Intro
Diabetic ketoacidosis diagnosis simplified with DKA diagnostic template ATIs. Learn key assessment, lab results, and treatment plans with this guide, covering hyperglycemia, ketosis, and acidosis management.
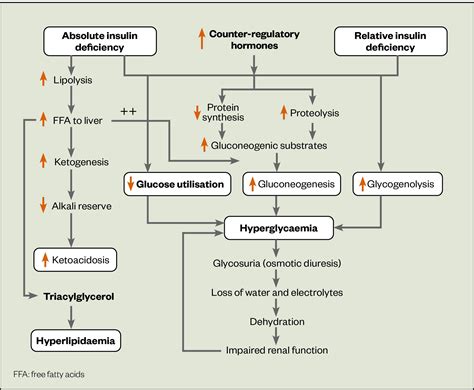
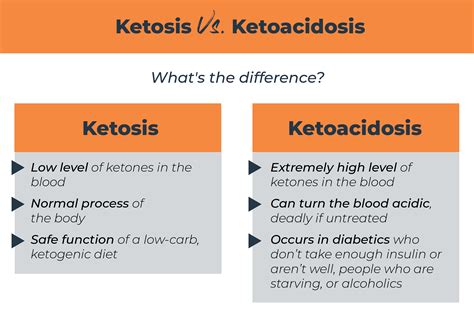
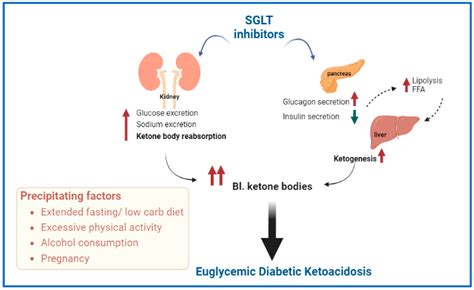
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes. It occurs when the body produces high levels of ketones, which are acidic substances that can poison the body. DKA is most commonly associated with type 1 diabetes, but it can also occur in people with type 2 diabetes. The ATIs (Assessment Technologies Institute) guide for DKA diagnostic template is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage this condition effectively.
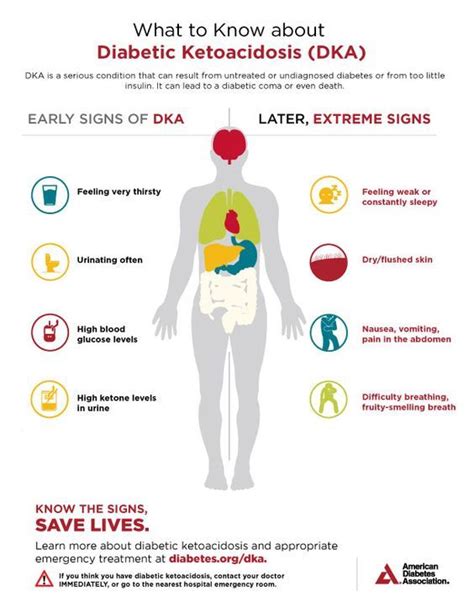
DKA is a medical emergency that requires prompt recognition and treatment. The condition is characterized by hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketosis. The symptoms of DKA can include excessive thirst and urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. If left untreated, DKA can lead to serious complications, such as cerebral edema, cardiac arrest, and even death. Therefore, it is crucial to diagnose DKA quickly and accurately to initiate appropriate treatment.
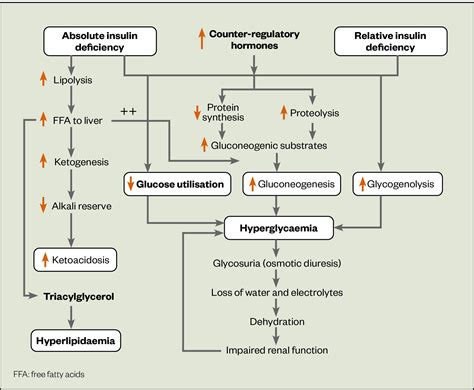
The ATIs guide for DKA diagnostic template provides a comprehensive framework for healthcare professionals to assess patients with suspected DKA. The template includes a series of questions and assessments to help healthcare professionals evaluate the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results. The guide also provides a scoring system to determine the severity of DKA and guide treatment decisions. By using the ATIs guide, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients with DKA receive timely and effective treatment, which can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes.
Introduction to DKA Diagnostic Template
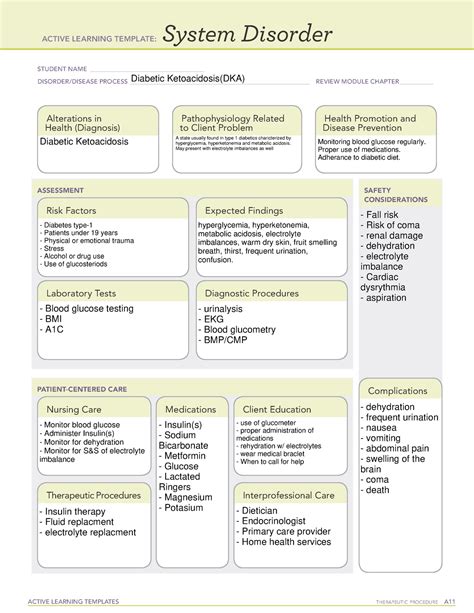
The DKA diagnostic template is a systematic approach to assessing patients with suspected DKA. The template includes a series of questions and assessments to evaluate the patient's symptoms, medical history, and laboratory results. The template also provides a scoring system to determine the severity of DKA and guide treatment decisions. The ATIs guide for DKA diagnostic template is based on the latest clinical evidence and guidelines, ensuring that healthcare professionals have access to the most up-to-date information and best practices for diagnosing and managing DKA.
Assessment of DKA Symptoms

The assessment of DKA symptoms is a critical component of the diagnostic template. Healthcare professionals should evaluate the patient's symptoms, including excessive thirst and urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath. The template also includes a series of questions to assess the patient's medical history, including their diabetes diagnosis, medication regimen, and any recent changes to their treatment plan. By evaluating the patient's symptoms and medical history, healthcare professionals can determine the likelihood of DKA and guide further diagnostic testing.
DKA Diagnostic Criteria

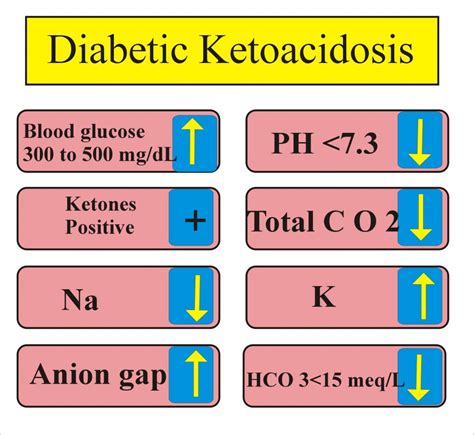
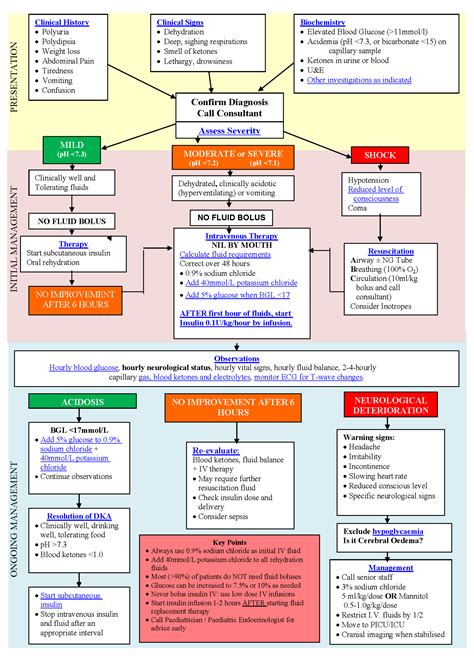
The DKA diagnostic criteria are based on the presence of hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketosis. The criteria include:
- Hyperglycemia: blood glucose level > 250 mg/dL
- Metabolic acidosis: arterial pH < 7.3 or serum bicarbonate < 18 mmol/L
- Ketosis: presence of ketones in the blood or urine By evaluating these criteria, healthcare professionals can determine the presence and severity of DKA.
DKA Treatment Options

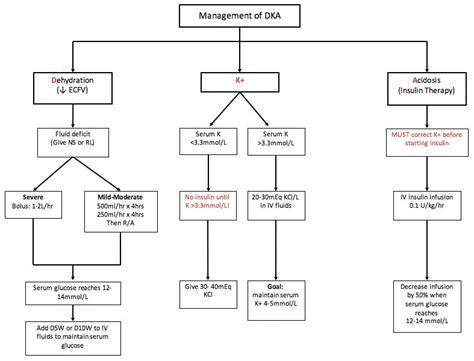
The treatment of DKA typically involves a combination of insulin therapy, fluid replacement, and electrolyte management. The goal of treatment is to correct the metabolic acidosis, reduce the blood glucose level, and prevent complications. The ATIs guide for DKA diagnostic template provides a comprehensive framework for healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan for patients with DKA.
DKA Prevention Strategies

Prevention is a critical component of DKA management. Healthcare professionals should educate patients with diabetes on the risk factors for DKA, including poor glucose control, infection, and dehydration. Patients should also be instructed on how to recognize the symptoms of DKA and seek medical attention promptly if they occur. By preventing DKA, healthcare professionals can reduce the risk of serious complications and improve outcomes for patients with diabetes.
DKA Management in Special Populations

DKA management in special populations, such as children, pregnant women, and older adults, requires careful consideration of their unique needs and risk factors. Healthcare professionals should be aware of the potential complications and comorbidities that may affect these populations and develop individualized treatment plans accordingly. The ATIs guide for DKA diagnostic template provides a comprehensive framework for healthcare professionals to manage DKA in these special populations.
DKA and Mental Health

DKA and mental health are closely linked. The stress and anxiety associated with DKA can exacerbate mental health conditions, such as depression and anxiety disorders. Healthcare professionals should be aware of the potential mental health implications of DKA and provide patients with access to mental health resources and support.
DKA and Nutrition
DKA and nutrition are also closely linked. A healthy diet and adequate nutrition are essential for managing diabetes and preventing DKA. Healthcare professionals should educate patients on the importance of a balanced diet and provide guidance on meal planning and nutrition management.
Gallery of DKA Images
DKA Image Gallery



What are the symptoms of DKA?
+The symptoms of DKA include excessive thirst and urination, nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, and shortness of breath.
How is DKA diagnosed?
+DKA is diagnosed based on the presence of hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketosis.
What is the treatment for DKA?
+The treatment for DKA typically involves a combination of insulin therapy, fluid replacement, and electrolyte management.
How can DKA be prevented?
+DKA can be prevented by maintaining good glucose control, staying hydrated, and seeking medical attention promptly if symptoms occur.
What are the complications of DKA?
+The complications of DKA include cerebral edema, cardiac arrest, and death.
In conclusion, the ATIs guide for DKA diagnostic template is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals to diagnose and manage DKA effectively. By using this template, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients with DKA receive timely and effective treatment, which can help prevent serious complications and improve outcomes. We encourage readers to share their experiences and insights on DKA diagnosis and management in the comments section below. Additionally, we invite readers to share this article with others who may benefit from this information, and to take action to promote awareness and education on DKA prevention and management.
