Intro
Discover 5 essential tips for heart failure diagnostic, including symptom identification, echocardiogram tests, and cardiovascular risk assessment to improve diagnosis accuracy and patient outcomes in cardiac care.
Heart failure is a chronic and progressive condition where the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It is a major public health concern, affecting millions of people worldwide. Early diagnosis and treatment of heart failure are crucial to improve patient outcomes and reduce mortality rates. In this article, we will discuss 5 tips for diagnosing heart failure, highlighting the importance of a comprehensive approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Heart failure diagnosis requires a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential to identify signs and symptoms of heart failure, such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and feet. Laboratory tests, including blood work and urine analysis, can help identify underlying causes of heart failure, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease. Imaging studies, including echocardiography and chest X-rays, can help assess the heart's structure and function.
The diagnosis of heart failure can be challenging, as the symptoms can be nonspecific and similar to those of other conditions. Therefore, it is essential to have a systematic approach to diagnosis, using a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. By following these 5 tips, healthcare providers can improve their ability to diagnose heart failure accurately and provide effective treatment to patients.
Tip 1: Take a Comprehensive Medical History

Tip 2: Perform a Physical Examination

Tip 3: Use Laboratory Tests
Tip 4: Use Imaging Studies
Tip 5: Consider Other Diagnostic Tests

Benefits of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis and treatment of heart failure can improve patient outcomes and reduce mortality rates. With early diagnosis, healthcare providers can initiate treatment, including medications, lifestyle modifications, and device therapy, to improve symptoms and slow disease progression. Early diagnosis can also help healthcare providers identify underlying causes of heart failure, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and kidney disease, and treat them accordingly.Challenges in Diagnosing Heart Failure
Diagnosing heart failure can be challenging, as the symptoms can be nonspecific and similar to those of other conditions. Healthcare providers must have a systematic approach to diagnosis, using a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. They must also consider the patient's medical history, lifestyle habits, and underlying conditions to make an accurate diagnosis.Future Directions in Heart Failure Diagnosis
Future directions in heart failure diagnosis include the use of biomarkers, genetic testing, and advanced imaging modalities. Biomarkers, such as natriuretic peptides, can help healthcare providers diagnose heart failure and monitor disease progression. Genetic testing can help healthcare providers identify genetic mutations that contribute to heart failure. Advanced imaging modalities, such as cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), can help healthcare providers assess the heart's structure and function in greater detail.Heart Failure Image Gallery
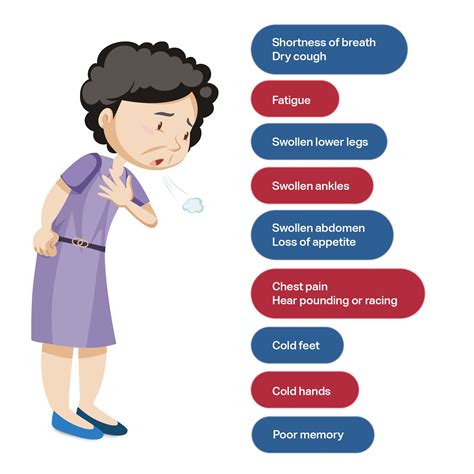
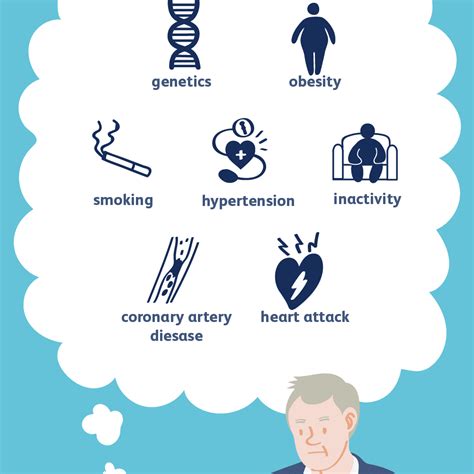
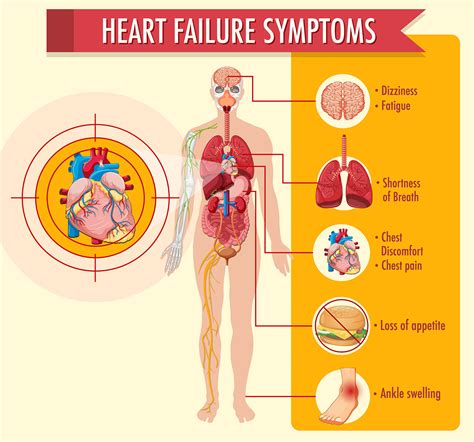
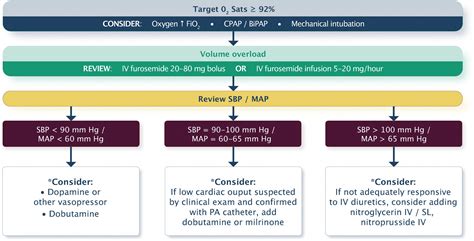
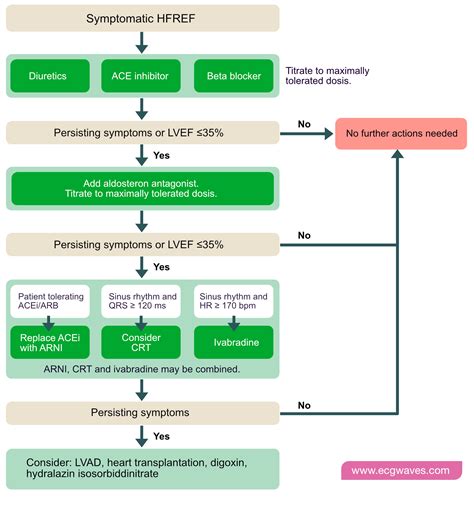




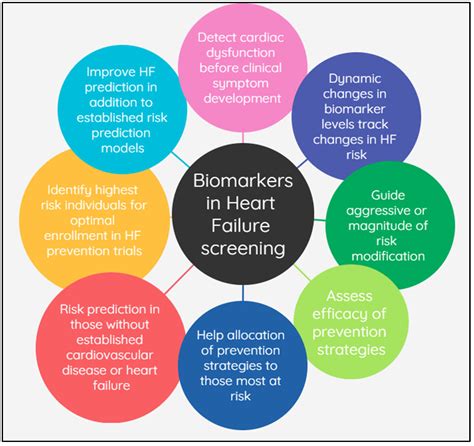
What are the symptoms of heart failure?
+The symptoms of heart failure include shortness of breath, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and feet.
How is heart failure diagnosed?
+Heart failure is diagnosed using a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies.
What are the treatment options for heart failure?
+The treatment options for heart failure include medications, lifestyle modifications, and device therapy.
Can heart failure be prevented?
+Yes, heart failure can be prevented by controlling underlying conditions, such as high blood pressure and diabetes, and making lifestyle modifications, such as exercising regularly and eating a healthy diet.
What is the prognosis for heart failure?
+The prognosis for heart failure varies depending on the severity of the condition and the effectiveness of treatment.
In conclusion, diagnosing heart failure requires a comprehensive approach, using a combination of clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. By following these 5 tips, healthcare providers can improve their ability to diagnose heart failure accurately and provide effective treatment to patients. Early diagnosis and treatment can improve patient outcomes and reduce mortality rates. We encourage readers to share this article with others and to take action to learn more about heart failure diagnosis and treatment. Together, we can improve the lives of patients with heart failure and reduce the burden of this condition on individuals, families, and society.
