Intro
Improve incident analysis with 5 After Action Report tips, enhancing debriefing, risk assessment, and corrective action through effective review and evaluation techniques.
The importance of after-action reports (AARs) cannot be overstated, as they provide valuable insights into the successes and failures of various projects, operations, and events. By documenting and analyzing what went right and wrong, individuals and organizations can identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and ultimately achieve better outcomes in the future. In this article, we will delve into the world of AARs, exploring their significance, benefits, and best practices. Whether you are a project manager, team leader, or simply someone looking to improve your performance, this article is for you.
Effective after-action reporting is a skill that takes time and practice to develop, but the payoff is well worth the effort. By conducting thorough and honest AARs, you can gain a deeper understanding of your strengths and weaknesses, as well as those of your team or organization. This knowledge can then be used to inform decision-making, optimize processes, and drive growth. In the following sections, we will provide tips and guidance on how to create high-quality AARs that drive meaningful change and improvement.
The process of creating an AAR can be daunting, especially for those who are new to it. However, with the right approach and mindset, it can be a valuable learning experience that yields significant benefits. To get the most out of your AARs, it is essential to approach them with a critical and reflective mindset, being honest about what worked and what did not. By doing so, you can identify key takeaways and develop strategies for improving future performance. In the next section, we will explore the first tip for creating effective AARs.
Tip 1: Be Honest and Objective

To be honest and objective in your AARs, try to separate facts from opinions and assumptions. Stick to what actually happened, rather than what you think or feel about it. Additionally, avoid making judgments or jumping to conclusions, and instead focus on gathering and analyzing data. By doing so, you can create AARs that are grounded in reality and provide a clear understanding of what went right and wrong.
Tip 2: Focus on Key Lessons Learned

To focus on key lessons learned, try to identify the most significant successes and failures, and analyze their causes and effects. Ask yourself questions like "What went right and wrong?", "Why did it happen?", and "What can we do differently next time?". By answering these questions, you can gain a deeper understanding of what worked and what did not, and develop strategies for improving future performance.
Tip 3: Use a Standardized Format

To use a standardized format, try to develop a template or checklist that includes key sections and questions. This can include sections on background, objectives, successes, failures, lessons learned, and recommendations. By using a standardized format, you can ensure that your AARs are comprehensive, consistent, and actionable.
Tip 4: Involve Stakeholders and Team Members

To involve stakeholders and team members, try to identify key individuals who were involved in the project, operation, or event. Ask them to provide feedback, insights, and suggestions, and incorporate their input into the AAR. By doing so, you can create AARs that reflect the experiences, perspectives, and ideas of those who were directly involved.
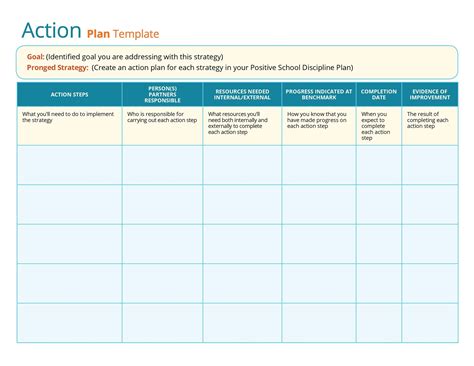
Tip 5: Take Action and Follow Up

To take action and follow up, try to develop an action plan that outlines key steps, responsibilities, and timelines. Assign tasks and responsibilities to team members, and establish a system for tracking progress and monitoring results. By doing so, you can ensure that the AAR is not just a report, but a catalyst for meaningful change and improvement.
Benefits of After-Action Reports
The benefits of AARs are numerous and significant. By creating and using AARs, individuals and organizations can improve performance, reduce errors, and increase efficiency. AARs can also help to identify and address systemic issues, improve communication and collaboration, and enhance accountability and transparency.Some of the key benefits of AARs include:
- Improved performance and outcomes
- Reduced errors and mistakes
- Increased efficiency and productivity
- Enhanced communication and collaboration
- Improved accountability and transparency
- Increased learning and development
Common Challenges and Pitfalls
Despite the many benefits of AARs, there are also common challenges and pitfalls to be aware of. These can include: * Lack of honesty and objectivity * Insufficient data and information * Poor communication and collaboration * Inadequate follow-up and action * Resistance to change and improvementTo overcome these challenges and pitfalls, it is essential to approach AARs with a critical and reflective mindset, being honest about what worked and what did not. By doing so, you can create AARs that are accurate, reliable, and actionable, and drive meaningful change and improvement.
After Action Report Image Gallery

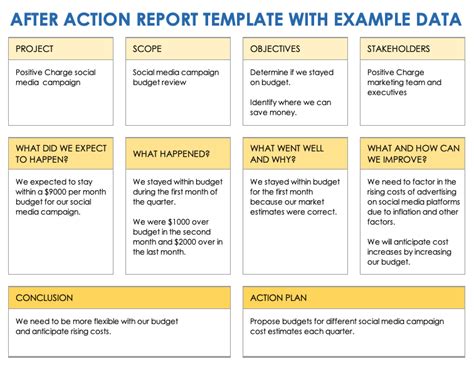







What is an after-action report?
+An after-action report (AAR) is a document that summarizes the key events, successes, and challenges of a project, operation, or event. It provides a critical analysis of what happened, what worked and what did not, and identifies key lessons learned and areas for improvement.
Why are after-action reports important?
+After-action reports are important because they provide a valuable opportunity for reflection, learning, and improvement. By documenting and analyzing what happened, individuals and organizations can identify areas for improvement, implement changes, and ultimately achieve better outcomes in the future.
How do I create an effective after-action report?
+To create an effective after-action report, follow the tips outlined in this article, including being honest and objective, focusing on key lessons learned, using a standardized format, involving stakeholders and team members, and taking action and following up. Additionally, ensure that your AAR is well-organized, clear, and concise, and includes all necessary information and data.
What are some common challenges and pitfalls to be aware of when creating after-action reports?
+Some common challenges and pitfalls to be aware of when creating after-action reports include lack of honesty and objectivity, insufficient data and information, poor communication and collaboration, inadequate follow-up and action, and resistance to change and improvement. To overcome these challenges, approach AARs with a critical and reflective mindset, being honest about what worked and what did not.
How can I use after-action reports to drive continuous improvement?
+To use after-action reports to drive continuous improvement, ensure that you take action and follow up on the lessons learned and recommendations. Implement changes, address issues, and monitor progress. Additionally, use AARs to identify and address systemic issues, improve communication and collaboration, and enhance accountability and transparency.
In
