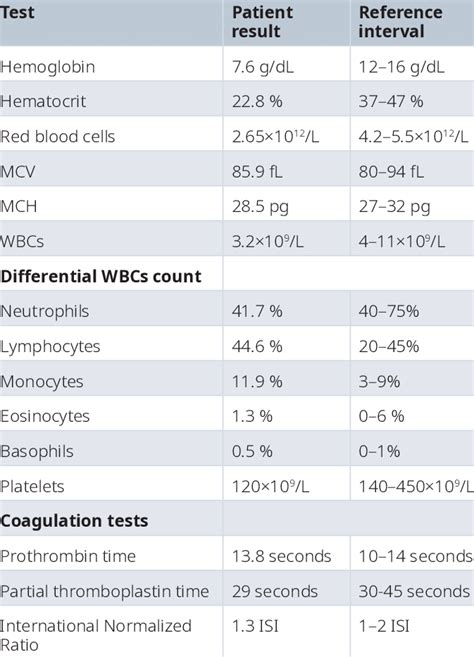
The CBC test measures several components of the blood, each providing unique information about the body's condition. These components include:
- Red Blood Cell (RBC) count: Indicates the number of red blood cells in the blood, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
- White Blood Cell (WBC) count: Reflects the number of white blood cells, which are vital for fighting infections.
- Platelet count: Measures the number of platelets, which are crucial for blood clotting.
- Hemoglobin (Hb): The protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen to the body's tissues.
- Hematocrit (Hct): The proportion of blood volume made up by red blood cells.
- Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV): The average size of red blood cells, which helps in diagnosing anemia.
Interpretation of CBC Results
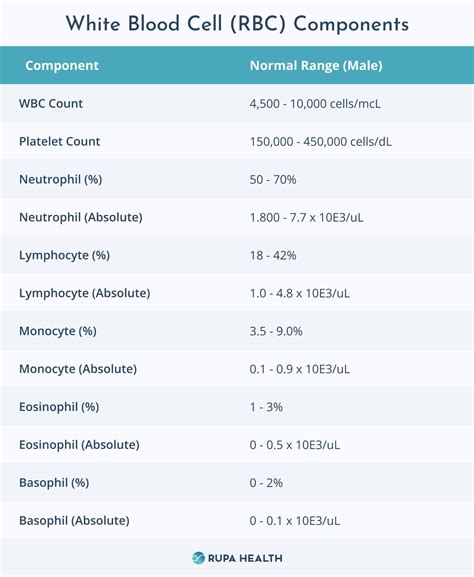
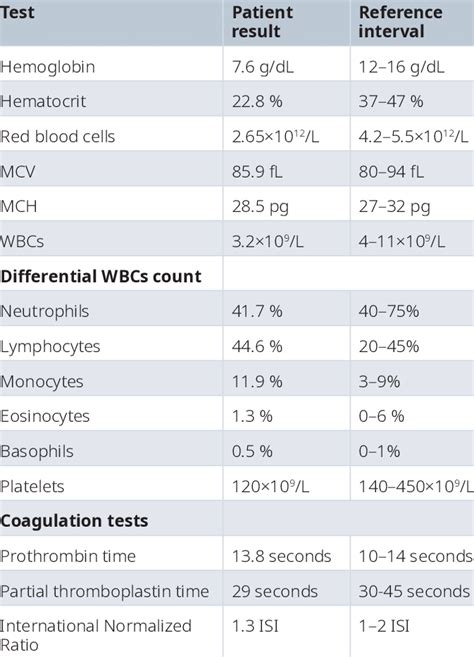
Interpreting CBC results requires a thorough understanding of the normal ranges for each parameter and how they relate to various health conditions. For instance, an elevated white blood cell count may indicate the presence of an infection or inflammation, while a low red blood cell count could suggest anemia. The interpretation of CBC results should always be done in the context of the patient's clinical presentation and medical history.
Clinical Applications of CBC
The CBC has a wide range of clinical applications, including:
- Diagnosing and monitoring anemia, which can be caused by iron deficiency, vitamin deficiency, or chronic diseases.
- Detecting infections and inflammatory conditions, as indicated by changes in the white blood cell count.
- Evaluating blood clotting disorders through platelet count and other specialized tests.
- Monitoring the response to treatments, such as chemotherapy or medications that affect blood cell production.
Limitations and Considerations
While the CBC is a valuable diagnostic tool, it has its limitations. It may not detect all types of blood disorders or other conditions, and abnormal results can sometimes be seen in healthy individuals. Additionally, the interpretation of CBC results can be influenced by various factors, including the patient's age, sex, and the presence of chronic diseases.
Future Directions in CBC Diagnostic Procedure
Advancements in technology and medical science are continually improving the CBC diagnostic procedure. Automated analyzers have increased the speed and accuracy of blood cell counting, and new parameters are being developed to provide more detailed information about the blood and its components. Furthermore, the integration of CBC results with other diagnostic tests and clinical information is enhancing the ability to diagnose and manage diseases effectively.
Gallery of CBC Diagnostic Images
CBC Diagnostic Image Gallery


What is a CBC test used for?
+A CBC test is used to evaluate a patient's overall health and detect a wide range of conditions, including anemia, infection, and blood disorders.
How is a CBC test performed?
+A CBC test is performed by collecting a blood sample from a vein in the arm, which is then sent to a laboratory for analysis.
What are the components of a CBC test?
+The components of a CBC test include red blood cell count, white blood cell count, platelet count, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV), among others.
In conclusion, the CBC diagnostic procedure is a vital tool in medical practice, offering insights into various aspects of a patient's health. Its applications are diverse, ranging from the diagnosis of anemia and infection to the monitoring of treatments and diseases. As medical science continues to evolve, the CBC test will remain a cornerstone of diagnostic medicine, with ongoing advancements aimed at improving its accuracy and utility. We invite readers to share their thoughts and experiences with the CBC diagnostic procedure, and we look forward to continuing the conversation on the importance of this test in modern healthcare.
