Intro
Master accurate medicine labeling with 5 expert tips, ensuring compliance and patient safety through clear dosage instructions, warning labels, and pharmaceutical packaging design, optimizing medication management and adherence.
Medicine labels play a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and effective medication management. With the increasing complexity of pharmaceutical treatments, it's essential to have clear, concise, and accurate labeling to avoid errors and adverse reactions. In this article, we'll delve into the importance of medicine labels and provide valuable tips for creating effective and compliant labels.
The accuracy and clarity of medicine labels are vital for patients, caregivers, and healthcare professionals. A well-designed label can help prevent medication errors, improve patient outcomes, and reduce healthcare costs. On the other hand, poorly designed labels can lead to confusion, misuse, and potentially life-threatening consequences. As the pharmaceutical industry continues to evolve, the demand for innovative and user-friendly labeling solutions is on the rise.
The development of medicine labels involves a multidisciplinary approach, requiring input from pharmacists, clinicians, designers, and regulatory experts. By combining their expertise, manufacturers can create labels that balance regulatory requirements with patient-centered design principles. Effective medicine labels should be easy to read, understand, and use, even for individuals with limited health literacy or visual impairments. In the following sections, we'll explore five essential tips for creating compliant and patient-friendly medicine labels.
Understanding Regulatory Requirements

Key Regulatory Considerations
When designing medicine labels, it's essential to consider the following regulatory aspects: * Label format: The label should be easy to read and understand, with clear headings, concise language, and adequate white space. * Content: The label should include essential information such as the product name, active ingredients, dosage instructions, warnings, and precautions. * Typography: The font size, style, and color should be consistent and meet FDA guidelines for readability.Designing Patient-Centered Labels

Principles of Patient-Centered Design
When designing patient-centered labels, consider the following principles: * Simple language: Use clear, concise language that is easy to understand, avoiding technical jargon or complex terminology. * Visual hierarchy: Organize content using a clear visual hierarchy, with the most important information prominently displayed. * Color and typography: Select colors and typography that are visually appealing, consistent, and meet regulatory requirements.Using Clear and Concise Language

Best Practices for Clear Language
When using clear and concise language on medicine labels, follow these best practices: * Use short sentences and bullet points to break up complex information. * Avoid abbreviations or acronyms that may be unfamiliar to patients. * Use active voice, as it is generally easier to read and understand than passive voice.Ensuring Label Legibility
Factors Affecting Label Legibility
When designing labels, consider the following factors that affect legibility: * Font size: The font size should be adequate for the label size and content, with a minimum of 6 points for body text. * Font style: The font style should be clear and easy to read, with sans-serif fonts generally preferred for digital labels. * Color contrast: The color contrast between the text and background should be sufficient to ensure readability, with a minimum contrast ratio of 4.5:1.Testing and Validation

Methods for Testing and Validation
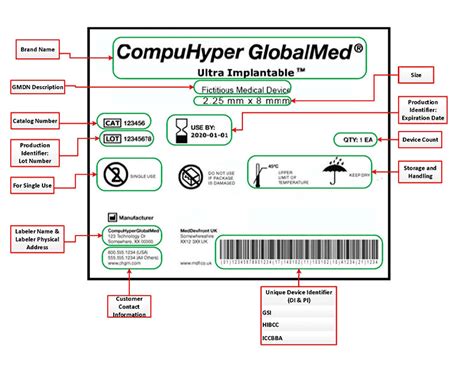
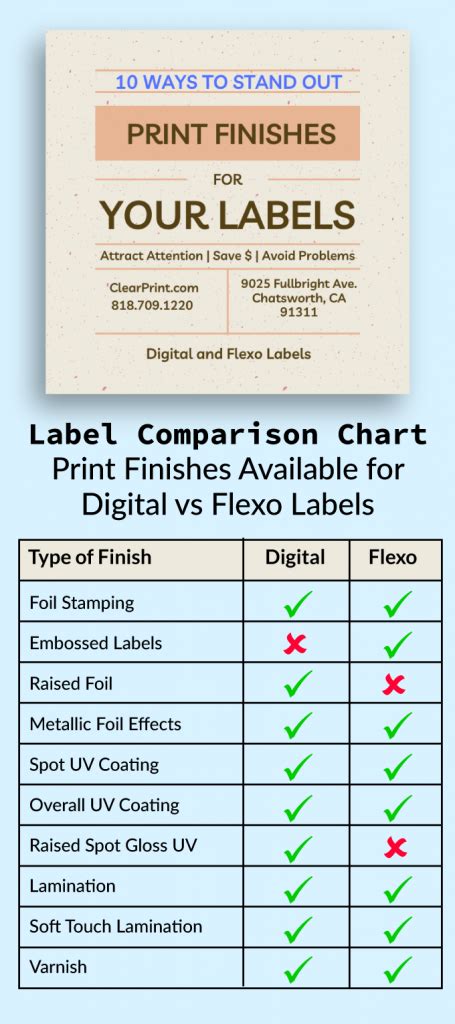
When testing and validating medicine labels, use the following methods: * Usability testing: Conduct usability testing with a diverse group of participants to identify potential issues and areas for improvement. * Regulatory review: Review labels against regulatory requirements and industry standards to ensure compliance and accuracy. * Pilot testing: Conduct pilot testing with a small group of participants to validate label design and content.Medicine Label Gallery








What are the regulatory requirements for medicine labels?
+The regulatory requirements for medicine labels vary by country and region, but generally include guidelines for label format, content, and typography. In the United States, the FDA sets strict guidelines for labeling pharmaceutical products.
How can I ensure that my medicine labels are patient-centered?
+To ensure that your medicine labels are patient-centered, involve patients and caregivers in the design process, use simple language, and prioritize clear and concise information.
What are the best practices for testing and validating medicine labels?
+The best practices for testing and validating medicine labels include usability testing with patients and caregivers, regulatory review, and pilot testing with a small group of participants.
How can I ensure that my medicine labels are legible and easy to read?
+To ensure that your medicine labels are legible and easy to read, use a clear font, adequate font size, and sufficient color contrast between the text and background.
What are the consequences of non-compliant medicine labels?
+The consequences of non-compliant medicine labels can include delays in approval, recalls, legal action, and potentially life-threatening consequences for patients.
In conclusion, creating effective and compliant medicine labels requires a deep understanding of regulatory requirements, patient-centered design principles, and best practices for testing and validation. By following these guidelines and tips, manufacturers can develop labels that prioritize patient safety, improve medication management, and reduce healthcare costs. We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with medicine labels, and to explore our resources and expertise in label design and development. Together, we can create a safer and more effective healthcare system, one label at a time.
