Intro
Master blood sugar control with our 5 A1c chart tips, featuring glucose monitoring, diabetes management, and hemoglobin tracking for optimal health outcomes.
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, and one of the key tools in this management is the A1c chart. The A1c test, also known as the hemoglobin A1c or HbA1c test, measures the average level of glucose in the blood over the past 2 to 3 months. It's a vital marker for assessing how well diabetes is being controlled. Understanding and interpreting the A1c chart effectively can help individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. Here are some tips on using the A1c chart to improve diabetes management.
The importance of monitoring and managing blood glucose levels cannot be overstated. High blood sugar levels over a prolonged period can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage. On the other hand, maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range can significantly reduce the risk of these complications. The A1c chart provides a snapshot of blood glucose control over time, making it an indispensable tool for both healthcare providers and individuals with diabetes.
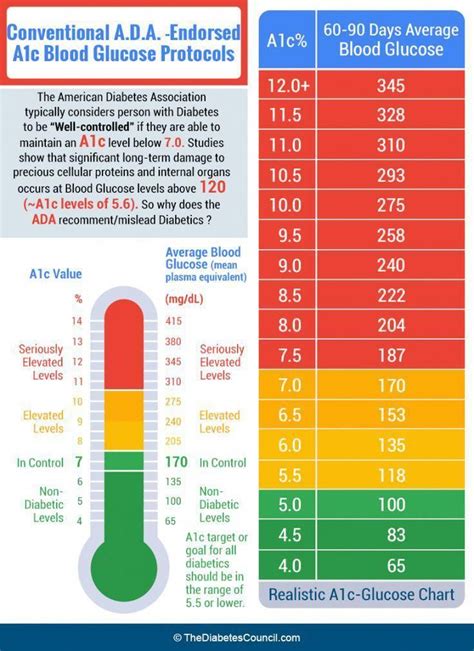
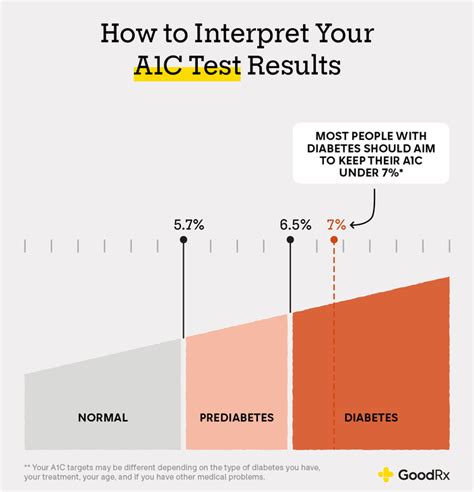
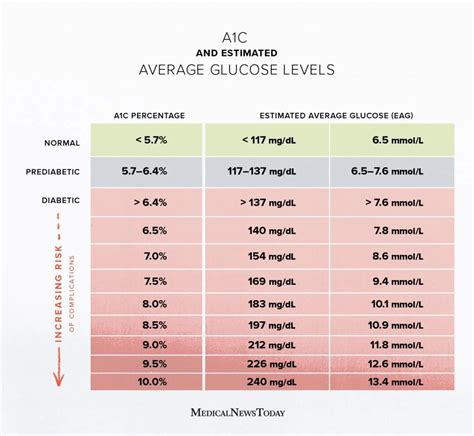
For individuals living with diabetes, understanding the A1c chart is not just about knowing the numbers; it's about interpreting what those numbers mean for their health and well-being. The chart typically ranges from 4% to 14%, with lower percentages indicating better blood sugar control. For people without diabetes, a normal A1c level is usually below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c goal of less than 7% for most adults, though this target may vary based on individual factors such as age, other health conditions, and the risk of hypoglycemia.
Understanding A1c Levels
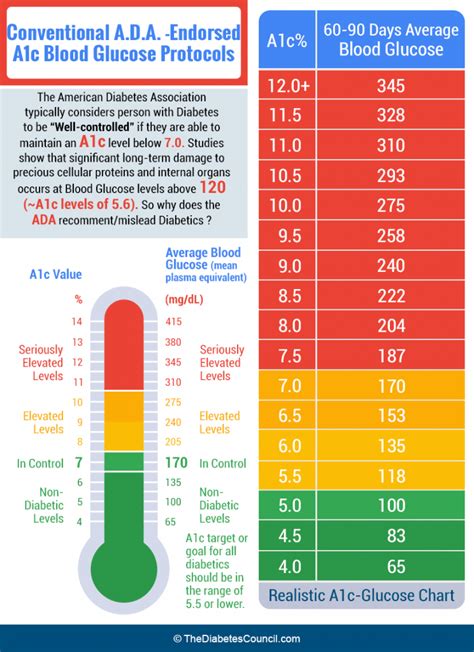
Understanding A1c levels is the first step in effectively using the A1c chart. The A1c test measures the percentage of glucose that has attached to hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen. This attachment is called glycation. The higher the blood glucose levels, the more hemoglobin gets glycated. Since red blood cells live for approximately 3 months, the A1c test reflects average blood glucose levels over that period. This provides a broader view of glucose control than daily blood glucose monitoring, which only shows glucose levels at a specific point in time.
Interpreting A1c Results
Interpreting A1c results correctly is crucial for diabetes management. Here are some general guidelines on what different A1c levels mean: - **Below 5.7%**: Normal, indicating that blood sugar levels are within the target range for people without diabetes. - **5.7% to 6.4%**: Prediabetes, suggesting a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes. - **6.5% or above**: Diabetes, indicating that blood sugar levels are high enough to be classified as diabetes.Using the A1c Chart for Diabetes Management
The A1c chart can be a powerful tool for managing diabetes when used correctly. Here are some tips on how to use it effectively:
- Set Realistic Goals: Work with your healthcare provider to set an A1c goal that's right for you. This goal should balance the benefits of tight blood sugar control with the risks of hypoglycemia and other factors.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly review your A1c results to see how your diabetes management plan is working. This can help identify areas for improvement.
- Adjust Your Plan: Based on your A1c results, you may need to adjust your diet, exercise routine, or medication. For example, if your A1c levels are too high, you might need to increase your physical activity or adjust your insulin doses.
- Combine with Daily Monitoring: Use your A1c results in conjunction with daily blood glucose monitoring to get a complete picture of your blood sugar control.
A1c Chart Limitations
While the A1c chart is a valuable tool, it has its limitations. For instance, it may not accurately reflect blood glucose control in individuals with certain conditions, such as hemolytic anemia, where red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made. In such cases, other measures of glucose control may be necessary.Improving A1c Levels
Improving A1c levels requires a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle changes and, when necessary, medication. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet that's low in added sugars, saturated fats, and sodium. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein sources.
- Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise, or a combination of both, per week. Also, incorporate strength-training activities into your routine.
- Stress Management: High levels of stress can raise blood sugar levels. Engage in stress-reducing activities like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Medication Adherence: If you're on medication for diabetes, take it as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Lifestyle Changes for Better A1c Control
Lifestyle changes are fundamental to achieving better A1c control. These changes not only help in managing diabetes but also contribute to overall health and well-being. Some key lifestyle adjustments include: - **Weight Management**: Maintaining a healthy weight can improve insulin sensitivity and lower A1c levels. - **Sleep**: Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep per night, as poor sleep quality and duration can affect blood sugar control. - **Limit Alcohol and Tobacco**: Both alcohol and tobacco use can worsen diabetes management and overall health.A1c Chart and Technology
Technology has made managing diabetes easier and more efficient. Various apps and devices can help track blood glucose levels, monitor medication adherence, and even provide personalized advice based on glucose data. When using the A1c chart, integrating technology can enhance its effectiveness:
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs): These devices provide real-time glucose data, helping identify patterns and trends that can inform A1c management.
- Insulin Pumps and Pens: Automated insulin delivery systems can make dosing more accurate and convenient.
- Mobile Apps: Apps can help track glucose levels, carbohydrate intake, and physical activity, offering insights that can guide A1c improvement strategies.
Future of A1c Management
The future of A1c management looks promising, with advancements in technology and medicine offering new avenues for diabetes care. Emerging trends include: - **Personalized Medicine**: Tailoring diabetes management to the individual, considering genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. - **Artificial Intelligence (AI)**: AI can analyze glucose data to predict blood sugar spikes and dips, suggesting preventive measures. - **Telehealth**: Remote healthcare services can improve access to diabetes care, especially for those in underserved areas.Gallery of A1c Management
A1c Management Image Gallery








Frequently Asked Questions
What is the normal range for A1c levels?
+For people without diabetes, a normal A1c level is usually below 5.7%. For those with diabetes, the American Diabetes Association recommends an A1c goal of less than 7% for most adults.
How often should I get an A1c test?
+The frequency of A1c testing depends on the type of diabetes and how well it is controlled. Generally, the test is recommended at least twice a year for people with type 2 diabetes who are meeting treatment goals and have stable blood glucose control.
Can I lower my A1c levels through diet and exercise alone?
+Yes, for some people, especially those with prediabetes or newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet and regular physical activity can be enough to lower A1c levels. However, this depends on individual factors and the severity of the diabetes.
What are the risks of high A1c levels?
+High A1c levels over time can increase the risk of serious diabetes complications, including heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems.
How does smoking affect A1c levels and diabetes management?
+Smoking can worsen diabetes management by damaging blood vessels and nerves, increasing the risk of heart disease, and potentially raising A1c levels. Quitting smoking is highly recommended for individuals with diabetes.
In conclusion, mastering the use of the A1c chart is a significant step towards effective diabetes management. By understanding what A1c levels mean, setting realistic goals, and making informed lifestyle and treatment decisions, individuals with diabetes can improve their blood sugar control and reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications. Remember, managing diabetes is a journey that requires patience, persistence, and the right tools. The A1c chart, when used wisely, can be a powerful ally in this journey. We invite you to share your experiences with using the A1c chart and any tips you might have for improving diabetes management. Together, we can work towards better health outcomes for all individuals living with diabetes.
