Intro
Master bipolar disorder management with our template guide, featuring mood tracking, symptom management, and treatment planning strategies to help cope with manic depression, anxiety, and emotional instability.
Bipolar disorder is a complex and chronic mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by extreme mood swings, ranging from manic highs to depressive lows, which can significantly impact an individual's daily life, relationships, and overall well-being. Despite its prevalence, bipolar disorder remains poorly understood, and many people struggle to find accurate and reliable information about the condition. In this article, we will delve into the world of bipolar disorder, exploring its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
Living with bipolar disorder can be challenging, not only for the individual but also for their loved ones. The unpredictable nature of the condition can make it difficult to maintain relationships, pursue careers, and engage in daily activities. Moreover, the stigma surrounding mental health conditions can prevent people from seeking help, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. However, with the right approach and support, individuals with bipolar disorder can learn to manage their symptoms, stabilize their mood, and improve their overall quality of life.
The importance of understanding bipolar disorder cannot be overstated. By educating ourselves about the condition, we can break down stigmas, promote awareness, and encourage individuals to seek help. Moreover, research into bipolar disorder has led to the development of effective treatments and management strategies, which can significantly improve the lives of those affected. In this article, we will explore the latest research, expert insights, and personal stories to provide a comprehensive guide to bipolar disorder.
What is Bipolar Disorder?
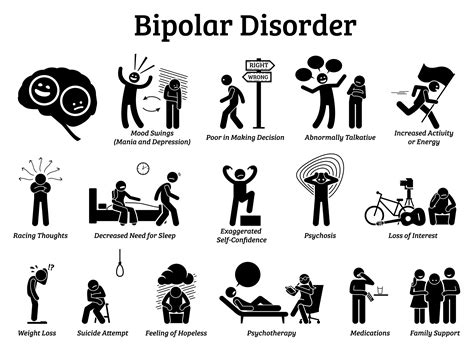
Types of Bipolar Disorder
The different subtypes of bipolar disorder are distinguished by the severity and frequency of manic and depressive episodes. Bipolar I disorder is the most severe form, characterized by at least one manic episode, which may be accompanied by depressive episodes. Bipolar II disorder is less severe, with at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode. Cyclothymic disorder is a milder form, characterized by periods of hypomania and depression that last for at least two years. Other specified bipolar and related disorders include conditions that do not meet the full criteria for the other subtypes.Causes and Risk Factors
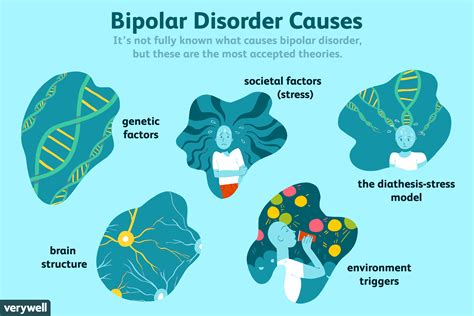
Genetic Factors
Studies have identified several genes that may contribute to the development of bipolar disorder. Individuals with a first-degree relative, such as a parent or sibling, with bipolar disorder are more likely to develop the condition. However, the presence of a genetic predisposition does not guarantee the development of bipolar disorder, and many people with a family history of the condition never develop it.Symptoms and Diagnosis

Diagnostic Criteria
The diagnostic criteria for bipolar disorder are outlined in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). A diagnosis of bipolar I disorder requires at least one manic episode, while a diagnosis of bipolar II disorder requires at least one major depressive episode and at least one hypomanic episode. The diagnosis of cyclothymic disorder requires periods of hypomania and depression that last for at least two years.Treatment and Management

Treatment Options
The treatment options for bipolar disorder depend on the subtype, severity, and individual needs. Medications, such as lithium and valproate, are commonly used to stabilize mood and reduce symptoms. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy, can help individuals develop coping skills and improve relationships. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) may be used in severe cases, particularly during manic or depressive episodes.Coping and Support

Support Groups
Support groups, such as the National Alliance on Mental Illness (NAMI) and the Depression and Bipolar Support Alliance (DBSA), can provide individuals with bipolar disorder and their loved ones with a sense of community and connection. Support groups offer a safe and supportive environment where individuals can share their experiences, receive support and guidance, and connect with others who understand the challenges of living with bipolar disorder.Bipolar Disorder Image Gallery










What are the symptoms of bipolar disorder?
+The symptoms of bipolar disorder can vary depending on the subtype and the individual. Manic episodes are characterized by feelings of euphoria, increased energy, and impulsivity, while depressive episodes are marked by feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
How is bipolar disorder diagnosed?
+A diagnosis of bipolar disorder is typically made based on a comprehensive psychiatric evaluation, which includes a physical exam, laboratory tests, and a thorough medical history.
What are the treatment options for bipolar disorder?
+The treatment options for bipolar disorder depend on the subtype, severity, and individual needs. Medications, such as mood stabilizers and antipsychotics, can help to stabilize mood and reduce symptoms. Psychotherapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy and interpersonal therapy, can help individuals develop coping skills and improve relationships.
Can bipolar disorder be managed?
+Yes, bipolar disorder can be managed with the right treatment and support. Individuals with bipolar disorder can benefit from developing a daily routine, engaging in regular exercise, and practicing stress management techniques, such as meditation and yoga. Social support from family, friends, and support groups can also help individuals cope with the challenges of bipolar disorder.
What are the benefits of seeking help for bipolar disorder?
+Seeking help for bipolar disorder can have numerous benefits, including improved symptom management, enhanced quality of life, and increased social support. With the right treatment and support, individuals with bipolar disorder can learn to manage their symptoms, stabilize their mood, and improve their overall well-being.
In conclusion, bipolar disorder is a complex and chronic mental health condition that requires a comprehensive approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies, individuals with bipolar disorder can take the first step towards recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling with bipolar disorder, it is essential to seek help from a qualified mental health professional. With the right support and treatment, individuals with bipolar disorder can learn to manage their symptoms, stabilize their mood, and improve their overall quality of life. We invite you to share your thoughts, experiences, and questions about bipolar disorder in the comments section below. By working together, we can promote awareness, reduce stigma, and improve the lives of those affected by this condition.
